Political Science - Society, state and Government | 11th Political Science : Chapter 2 : State
Chapter: 11th Political Science : Chapter 2 : State
Society, state and Government
Society, state and Government
Let us examine what Society,
State and Government mean and how are they interrelated.

Society, State and Government – How are they interrelated?
Each one of us live simultaneously in family,
society, and State. What does this mean? How society and State are
interrelated? What is government to do with the State and the society?
Historically when humans evolved from hunters and
gatherers to a settled community, they started to produce goods. Group of
families constituted a community and a group of communities constituted what we
call as a society. Individuals for their emotional need that is often
reciprocal lived in the family.
Families came together under the
umbrella of the community for a greater objective of security. The communities
so formed made a higher level of organization called society solely to live in
an organized manner where each ones’ need is met out by the collective output
of the whole. Thus when an individual is labouring for earning his food there
arose an inevitable situation that labour results in productivity. The produced
goods thus required a market supplemented by the invention of another
institution called trade. When goods are produced and marketed, it is clear
that the situation could turn in favour of a few who are mighty. When society
is governed by the rule of might, then ultimately that would cause the society
to disintegrate and fall apart.
When society degenerates, it has
a consequent effect on the communities and ultimately upon its constituent
families and each and every individual would lead to suffering. Thus, it was,
for this reason, humans came together, guided by reason felt the need of the
State.
State came into existence out of
an imminent need that in the absence of a centralized and a coercive authority
human cannot be saved from each other. This control in modern States is done
legally through a set of rules and regulations. In a democracy, these rules and
regulations are framed by the legislature, enforced by the executive and the
judiciary adjudicates the made laws and the implemented laws on the basis of
their legality and judiciousness. The function of law making, implementing and
interpreting is the function of government. You will read more about this as
separation of powers.
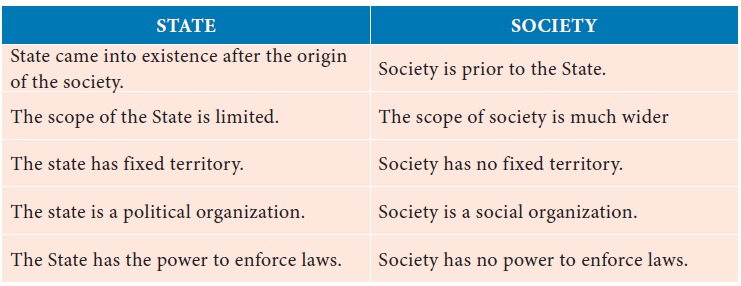
Major Differences between State and society
The society consists of a large
number of individuals, families, groups, and institutions. The early political
thinkers considered both State and society as one. The state is a part of
society but is not a form of society.
The membership of the State and
society are the same. But they differ as regards to their purpose. The State
exists for one great but single, purpose; society exists for a number of
purposes; some great and some small. From the point of view of the organization,
the State is a single organization – legal, whereas society comprises within
itself many organizations. The State exercises its control over humans by
coercion and exact obedience. On the other hand, the society employs a method
of voluntary action. The purposes for which society exists makes the persuasive
methods necessary. The multiplicity of the organization of society gives ample
opportunity to the members to relinquish one association and join another in
the event they are subject to any coercion. Thus you must understand a State
without a centralized authority of coercive force and a society without the
method of persuasion will fall apart.
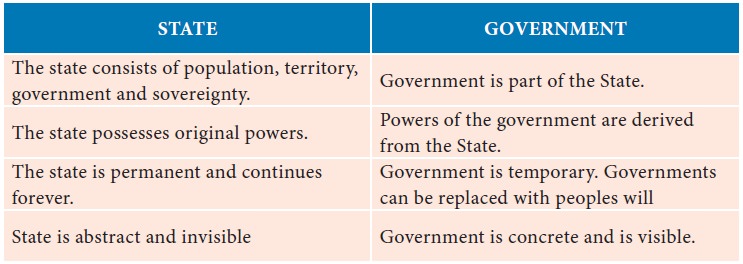
State and Government
Government is often used with the
‘State’ as a synonym. But both the government and the State are two different
entities. There are differences between the State and the government. They are
explained in the table given below.
Modern State
Before examining the functions of
Modern State, you must understand what is Modernity?
What is called as a Modern State?
Modernity in historical term
means the period of questioning the tradition or rejecting the age-old set of
beliefs, practices and socio-cultural norms. Modernity laid the foundations of
the prioritization of individualism, freedom, equality, fostering of scientific
temper in every walk of life and thus modernity led humans from agrarianism
towards industrialization, urbanization, and secularization. This intellectual
shift drastically influenced the understanding of the society, State and
government. For instance, the efforts of Raja Ram Mohan Roy to reform the
Indian society are directly linked with the influence of western modernity on
Indian thinkers.
In Political science, modernity
impacted on the concepts of State, liberty, equality, justice and so on. For
instance, the meaning of patriots, revolution, rights, privileges, sovereignty
was understood differently given their historical context. Similarly, the term
State was understood differently during the time of the Greek City State. State
means completely different when it is referred to a modern State as a form of
political organization evolved in modern western Europe dating to medieval
ages. The rational foundation of modern State is often argued to be the treaty
of Westphalia signed in the year 1648.
The idea of modern State was
exported throughout the world during the nineteenth century by the process of
European Colonization. The South Asian States that became independent from
colonial control after second world war can be brought under the umbrella of
post-colonial States and can be compared with the post-colonial States of the
other parts of the world to assess their relative merits and drawbacks for
improving their governance systems.
ACTIVITY
List the contribution of modernity to science and technology. Occidentalism is the term associated with modernity. Have you come across the works of Avishai Margalit on Occidentalism?
Why Mahatma Gandhi criticized modernity in his work “Hind Swaraj’?
DEBATE
Is M. K. Gandhi against Modernity?
Do you agree with M. K. Gandhi’s view? Conduct a critical debate in the classroom.
Related Topics