Chapter: Business Science : Services Marketing : Service Marketing Opportunities
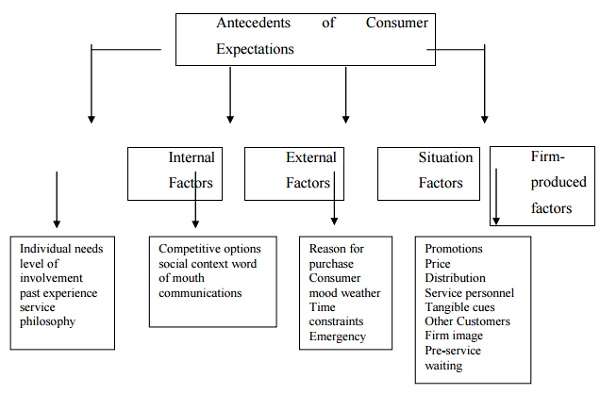
Antecedents of Consumer Expectations
ANTECEDENTS OF CONSUMER
EXPECTATIONS:
I INTERNAL FACTORS:
Internal Factors impacting a consumer‟s
expectations of a service include the consumer‟s personal needs, level of
involvement, past experience, and service philosophy.
a.
Individual needs:
The
personal needs of consumers are based
on Maslow‟s hierarch Maslow, lower order needs must be
fully, or at least partially, satisfied in a sequential order before
higher-order needs will affect human behaviour.
Physiological
Needs: Human need for food, shelter and
clothing
Safety
Needs: Human need for security,
protection from physical Harm, and
avoidance of the unexpected.
Social-belongingness
needs: Desire to be accepted by members of family, groups and other
individuals.
Self-esteem
Needs: Desire for status, esteem, and to be respected by others.
Self-actualization: Attainment by an individual of all he or she
can be.
b.
LEVEL
OF INVOLVEMENT:
The second personal
factor affecting consumer expectations is th with the service. Involvement has
two effects on expectations. First as the level of involvement increases, the
gap between the ideal level of service and the desired level of service
narrows. Second, as the level of involvement increases, the zone of tolerance
decreases. Consumers are less tolerant when service is less than ideal.
c. PAST EXPERIENCE:
The most important
factor affecting consumepast experience. Past experience includes experience
with a particular service vendor, experience with other vendors within the same
industry, and experience with related services.
d. SERVICE PHILOSOPHY:
Consumer‟s Expectationshisorherpersonalarephilosophyalsoconcerningaffected
the delivery by of services. Some consumers, by nature, have high standards
concerning the quality of service delivery and very little tolerance for
deviation. Other consumers have lower standards and tend to be more tolerant of
service deviations.
Individuals develop
their personal service philosophy through a combination of two inputs:
hereditary and past experience. A major part of how individuals look at
services is inherited or what they expect from services is based on their
personality and temperament. However, past experience molds and tempers the
personality. In early childhood, individuals learn from observing others. Later
in life, they learn from their own experiences.
II EXTERNAL FACTORS:
The three external
factors that affect consumer expectations are competitive options, social
context, and word-of-mouth communications.
a.
Competitive Options:
impacted by the alternatives available to the
consumer. In many cases, expectations of services will not only be affected by
other vendors in the same industry but by what is available in other service
industries.
b. Social Context:
A consumer‟s
socialaveansituationimpactoncanhis or her e desired level of expectations will
often increase when they are with others who are important to them, while their
zone of tolerance is normally reduced.
c. Word-of-mouth Communications:
The third external
factor is word of mouth communications. It is the strongest source of
information used by consumers in forming expectations Consumers will often seek
the opinion of others before purchasing a service. Word of mouth communication
can come from three sources: personal sources, expert sources, and derived
sources and is used to solidify or establish the predicted level of service.
For services with which consumers have little knowledge or experience, word of
mouth communications can be used to establish the desired and ideal levels of
service.
Personal sources
include friends, relatives and work associates. Expert sources are sometimes
sought out, especially for high-involvement purchases. Experts will often
provide information that consumers can use in forming expectations about the
technical nature of the service, while personal sources usually discuss only
the way they were treated by the when consumers lack knowledge of the service
and do not know the ideal or desired level of service they should expect.
Derived sources are third party sources.
III SITUATIONAL FACTORS:
Consumer expectations
of a service are affected by such situational factors as the reason for the
purchase, the consumer‟s mood, the weather, time Situational factors are
temporary changes in the normal state of things. These temporary changes impact
what consumers expect from a service.
a.
Reason for purchase: The
reason the service is purchased can alter consumer expectations
b.
Consumer Mood:
Consumer mood states
will impact expectations. Individuals in good mood tend to be more tolerant of
service personnel. Their zone of tolerance is greater and their expectation
level of adequate service is lower. Individuals in a bad mood demonstrate the
reverse characteristics. The tolerance zone is reduced and the expectation
level of adequate service is higher.
c. Weather:
Weather also plays a
role in consumer expectations. In normal weather, passengers expect airlines to
arrive on time, but in bad weather, passengers realize there may be a delay.
The desired level of service remains the same but the
passenger‟sduetotheinclementpredictedweather conditions.
d. Time Constraints:
It also impact customer
expectations. Firms who use Manpower for temporary workers modify their
expectations when faced with time constraints. If a firm needs help
immediately, they will expect manpower to be able to meet the need, but they
will normally lower their predicted expectations of the person‟s work ability.
Their zone of tolerance time to locate the best individual.
e. Emergencies: Emergencies and catastrophes
have an impact on consumer expectations.
IV FIRM PRODUCED FACTORS:
Consumer
expectations are affected by the 3 primary factors discussed in Promotions,
pricing and distribution.
•Promotions - promises
made in advertisements and
sales promotions will
be used by consumers in forming their predicted level
of service for a particular firm. Advertising can also modify a consumer‟s
desired level of
service, adequate
•Pricing
- Consumer expectations are affected by the price of the service. The general
rule is that the higher
the price, the
higher the zone of tolerance.
Determination of a high or low price, however, is relative to the competition
and to other service alternatives.
•Distribution - Distribution has an
impact
on service expectations.
The availability and accessibility of a service to customers
has an impact on their expectations. Many banks, such as Bank Boston, are now
offering on-line computer banking services that include paying bills, monitoring
daily account activities, and transferring funds.
a.
Service Personnel: Conversations
with service personnel also have an impact on expectations.
b.
Tangible Cues:
It consists of such
things as the appearance of the interior and exterior of the facility, the
furniture, and the equipment used in the service, interior décor, cleanliness,
point-of-purchase displays, and the appearance of theormostfirm‟sservices,the
appearancepersonneloftheservice.personnelF is very important. Patients have
certain expectations concerning the appearance of doctors, nurses, and
receptionists.
c.
Other Customers:
Expectations of a service can be affected by other customers.
d.
Firm Image:
The image consumers
have of a firm will have an impact on their expectations of the service. If
they have a high image of the firm, they will have high expectations. If the
image is low, expectations will be low. The image a consumer has can also
affect the zone of tolerance. Individuals will be more tolerant of service
deviations if they have a high image of the firm than if they have a low image.
Related Topics