Chapter: Basic Concept of Biotechnology : Macromolecules and Analytical Techniques
Spectroscopy - Analysis of biomolecules
Spectroscopy
Atoms
and molecules interact with electromagnetic radiation and may absorb and/or
emit Electromagnetic radiation. The patterns of absorption and/or emissions are
called ‘spectra’. Spectroscopy is
concerned with the interpretation of these spectra. In other words it is a study of interaction between
electromagnetic radiation and matter. Different regions of the electromagnetic
spectrum provide different kinds of information as a result
of such interactions. A spectrophotometer is an instrument that measures the
amount of light or electromagnetic radiation that is absorbed or emitted by a
sample. Arnold J. Beckman at the National Technologies Laboratory (NTL)
invented the Beckman DU spectrophotometer in 1940. Some of the electromagnetic
wave parameters is useful in understanding the spectroscopy.Wavelength (λ ):
Wavelength is the distance between the consecutive peaks or crests and is
expressed in nanometers 1nm=10-8 meters.Frequency (ν): Frequency is
the number of waves passing through any point per second and is usually expressed
as Hertz(Hz).Wave number (ν ): Wave number is the number of waves per
cm.Wavelength, Wave number and Frequency are interrelated as,
1/l=ṽ=v/c
Where,
λ is wave length, ṽ is wave number, ν is frequency, c is velocity
of light in vacuum. i.e., 3 x 10-8 m/s

The
principle of the spectroscopy is based on Beer–Lambert law / Beer –Lambert –
Bouguer law which states that the amount of light absorbed is proportional to
the concentration of the absorbing substances and to the thickness of the
absorbing material (path length).
Log(I/I)=ε
cl=A
Where, I0- the intensity of
incident light I- the intensity of transmitted light, ε - molar absorptivity /
molar extinction coefficient in cm 2 mol-1 or L mol-1 cm-1.
c - concentration in mol L-1, l - path length in cm, A- absorbance
(unitless).
This
law can be used to find the concentration of solutions absorbing in UV or
visible region. However there are deviations from this law or the limitations
of the Beer–Lambert law is that Beer’s Law successfully describes the behaviour
of dilute solutions only. At high concentrations (i,e. greater than 102
M) there is interaction between absorbing particles such that the absorption
characteristics of the analyte are affected. The voltage fluctuation,
sensitivity changes in the detector and solution containing more than one
complex which absorb different wavelength are the other deviating factors of
this law. Spectroscopy can be used for qualitative analysis and quantitative
analysis. In qualitative analysis the characteristic wavelength are used for a
given analyte and through which we can identify the sample and such type of
spectrometers are called as photometers (e.g., HPLC detectors). Whereas in
quantitative analysis the intensity of absorption or emission from the analyte
is used to find out the concentration of the analyte in a given sample and
quantitative measurements can be made at any desired wavelength, such type of
spectrometers are called as spectrophotometer (e.g.,UV-Visible spectrometer).
There are three types of spectrophotometer viz;
single, double and split beam spectrophotometer. In single beam all the light
passes through the sample and to measure the intensity of the incident light
samplemust be removed so that all the light can pass through. It is cheap and
less complicated. In double beam spectrophotometer it compares the light
intensity between two light paths, one path containing a reference sample and
the other the test sample. The readings are stable. The disadvantagesare higher
cost, lower sensitivity because of the more complex optics. Split beam is
similar to the double beam spectrophotometer but it uses a beam splitter
instead of a chopper to send light along the blank. The essential components of
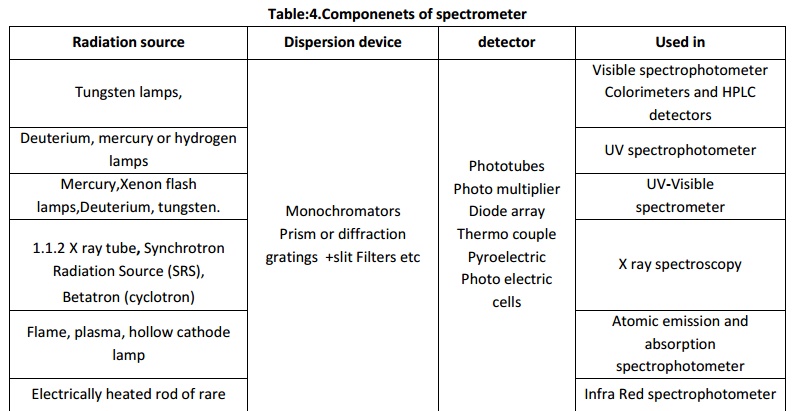
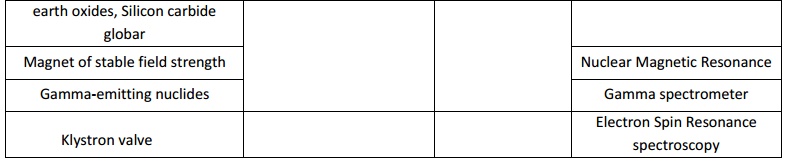
a typical spectrometer are,

Some of the common types of analytical
spectroscopes are; Absorption, Fluoresence and Phosphorescence, Emission
(atomic with flames, arcs, sparks, and plasmas), Chemilumenesence and
Bioluminescence and Reflection spectroscopy. Few important spectroscopy methods
are described here.
Related Topics