Non Communicable Diseases - Causes, Risk factor, Signs and Symptoms, Diagnosis, Management - Endocrine Disorders | 12th Nursing : Chapter 3 : Non Communicable Diseases
Chapter: 12th Nursing : Chapter 3 : Non Communicable Diseases
Endocrine Disorders
ENDOCRINE
DISORDERS
·
Diabetes Mellitus (DM)
·
Poly cystic ovarian syndrome (PCOD)
·
Hyperthyroidism
·
Hypothyroidism
1. Diabetes Mellitus (DM)
Diabetes mellitus is a
metabolic disorder characterized by hyperglycemia (raised blood sugar level)
and results from the defective insulin production, secretion, or utilization.
Types of DM
·
IDDM: Insulin dependent diabetes mellitus
· NIDDM: Non-Insulin dependent diabetes mellitus
Causes
·
Lack of insulin produced by the beta cell resulting in
hyperglycemia
·
Defects of the cell receptor site, impaired secretary response of
insulin (glyconeogenosis)
·
Viral, Autoimmuno, and environmental theories are under review
(IDDM)
·
Heredity/genetics and obesity plays a major role (NIDDM)
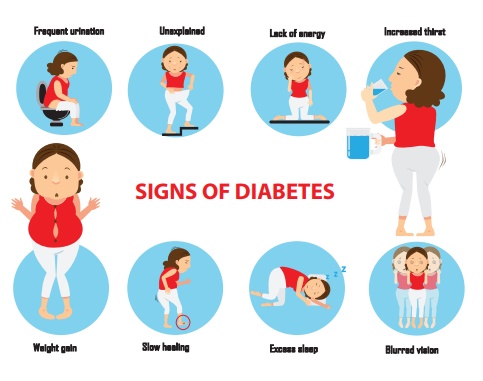
Signs and Symptoms
Diagnosis
·
Fasting Blood sugar (FBS)
·
Post Prandial Blood sugar (PPBS)
·
HbA1c
Management
·
Diet
·
Exercise
·
Medication.
·
Health education.
Diet:
·
Dietary control with calorie restriction of carbohydrates nd
saturated fats are to maintain ideal body weight
·
Advise patient about the importance of an individualized meals
plan in meeting weight loss goals
·
Explain the importance of exercise in maintaining / reducing body
weight. Calorie expenditure for energy in exercise
·
Strategise with the patient to address the potential social
pitfalls of weight reduction
Exercise:
Weight reduction is the
primary management for NIDDM regular scheduled exercise to promote the utilization
of carbohydrate, assist with weight control, enhance the action of insulin, and
improve cardio vascular fitness.
Medication:
·
Oral hypoglycaemic agents for patient where NIDDM do not achieve
glucose control with diet and exercise only
·
Insulin therapy for patients with IDM who require replacement.
(May also be used for NIDDM when unresponsive to diet, exercise and oral
hypoglycaemic agent therapy. Hypoglycemic may result, as well as rebound
hyperglycaemic effect
·
Demonstrate and explain thoroughly the procedure for insulin
self-injection
·
Help [patient to master technique by taking a step-by-step
approach
·
Allow patient time-to-time handle insulin and syringe to become
familiar with the equipment
·
Teach self-injection first to alleviate fear from injection
·
Instruct patient in filling the syringe when he or she expresses
confidence in self-injection procedure
·
Review dosage and time injections in relation to meals activity,
and bedtime based on patient’s individualized insulin regimen
Health Education:
Preventing injury secondary
to Hypoglycemia:
1.
Closely monitor blood glucose levels to detect hypoglycaemia.
2.
Asses patient for the signs and symptoms of hypoglycaemia.
3.
Sweating, cardiac palpitation and nervousness.
4.
Head ache, light-headedness,. Confusion, irritability, slurred
speech, lack of co-ordination staggering gait from depression of central
nervous system as glucose level progressively falls.
5.
Treat hypoglycaemia promptly with 10-15 gms of fast acting
carbohydrates.
6.
Half-cup juice, 3 glucose tablets, 4 sugar cubes, 5-6 pieces of
sugar candy may be taken orally.
7.
Encourage patient to carry a portable management for hypoglycaemia
at all times.
8.
Encourage patients to wear an identification bracelet opr card
that may assist in prompt management in a hypoglycaemia emergency.
9.
Identification bracelet may be obtained from Medic Alert
Foundation.
10. Identification card may
be requested from the Indian Diabetes Association.
11. Between meal snacks as
well as extra food taken before exercise should be encouraged to prevent
hypoglycaemia.
Improving activity
tolerance:
·
Advice patient to asses blood glucose level before strenuous
exercise.
·
Advice patient that prolonged strenuous exercise may require
·
increased food at bedtime to avoid nocturnal hypoglycaemia.
·
Instruct patient to avoid exercise whenever blood glucose levels
exceeds 250 mgs per day.
Providing information
about oral hypoglycaemic agents:
·
Identify any barriers to learning, such as visual, hearing, low
literacy, distractive environment.
·
Teach the action, use and side effects of oral hypoglycemic
agents.
Maintain skin integrity:
·
Maintain skin integrity.
·
Use-heal protection, special mattress, foot cradles, for patients
on bed rest.
·
Avoid drying agents to skin.(e.g. Alcohol)
·
Apply skin moisturizes to maintain supplement and prevent
cracking, fissures.
Improving coping
strategies:
·
Encourage patient and family participation is diabetes self care
regimen to foster confidence.
Complication
·
Hypoglycemia
·
Diabetic ketoacidocis
·
Hyperglycemic syndrome.
·
Micro vascular complication e.g. Retinopathy, Nephropathy,
Neuropathy.
·
Micro vascular complications in Cardiovascular disease occurring
both in NIDDM and IDDM.
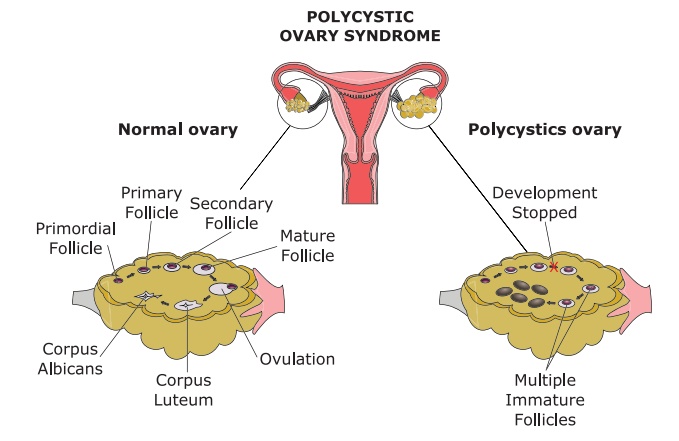
2. Poly Cystic Ovarian Syndrome/Disease (PCOD)
Polycystic ovary
syndrome (PCOS) is a disorder that includes ovulatory dysfunction, polycystic
ovaries, and hyper and rogenism. It most commonly occurs in women under 30
years old and is a cause of infertility.
Causes
·
The causes are unknown.
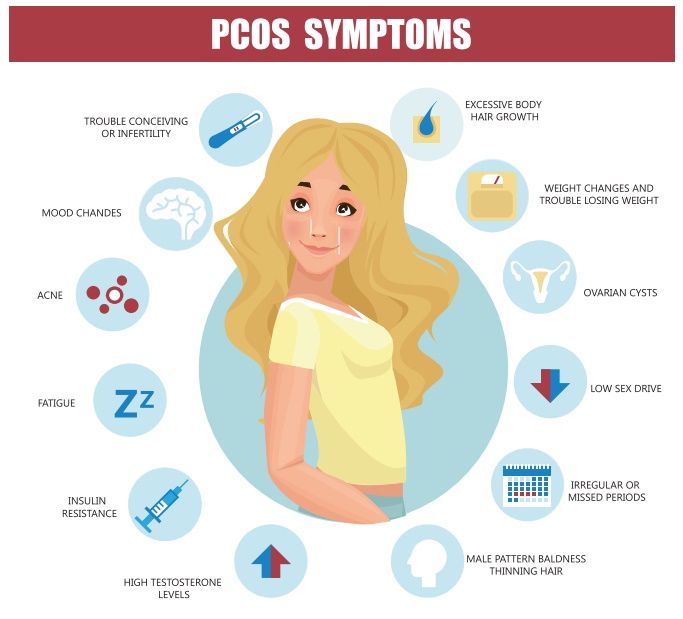
Signs and Symptoms
·
Hormonal imbalance
·
Ovulation fails and multiple fluids filled cysts
·
Irregular menstrual periods Amenorrhea
·
Hirsutism and obesity. (80% of women)
·
Oligomenorrhea and infertility
·
Insulin resistance
Management
·
Early diagnosis (pelvic ultrasound)
·
To improve quality of life and decrease the risk of complications
·
OCPs are useful in regulating menstrual cycles
·
Hirsutism may be treated with
·
spironolactone
·
Hyper and rogenism can be treated with flutamide and a GnRH
agonist such as leuprolide
·
Metformin (glucophage) reduces
hyperinsulinemia
·
Improves hyperandrogenism
·
Restores ovulation
·
Fertility drugs may be used to induce ovulation.
Nursing Management
·
A woman with PCOD includes teaching about the importance of
weight management
·
Exercises to decrease insulin resistance
·
Obesity exacerbates the problems related to
·
PCOD
·
Monitor lipid profile and fasting glucose levels
·
Support the patient as she explores measures to remove unwanted hair
·
Stress the importance of regular follow up care to monitor the
affective ness of therapy and to detect any complications.
3. .HYPERTHYROIDISM:
It is defines as
sustained increased in synthesis and relaxes of thyroid hormone by the thyroid
glands.
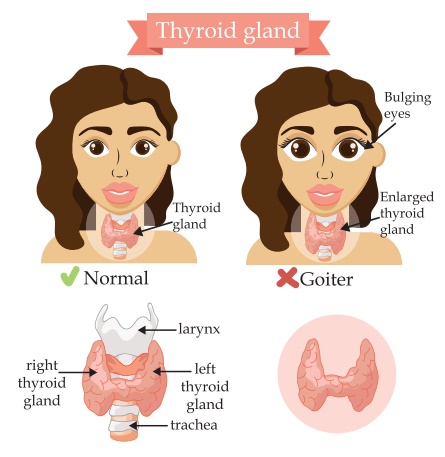
It is highly prevented
endocrine disorders.
Causes
·
Graves’ disease
·
Toxic, diffuse goiter
·
Toxic adenoma
·
Thyroid carcinoma
Signs and Symptoms
·
Heat intolerance
·
Exophthalmos
·
Loose bowel movements
·
Profuse diaphoresis
·
Tachycardia
·
Hypertrophy of thyroid cells
Investigation
·
History and physical examination Ophthalmologic
examination
·
Laboratory tests such as serum T3, T4, TSH, FT3, FT4, FTSH levels.
·
Thyroid scan
Management
Medical management:
·
Antithyroid drugs which inhibits synthesis of thyroid hormone, e.g.
prophylthiouracil and methimazole
·
Iodine e.g. Radioactive iodine Beta adrenergic blockers
Surgical management:
·
Subtotal thyroidectomy : Removal of one lobe of the thyroid
gland.
·
Total thyroidectomy : Removal of thyroid gland.
Complication of thyroidectomy:
·
Hemorrhage or infection
·
Risk of thyroidectomy tetany
·
Respiratory obstruction
·
Laryngeal edema
·
Vocal cord edema
Complications:
The Major complications
of graves’ disease are
·
Exophthalmos
·
Thyroid storm
·
Thyroid crisis
·
Thyroid toxicosis
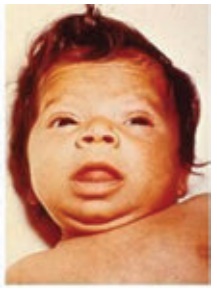
3. Hypothyroidism
It is a metabolic state
resulting from a deficiency of thyroid hormone that may occur at any age.
Congenital hypothyroidism results in a condition called cretinism.
Causes
1.
Congenital defects of the thyroid gland
2.
Defective hormone synthesis
3.
Iodine deficiency (prenatal and post natal)
4.
Anti thyroid drugs
5.
Surgery of management with radioactive agents for hyperthyroidism
6.
Chronic inflammatory (acute immune) disease such as hashimoto’s
disease, amylodois sarcoidosis
Signs and Symptoms
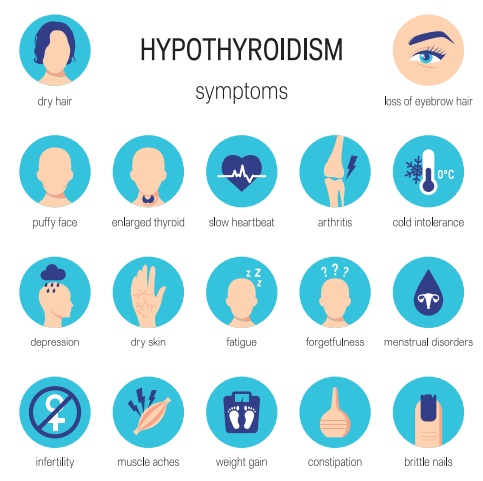
The manifestation of the
hypothyroidism depend on whether it is mild, severe (Myxedema) or complicated
(Myxedema coma)
Myxedema:
1.
Respiratory failure
2.
Heart failure
3.
Cerebral vascular accident
4.
Trauma (injury)
5.
Metabolic disturbances
Myxedema coma:
·
Drastic increase in metabolic rate
·
Hypoventilation
·
leading to respiratory acidosis
·
Hypothermia
·
Hypotension
·
Hyponatremia
·
Hypocalcaemia
·
Hypoglycemia
Diagnostic evaluation:
·
History and physical examination
·
Serum TSH and free T4
·
TRH stimulation test
Management
Medical management:
·
Antithyroid drugs such as Propylathiouracil (PTU) which inhibits
thyroid hormone synthesis
·
Radioactive iodine offers a more permanent option because it
destroys thyroid tissue
·
Client with hypothyroidism must receive lifelong thyroid hormone
replacement therapy
Related Topics