Chapter: 11th Microbiology : Chapter 3 : Stains and Staining Methods
Stains
Stains
Stains are dyes used to increase
colour contrast. Dye is a coloured organic compound that adheres to microbial
cells, giving colour to the cell. Today several stains and staining procedures
are available to study the morphological details of various microorganisms. The
process of imparting colour to the microbial cell is known as staining.
Stains are organic compounds
containing chromophore and auxochrome groups linked to benzene ring.
A chromophore group imparts colour to
the compound. Compounds of benzene containing chromophore radicals are called
chromogens. Such a compound, even though it is coloured, is not a dye. In order
for a compound to be a dye, it must contain not only a chromophore group but also
another group known as auxochrome that imparts the property of electrolytic
dissociation. Auxochrome gives salt forming properties to the compound.
Hence, each stain or dye is composed
of three components:
i.Benzene ring: It is
the basic colourless structural component of a stain or dye.
ii.Chromophore: It is
the functional group that gives colour.
iii.Auxochrome: It is
the group that gives ionic properties to the stain.
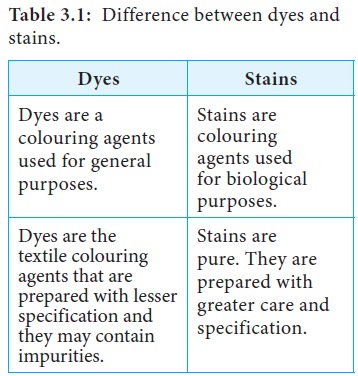
The term stain and dye are not the
same. The basic differences between dye and stain are given in Table 3.1.
Related Topics