Electricity | Term 2 Unit 2 | 7th Science - Sources of Electric current - Electro chemical cells or electric cells | 7th Science : Term 2 Unit 2 : Electricity
Chapter: 7th Science : Term 2 Unit 2 : Electricity
Sources of Electric current - Electro chemical cells or electric cells
Sources of
Electric current - Electro chemical cells or electric cells
An electric cell is something that pro- vides electricity to different devices that are not
fed directly or easily by the supply of electricity.
ACTIVITY 2
Shall we produce electricity at our
home?
Materials required:
Zinc and copper electrodes, a light
blub, connecting wires, and fruits such as lemons, orange,apples, grapes, and
bananas.
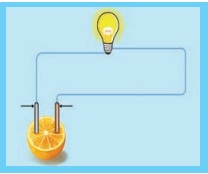
Procedure:
1. Set up a circuit as shown in
figure
2. Note the brightness of the blub
when the circuit is connected to a lemon.
3. Repeat the
experiment using the other fruits listed above. Do you notice the differences
in the brightness of the bulb when it is connected to different fruits? Which
fruit gives the greatest brightness? Why? (If you do not know please get the
appropriate reason from your teacher)
Inference:
In the above activity what makes
enabled the bulb to glow. Why there is a difference in the brightness of the
bulb? The reason is that the fruits which you have connected to the bulb produces
the electric energy at different levels
The sources which produce the small
amount of electricity for shorter periods of time is called as electric cell or
electro chemical cells. Electric cell converts chemical energy into electrical
energy
In addition to electro chemical, we use electro
thermal source for generating electricity for large scale use.
It has two terminals. When electric cells are used, a chemical reaction takes place inside the cells which produces charge in the cell.
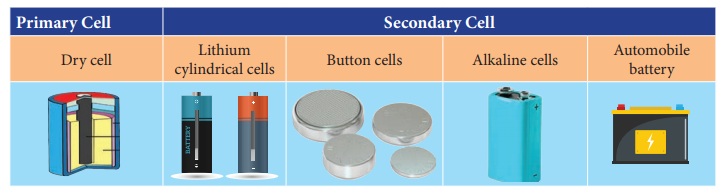
1. Types of
cell – primary cell and secondary cell
In our daily life we are using cells and batteries
for the functioning of a remote, toys cars, clock, cell phone etc. Event hough
all the devices produces electrical energy, some of the cells are reusable and
some of them are of single use. Do you know the reason why? Based on their type
they are classified into two types namely – primary cell and secondary cell.
Primary cell
The dry cell commonly used in torches is an
example of a primary cell. It cannot be recharged after use.
Secondary cells
Secondary cells are used in automobiles and
generators. The chemical reaction in them can be reversed, hence they can be
recharged. Lithium cylindrical cells, button cells and alkaline cells are the
other types that are in use.
ACTIVITY 3
I am so exhausted. I am going to
faint. What first aid will you give me to wake up?
I'll recharge the secondary cell by connecting it to an electrical circuit.
2. Difference between primary cell and secondary cell

PRIMARY
CELL
1. The chemical reaction inside the primary cell
is irreversible
2. It cannot be recharged.
3. Examples of secondary cells are lead
accumulator, Edison accumulator and Nickel – Iron accumulator.
4. Examples- simple voltalic cell, Daniel cell,
and lechlanche cell and dry cell
SECONDARY
CELL
1. The chemicalreaction inside the secondary cell
is reversible
2. It can be recharged
3. It is used to operate devices such as mobile
phones, cameras, computers, and emergency lights.
4. Examples of secondary cells are lead
accumulator, Edison accumulator and Nickel – Iron accumulator.
3. Primary cell
– simply Dry cell
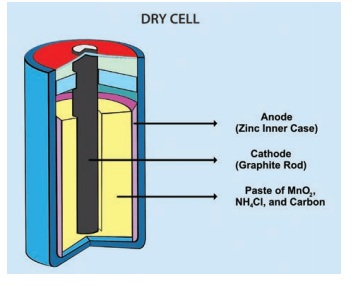
A dry cell is a type of chemical cell commonly
used in the common form batteries for many electrical appliances. It is a
convenient source of electricity available in portable and compact form. It was
developed in 1887 by Yei Sakizo of Japan.
Dry cells are normaly used in small devices such
as remote control for T.V., torch, camera and toys.
A dry cell is a portable form of a leclanche cell.
It consists of zinc vessel which acts as a negative electrode or anode. The
vessel contains a moist paste of saw dust saturated with a solution of ammonium
chloride and zinc chloride.
The ammonium chloride acts as an electrolyte.
Electrolytes are substances that
become ions in solution and acquire the capacity to conduct electricity.
The purpose of zinc chloride is to maintain the
moistness of the paste being highly hygroscopic. The carbon rod covered with a
brass cap is placed in the middle of the vessel. It acts as positive electrode
or cathode.
It is surrounded by a closely packed mixture of
charcoal and manganese dioxide (MnO2) in a muslin bag. Here MnO2
acts as depolarizer. The zinc vessel is sealed at the top with pitch or
shellac. A small hole is provided in it to allow the gases formed by the
chemical action to escape. The chemical action inside the cell is the same as
in leclanche cell.
The dry cell is not really dry in
nature but the quantity of water in it is very small, as the electrolyte is in
thefrom of a paste. In other cells, the electrolyte is usually a solution

4. Batteries
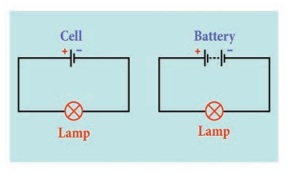
Batteries are a collection of one or more cells
whose chemical reactions create a flow of electrons in a circuit. All batteries
are made up of three basic components: an anode (the ‘+’ side), a cathode (the
‘–’ side), and some kind of electrolyte. Electrolyte is a substance that
chemically reacts with the anode and cathode.
5. Invention of
the Battery

One fateful day in 1780, Italian physicist,
physician, biologist, and philosopher, Luigi Galvani, was dissecting a frog
attached to a brass hook. As he touched the frog’s leg with an iron scapel, the
leg twitched.
Galvani theorized that the energy came from the
leg itself, but his fellow scientist, Alessandro Volta, believed otherwise.
Volta hypothesized that the frog’s leg impulses
were actually caused by different metals soaked in a liquid.
He repeated the experiment using cloth soakedin
brine instead of a frog corpse, which resulted in a similar voltage. Volta
published his findings in 1791 and later created the first battery, the voltaic
pile, in 1800.

The invention of the modern battery is often
attributed to Alessandro Volta. It actually started with a surprising accident
involving the dissection of a frog.

Related Topics