Chapter: Business Science : Services Marketing : Service Design and Development
Service Life Cycle
SERVICE LIFE CYCLE
SERVICE LIFE CYCLE
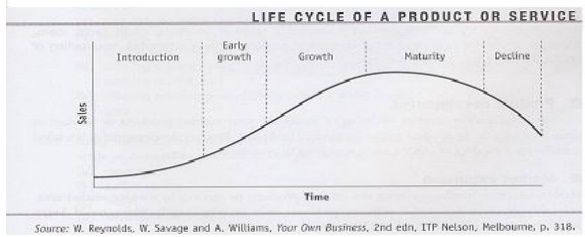
The service life cycle
consists of the same four stages at the product life cycle: introduction,
growth, maturity and decline. The characteristics of each stage are the same.
The only difference lies in the strategies that can be used.
I INTRODUCTORY STAGE
A new service or a new
form of a current service is said to be in the introductory stage when it is
first offered. As with goods, many new services never obtain acceptance by
customers and never get past the first stage of the service life cycle. An
advantage that services have over goods is that many new services can be introduced
on a small scale and expanded if acceptance grows. This small scale
introduction reduces the financial risk associated with the introduction,
making failure less costly.
II GROWTH STAGE
During the growth
stage, the industry is growing rapidly. Most firms offering the new service are
seeing a positive cash flow.
For eg: a
patient can learn about the incubation period for chicken pox by either talking
to a nurse or dialing into a vast library of prerecorded tapes. Second,
patients can seek advice about routine illnesses such as congestion or
abdominal pain.
III MATURITY STAGE
During the maturity
stage, industry sales level off. Competition becomes very intense since the
only way a firm can gain the market share or increase sales is to take them
away from a competitor. The result of this increased competition is a decrease
in overall industry profits. Weaker firms will be shaken out of the industry.
At this stage in the service life cycle, consumers see very few distinguishable
characteristics among the various firms in a service industry.
IV DECLINE STAGE
During the decline
stage, industry sales decline. This sales drop is often due to a new technology
that has been developed. For eg, typewriter repair services declined bcoz
typewriters were largely replaced by computers which resulted in a need for a
computer service technicians and computer programmers.
Companies with services in the decline
part of the life cycle have five options: divest, harvest,
prune, retrench, or rejuvenate.
a.
When using the divestment option, timing
is a critical decision. The highest price can be obtained if the divestment
decision is made early in the decline stage or even in the latter part of the
maturity stage.
b.
A second strategy available to firms is
to harvest the service. A harvesting strategy implies the firm wants to reduce
expenditures as far as possible to extract as much profit from the service as
possible. Recognizing demand will continue to fall allows a firm to reap the
maximum profit possible before the service is discontinued or sold. Due to
labour intensive nature of services, this strategy is seldom used.
c.
A third strategy is pruning. Pruning
involves reducing the number of services offered by a firm. The most
unprofitable services are discontinued while the most profitable services are
kept. Pruning is a common strategy for service operations.
d.
Retrenchment is
a fourth strategy and it involves selling off or closing the unprofitable
accounts while keeping or expanding the profitable ones. This strategy
is good for large firms with multiple outlets and for the business-to-business
service sector.
Developing Brand new services:
New Service
Characteristics:
Since services are intangible, it has to have 4
basic characteristics:
1.It must be objective, not subjective
2.It must be precise, not vague.
3.It must be fact driven, not opinion driven.
4.It must be methodological, not philosophical.
Related Topics