Chapter: Obstetrics and Gynecology: Sexually Transmitted Diseases
Sexually Transmitted Diseases(STDs) Screening
SCREENING
STD
screening for nonpregnant women depends on the age of the patient and
assessment of risk factors (Box 27.1).
The diagnosis of certain STDs
should also prompt screen-ing for other sexually transmitted infections. When a
patient is diagnosed with cervicitis, she should also be screened for PID,
chlamydial infection, gonorrhea, bacterial vaginosis, and trichomoniasis and
treated, if necessary. A woman diag-nosed with PID should be tested for
chlamydial infection, gonorrhea, and HIV.
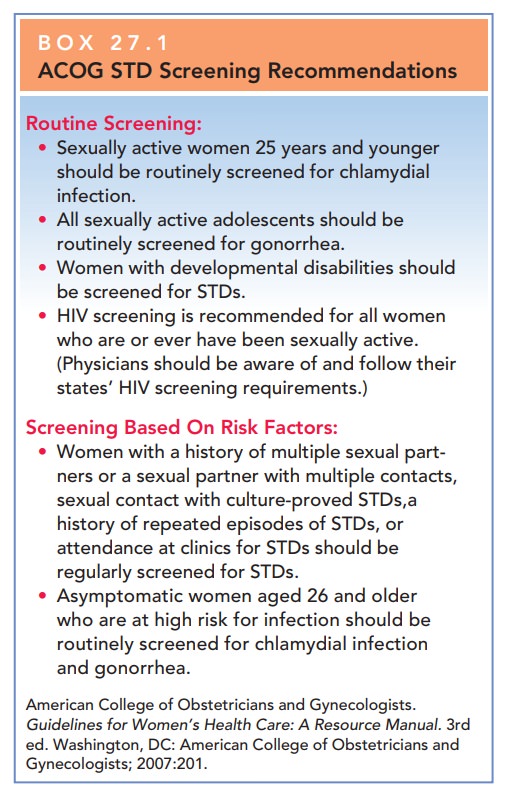
Box 27.1
ACOG STD Screening Recommendations
Routine Screening:
Sexually
active women 25 years and younger should be routinely screened for chlamydial
infection.
All
sexually active adolescents should be routinely screened for gonorrhea.
Women
with developmental disabilities should be screened for STDs.
HIV
screening is recommended for all women who are or ever have been sexually
active. (Physicians should be aware of and follow their states’ HIV screening
requirements.)
Screening Based On Risk Factors:
Women
with a history of multiple sexual part-ners or a sexual partner with multiple
contacts, sexual contact with culture-proved STDs,a history of repeated
episodes of STDs, or attendance at clinics for STDs should be regularly
screened for STDs.
Asymptomatic
women aged 26 and older who are at high risk for infection should be routinely
screened for chlamydial infection and gonorrhea.
American
College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Guidelines
for Women’s Health Care: A Resource Manual. 3rded. Washington, DC: American
College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists; 2007:201.
Related Topics