Chapter: Business Science : Services Marketing : Service Marketing Opportunities
Services Markets Segmentation
Services Markets Segmentation
Market segmentation is
the process of aggregating customers with similar wants, needs, preferences, or
buying behaviour. Market targeting involves evaluating the attractiveness of
the segments and selecting ones the firm will serve. In other words,
segmentation is the analysis conducted about customers and targeting is the
managerial decision about whom to serve. Both of these are required for
effective market positioning, which involves establishing he competitive
position for the service in the mind of the customer and creating or adapting
the service mix to fit the position.
The segmentation
process, shown in the following figure is concerned to divide a heterogeneous
follows four broad steps:
ď‚·The definition of the market to be addressed.
ď‚·The identification of
alternative bases for segmentation
ď‚·An examination of
these bases and the choice of the best base or bases for segmentation.
ď‚·The identification of
individual market segments, an assessment of their attractiveness and the
selection of specific target segments.
Once the market segment
has been selected, the process of target marketing involves developing a
positioning for the target segments selected and then developing a marketing
mix for each target market.
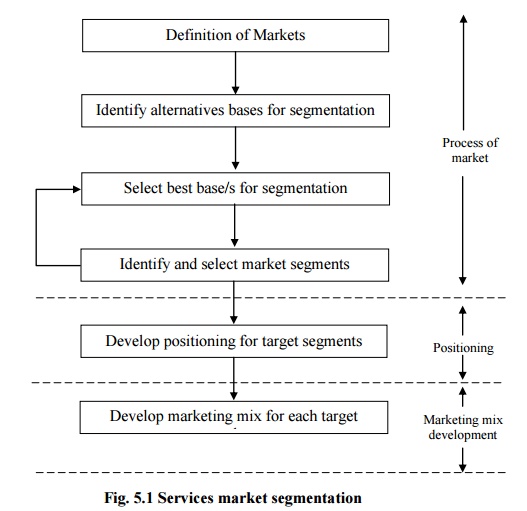
Fig. 5.1 Services market segmentation
Definition of Relevant Market
The definition of the
relevant market to be addressed involves specifying the customer group to which
the company is seeking to market its services. This can be a broad group such
as retail customers for a supermarket in a given geographic region, or a much
more specific group which can be further segmented.
Successful market
segmentation means satisfying the needs of existing and potential customers in
a clearly defined market. This involves understanding customer attitudes, and
customer preferences, as well as the benefits which are sought. Definition of
the target market and its requirements is the first essential step in the
segmentation process.
Bases of Segmentations
Market segments are
formed by grouping customers who share common characteristics that are in some
way meaningful to the design, delivery, promotion, or pricing of the service.
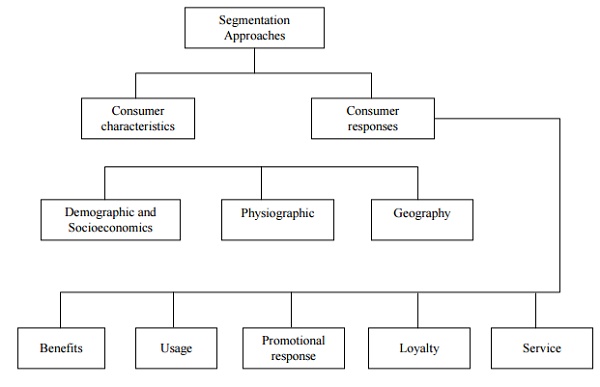
Demographics and socio-economic
segmentation
Demographic
segmentation includes a number of factors including sex, age, family size etc.
Socio-economic variables may also be considered here, including income
education, social class and ethnic origins. Many retail stores target different
customer group.
Psychographic segmentation
This form of
segmentation cannot be explained in clearly defined quantitative measures it is
concerned with people‟s behaviour and ways of living..
Geographic segmentation
Geographic segmentation
divides customers according to where they live or work and correlates this with
other variables.
A geographic analysis
is a relatively simple means of segmenting a market, it is frequently one of
the first segmentation variables to be considered by a service firm Geographic
segmentation dimensions are typically grouped into market scope factor and
geographic market measures.
1.
Market scope factors include a
consideration of where the markets to be served are located: this maybe local,
national, regional or global.
2.
Geographic market measures include
examination of population density, climate-related factors, and standardized
market areas. Geographic measures are especially important in the selection of
specialized mass communications media.
Benefit segmentation
The segmentation variables listed above focus on the
personal attributes of the customer. Segmentation can can also be carried out
on the basis of the customer‟s response.
Usage segmentation
Usage segmentation focuses
on the type and extent of usage patterns. Consumers are typically divided into
heavy users, medium users, occasional users or non-users of the service being
considered.
Promotional response segmentation
Promotional response
segmentation considers how customers respond to a particular form of
promotional activity. This may include response to advertising, sales
promotions, in-store displays and exhibitions.
Segmentation by service
One area which has
received relatively little attention is the consideration of how customers
respond to varying service offerings..
Segmenting markets by service involves addressing
the following issues:
ď‚·Can groupings of customers be identified with
similar service requirements?
ď‚·Can we differentiate our service offering?
ď‚·Do all our products require the same level of
service?
The types of
segmentation outlined above are illustrative of the main forms of segmentation
used by services companies. they are, however, by no means exhaustive. The
segmentation process should result in one of four basic decisions being
reached:
1.
The service firm may be decide to target
one segment of the market.
2.
The service firm may decide to target
several segments and so will develop different marketing mix plans for each
segment.
Management may decide
not to segment the market bout to offer the service to he mass market. This may
be appropriate if the market is very small and single portion would not be
profitable. It also may be the case that the service company dominates the
market so that targeting a few segments would not increase volume or profit.
4.
Analysis may show that there is no
viable market niche for the service offering.
The relevance of market segmentation if now being
increasingly recognized in the services sector.
Positioning and Differentiation of
Services
Services firms are not
identifying their key market segments and then determining how they wish
consumers to perceive both their company and its products and services.
Positioning can be defined as follows:
“Positioning is
concerned with the identificaifferentiated advantage which makes the
organization‟s produ those of its competitors in the mind of its ta
It is therefore important to select distinguishing
characteristics which satisfy the following criteria:
Importance –the difference is highly valued to a
sufficiently large market
Distinctiveness –the difference is distinctly
superior to other offering which are available.
Communicability –it is possible to communicate the
difference in a simple and strong way.
Superiority –the difference is not easily copied by
competitors.
Affordability –the
target customers will be able and willing to pay for the difference. Any
additional cost of the distinguishing characteristic(s) will be perceived as
sufficiently valuable to compensate for any additional cost.
ď‚·Profitability- the company will achieve additional
profits as a result of introducing the difference.
Related Topics