Term 2 Unit 2 | 7th Science - Electricity | 7th Science : Term 2 Unit 2 : Electricity
Chapter: 7th Science : Term 2 Unit 2 : Electricity
Electricity
Unit 2
ELECTRICITY


Learning Objectives
* Understanding the flow of electric
current and learning to draw the circuit diagram
* Understanding the difference
between conventional current and electron flow.
* Understanding the different types
of circuit based on flow of electricity and the connection of bulbs in a
circuit
* Distinguishing a cell and a
battery
* Understanding the effects of
electric current and factors affecting the effect of electric current
* Applying their knowledge in identifying the
components of electrical circuits.
* Understanding the discrimination between
different type of circuits.
* Doing numerical problems and drawing the
circuit diagram of their own.
Introduction
In 1882, when it was sun set in the west that
miracle happened in New york city. When Thomas Alva Edison gently pushed the
switch on 14,000 bulbs in 9,000 houses suddenly got lighted up. It was the
greatest invention to mankind. From then the world was under the light even in
the night.
Many countries began using electricity for
domestic purposes. Seventeen years after the New York, in 1899 electricity
first came to India. The Calcutta Electric Supply Corporation Limited
commissioned the first thermal power plant in India on 17 April 1899
Around 1900s, a thermal power station was set up
at Basin Bridge in Madras city and power was distributed to the government
press, general hospital, electric tramways and certain residential areas in
Madras. Today electricity is a common household commodity.

In your class 6, we learned about electricity and
their sources. From operating factories, running medical equipments like
ventilator, communications like mobile, radio and TV, drawing water to the
agricultural field and light up homes electricity is important. What is
electricity? We can see that. it is a form of energy, like heat and magnetism.
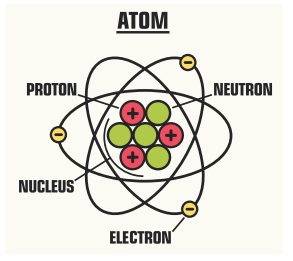
We have learnt that all materials are made up of
small particles called atoms. The centre of
the atom is called the nucleus. The nucleus consists of protons and neurtrons.
Protons are positively charged. Neutrons have no charge. Negatively charged
electrons revolve around the nucleus in circular orbits. Electricity is a form
of energy that is associated with electric charges that exists inside the atom
Electric charge is measured in a unit called
coulomb. One unit of coulomb is charge of approximately 6.242×1018
protons or electrons.
Electrical charges are generally denoted by the
letter `q`
ACTIVITY 1
Comb your dry hair. Immediately
after combing the dry hair, bring the comb closer to the bits of paper . what will you observe?

When you are getting up from the
plastic chair , the nylon shirt seems to be stuck tothe chair and make
crackling sound. What is the reason for the creation of the sound? A balloon
sticks to wall without any adhesive after rubbing on your hand. Do you know the
reason for all?
In all the above activities, when a
body is rubbed against some other body become charged.
Related Topics