Chapter: 11th Microbiology : Chapter 3 : Stains and Staining Methods
Preparation of Materials for Staining
Preparation of Materials for Staining
The essential steps in the
preparation of materials to be observed are
1.
Preparation of smear
2.
Fixation
3.
Application of one or more staining
solutions
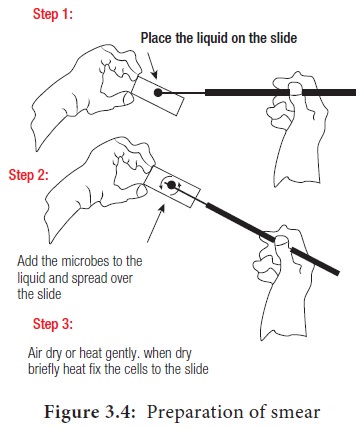
1. Preparation of Smear
Smears can be made from liquid or
solid cultures or from clinical specimens. Smear is prepared by placing a
loopful of culture on a clear glass slide with an inoculation loop. The culture
is spread on the glass slide so as to form a thin film. This film is allowed to
air dry (Figure 3.4).
2. Fixation
Fixation kills the microorganisms and
attaches them to the slide. This prevents washing away of microorganism in
further steps of staining procedure. It also preserves various parts of
microorganisms in their natural state with only minimal distortion. The two
fixation methods that are used to fix microbial cells are heat fixation and
chemical fixation.
Heat fixation
In this method the slide is gently
heated by passed through a flame (Figure 3.5). Heat fixation will preserve the
overall morphology of the cell without destroying the internal structures.

Chemical fixation
It involves the use of chemical
fixative to protect the fine cellular structures of delicate microorganisms.
For this purpose, Ethanol, Acetic acid, Formaldehyde, Glutaraldehyde and
Mercuric chloride are usually used.
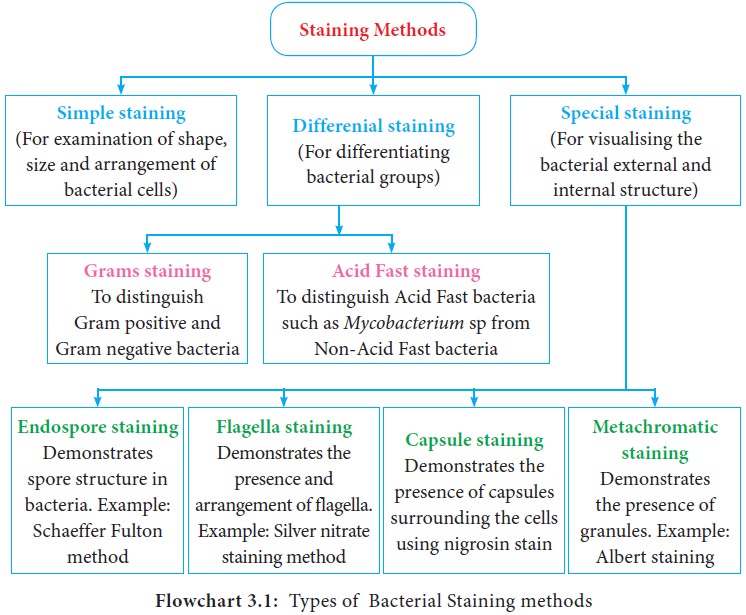
3. Bacterial Staining Methods
Different staining methods are
employed to study the bacterial morphology and to identify bacteria. Some
methods are used for general purposes and others are used for special purposes.
There are three categories of staining methods, they are:
i.
Simple staining method
ii.
Special staining method.
iii.
Differential staining method
Different types of bacterial staining
methods are summarized in Flowchart 3.1
Related Topics