Non Communicable Diseases - Causes, Risk factor, Signs and Symptoms, Diagnosis, Management - Respiratory Disorders | 12th Nursing : Chapter 3 : Non Communicable Diseases
Chapter: 12th Nursing : Chapter 3 : Non Communicable Diseases
Respiratory Disorders
RESPIRATORY
DISORDERS
·
Asthma
·
COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)
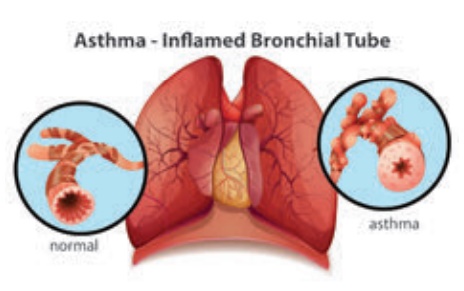
1. Asthma
Asthma is an
inflammatory disease of the airway causing mucosal oedema and increased mucous
production.
Causes
Exposure to indoor and
outdoor allergens Airway irritant
Risk factors
·
Family history of bronchial asthma
·
Exposure to airway irritants (weed, pollens, dust, strong odours,
smoke)
·
Signs and Symptoms:
·
Non-Productive cough
·
Dyspnea
·
Diaphoresis
·
Tachycardia
·
Tachypnea
·
Wheezing
·
Cyanosis
Investigations
·
Family and occupational history Increased esonophil
counts ABG-Analysis
·
Sputum for Culture
·
Pulmonary function test
Medical management
·
Corticosteroids
·
Bronchodilators
·
Oxygen therapy
·
Nebulization
Nursing Mangement
Ineffective air way
clearance related to inflammation and increased secretion.
·
Increased fluid intake
·
Coughing and breathing exercise
·
Change of position frequently
·
Administer broncho dilator
·
Chest physiotherapy
·
Suctioning
·
Artificial airway if required
Ineffective breathing
pattern related to tachycardia
·
Comfort position to facilitate breathing
·
Administer prescribed cough suppressants and analgesics
·
Monitor ABG
·
Observe signs of hypoxia
Activity intolerance
related to decreased energy
·
Schedule the activity after management
·
Use oxygen as needed
·
Avoid smoking, weight gain and stress which increases the oxygen
demand
·
Provide psychological support
·
Calm and quiet environment to reduce anxiety
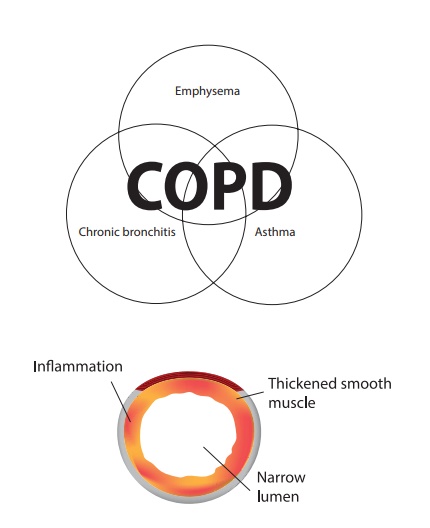
2. COPD (Chronic
Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)
This is characterized by
progressive airflow limitation that is not fully reversible. It includes chronic
bronchitis, pulmonary emphysema and bronchial asthma.
Chronic bronchitis, is a
chronic inflammation of the lower respiratory tract characterized by excessive
mucous secretion, cough, and dyspnea associated with recurring infections of
lower respiratory tract.
Pulmonary emphysema, is
a complex lung disease characterized by destruction of the alveoli enlargement
of distal air space, and break down of alveolar walls.
Causes
·
Cigarette smoking
·
Air pollution
·
Occupational exposure
·
Allergy
·
Autoimmunity
·
Infection
·
Genetic predisposition
·
Aging
Signs & Symptoms
Chronic bronchitis
·
Productive cough
·
Production of thick gelatinous sputum Wheezing and dyspnea
Emphysema
·
Dyspnea
·
Decreased exercise tolerance
·
Minimal cough with mild expectoration Barrel chest
Investigations
·
PFT – Pulmonary function Test
·
ABG levels
·
Chest X ray
Management
·
Cessation of smoking
·
Inhaled bronchodilators
·
Inhaled and or oral corticosteroids
· Chest physiotherapy
·
Oxygen administration
·
Pulmonary rehabilitation
·
Antimicrobial agents
·
Lung volume reduction surgery
Nursing Management
Improving airway
clearance
·
Eliminate pulmonary irritants Smoking cessation
·
Administer bronchodilators
·
Assess for adverse effect of medications
·
Auscultate chest before and after aerosol therapy
·
Postural drainage
·
Encourage increased fluid intake Avoid diary product.
Improving breathing
pattern
·
Teach and supervise breathing exercise
·
Teach diaphragmatic, lower costal, abdominal breathing using
relaxed breathing pattern
·
Use pursed – lip breathing at intervals and during dyspnea
·
Comfortable position
·
Relief from anxiety
Controlling infection
·
Recognize early sign of infection Sputum for culture and
sensitivity
Improving gas exchange
·
Observe the patient for any disturbance Monitor ABG, and oxygen saturation Assist mechanical ventilation
Improving nutrition
·
Collect nutritional history
·
Encourage small and frequent feeds
·
Liquid nutritional supplement Avoid gas producing food Encourage oral hygiene
·
Encourage pursed lip breathing in between the meals
·
Monitor body weight
Related Topics