Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Nursing Health Care Hospital Hygiene Higher secondary school College Notes
Respiratory system
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
Respiration is the process of gaseous exchange between an
organism and its environment. In the higher animals, and man the gaseous
exchange between the tissues and environment is termed as internal or tissue
respiration.
The exchange of gases between the body and the
environment-taking place in the lungs is termed as external respiration. The
external respiration constitutes processes of inspiration and expiration.
Inspiration is an active muscular contraction while expiration
is merely a passive act of the relaxation of respiratory muscles.
Structure of respiratory system
The
respiratory system is responsible for taking in oxygen and giving off
carbon-di-oxide and water. It is divided into the upper respiratory tract and lower
respiratory tract.
The upper respiratory tract : Nose, Mouth, the throat,
pharynx, the larynx, and
numerous sinus cavities in the head.
The lower respiratory tract : The trachea, the bronchi
and the lungs, which contain bronchial tube bronchioles
and alveoli or air sac.
The two lungs, which are the principal organs of the respiratory system are situated in the upper part of the thoracic cage.
They are inert organs, i.e. they do not work by themselves,
but function with the help of a muscular wall known as the diaphragm.
The pharynx is a tube approximately 12cm in length, which is
a common opening for both digestive and respiratory system.
It connects the oral cavity to the
oesophagus (food tube) and the nasal cavity to the larynx and wind pipe. The
opening into the larynx is oval in shape and guarded by the leaf like
epiglottis.
The epiglottis folds down over the opening like a trap door while food
or liquid is being swallowed, it prevents the entry of foreign substances into
the respiratory passage ways.
The closure of the epiglottis, when
we swallow, is a reflex action and can be interfered with, if one attempts to
talk and swallow at the same time.
If this happens one may choke to death in the absence of
immediate assistance. From the pharynx, air passes through the trachea, which
is 12cm long and 1.5cm in diameter. The tract, consists of a large number of C
shaped cartilage rings. The larynx or the voice
box is at the top of the trachea. It is the vocal cords inside the box,
which by its coming together and going away from one another produces different
sounds.
The trachea branches at its lower end into the right and
left bronchi which enters the lungs. Within the lungs these passageways
repeatedly divide, forming microscopic tubes called bronchioles.
Each bronchiole ends with several
clusters of microscopic elastic air sacs called alveoli, which are the
functional units of lungs. This resembles bunch of grapes.
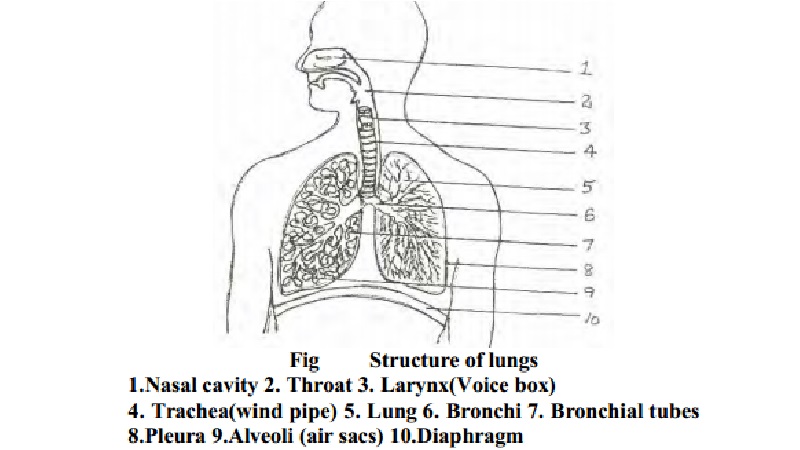
Structure of lungs :
1.Nasal cavity 2. Throat 3. Larynx(Voice box)
4. Trachea(wind pipe) 5. Lung 6.
Bronchi 7. Bronchial tubes 8.Pleura 9.Alveoli (air sacs) 10.Diaphragm
The paired lungs lie within the large cavity of the chest,
the thoracic cavity. The lungs are grayish colour and are spongy in appearance.
The right lungs has three lobes -
upper, middle and lower, and the left lung has two lobes - upper and lower. The
floor of the thoracic cavity is formed by a dome like muscular structure called
diaphragm. Each lung is enclosed by
two layers of membrane called the pleural
membranes.
The chest cavity is also lined with
this membrane. This layer being known as the parietal pleura, while visceral
pleura lines the lung parenchyma.
Respiration
We breathe continuously from birth
to death, day and night, in health and disease.
Respiration
may be defined as the mechanical process of breathing in and out, a function
which involves both the respiratory system and muscles of the respiration.
The 2 phases of breathing are
Inhalation -
during which the air is drawn into the lungs
Exhalation -
which refers to the expulsion of air from
the alveoli.
Inhalation
The diaphragm when relaxed is a flattened dome shape
structure pointing upwards to the lungs. During the process of inhalation it
contracts.
It flattens, pulls down the thorax,
increases the volume of the thorax, and thus decreases the atmospheric pressure
in the lungs. This causes air to rush in during inspiration.
Exhalation
During the process of exhalation,
the diaphragm relaxes, the thorax is pushed up, the volume decreases and the
atmospheric pressure increases and air rushes out of the lungs.
The inspired air, which contains
oxygen, passes down into the billions of minute air chambers or air cells known
as alveoli, which have very thin walls. Around these walls are the capillaries
of the pulmonary system.
It is at this point that the fresh
air gives off its oxygen to the blood and takes carbon di oxide from the blood
by diffusion, which is then expelled with the expired air.
Physiology of Respiration
The respiratory center of the brain is located in the
medulla, immediately above the spinal cord. From this center nerve fibers
extend down into the spinal cord. From the neck part of the cord, these nerve
fibers continue through the phrenic
nerve to the diaphragm.
The diaphragm does not continue to work if it is cut off
from its nerve supply. If one nerve is cut, the diaphragm of that side is
paralysed. This center is governed by variation in the chemistry of the blood.
If there is an increase in CO2 in the blood, the
cells of the respiratory center are stimulated and they in term send impulses
down the phrenic nerve to the diaphragm.
Respiratory rate
In adults, the respiratory rate is
14 to 18 times per minute. Children breath more superficially, and therefore
have a higher respiratory rate.
Importance of respiration
It supplies oxygen and eliminates
carbon di oxide.
It excretes volatile substances like
ammonia, ketone bodies, essential oils, alcohol and water vapour, etc.,
By adjusting the amount of
carbon-di-oxide elimination, it helps to maintain the acid base balance.
It helps to maintain the normal body
temperature.
It is necessary for the maintenance
of optimal oxidation-reduction process in the body.
Related Topics