Non Communicable Diseases - Causes, Risk factor, Signs and Symptoms, Diagnosis, Management - Neurological Disorders | 12th Nursing : Chapter 3 : Non Communicable Diseases
Chapter: 12th Nursing : Chapter 3 : Non Communicable Diseases
Neurological Disorders
NEUROLOGICAL
DISORDERS
·
Epilepsy
·
Uncouncious Status
1. Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a tendency
to have recurrent seizures, which results from disturbances in the normal
electrical activity of the brain.
The human brain is a
unique computer, which works for all 24 hours. It is built up of billions of
nerve cells called neuron. The neuron has electrical activity and this is
transmitted through the axons and dendrites. These electrical impulses are
transmitted from one neuron to another through the chemical messengers called
neurotransmitters, which are present in the synapse If a group of nerve cells
start sending these impulses excessively, it results into epileptic attacks.
Causes
Epilepsy is a symptom of
many diseases. Just as headache, it is a symptom, which has a number of causes.
Epilepsy can be caused by a number of illness in the brain.
Idiopathic
·
No demonstrable cause
Symptomatic
·
Prenatal injuries
·
Low sugar, sodium or calcium
·
Developmental defect of the brain
·
Cerebral infections like meningitis, encephalitis
·
Cerebral injuries
·
Cerebral tumors
·
Cerebro vascular attack
·
Cysticercus and tuberculomas
Signs & Symptoms
·
Unconsciousness
·
Rigid body
·
Jerking movements of arms and legs
·
Clenching of teeth
·
Grunting noises
·
Confusion (one or two minutes)
Partial seizures
In partial seizures the
abnormal electrical discharges occur in a localized area in the brain. Hence
the symptoms depend upon the area of brain involved, motor or sensory.
Simple partial seizures
Simple partial seizures do
not affect consciousness. Symptoms
may include rhythmic movements of the contralateral face, arm or leg and
possibly hallucinations involving smell, sight or hearing or feelings of fear
and panic or euphoria.
Complex partial seizures
Complex partial seizures
are the most common type of seizure in adults, commonly lasting less than three
minutes and associated with impairment in the consciousness they become complex
partial seizures.
Generalised seizures
Generalized seizures
affect the whole cortex with the patient’s level of consciousness usually being
impaired; there is often no aura or warning. Generalized seizures have varying
characteristics.
·
Typical absence seizures are distinguished by a transient loss of
consciousness and awareness of the environment with a vacant appearance, which
lasts just a few seconds
·
Atypical absence seizures resemble typical absence seizures but
last longer and are often associated with minor automatism
·
Myoclonic seizures are classified by sudden muscle contractions of
specific muscle groups with no loss of consciousness
·
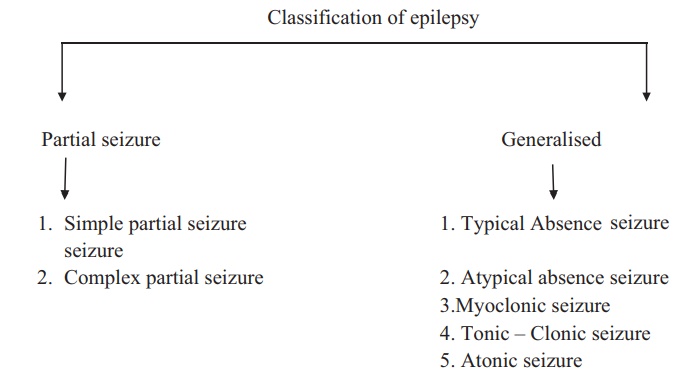
Tonic-clonic seizures involve bilateral extension of limbs
followed by synchronous jerking movements. There is often acry before the
seizure, a fall to the ground followed by incontinence, tongue biting, foaming
at the mouth and loss of consciousness. There is a post-ictal phase and when
patients wake they have muscle tenderness, transient confusion and exhaustion
·
Atonic seizures cause loss of muscle tone and a fall to the
ground, often resulting in injury; it may be so brief that the patient is
unaware of the loss of consciousness
Signs & Symptoms
·
Headache, fainting attack
·
Muscle spasms
· Black out or fall jerky movement
· Incontinence of bladder or bowel
· Tongue bite, breathing difficulty

Investigations
·
EEG
·
CT-Brain
·
MRI-Brain
Management
Medical Management
Drugs
·
Carbamazepine
·
Phenytoin
·
Valporic acid
Surgical Management
·
Reserve and palliative operations (temporal lobotomy, extra temporal
resection, corpus colostomy, hemisperectomy)
Nursing Management
·
Maintain a patient airway until patient is fully awake after a
seizure
·
Provide oxygen during the seizure if color change occurs
·
Stress the importance of taking medication regularly
·
Provide a safe environment by padding side rails and removing
clutter
·
Place a bed in a low position and place a patient on side during a
seizure to prevent aspiration
·
Do not restrain the patient during a seizure
·
Do not put anything in the patient mouth during a seizure
·
Protect the patient’s head during a seizure.
·
Stay with a patient who is ambulating or who is in a confused
state during seizure
·
Provide a helmet to the patient who falls during seizure
·
Consult with social worker for community resources for vocational
rehabilitation, counsellors and support groups
·
Teach stress reduction techniques that will fit into a patient
lifestyle
·
Answer questions related to use of computerized video EEG
monitoring and surgery for epilepsy management
Complication
·
Status epileptics
·
Injuries due to falls
2. Unconscious Status
Unconsciousness is a
condition in which there is depression of cerebral function ranging from stupor
to coma.
Coma may be defined as
no eye opening on stimulation, absence of comprehensible speech, a failure to
obey commands.
Unconsciousness is a
lack of awareness of one’s environment and the inability to respond to external
stimuli.
Therefore, observe the
patient’s condition and prevent any complications.

Causes
·
Head injuries
·
Meningitis, encephalitis
·
Diabetes mellitus
·
Renal failure
·
Poisonous drugs (stomach wash, refer practicals)
·
Asphaxia
·
Epilepsy
Diagnosis
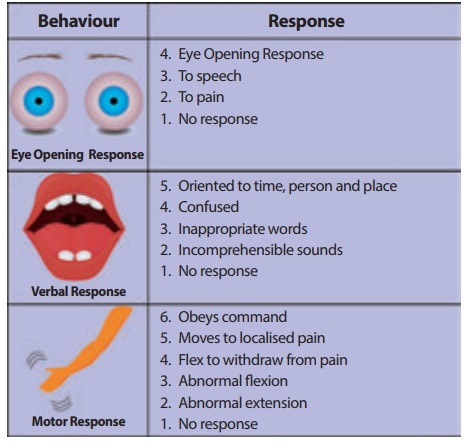
Assess the patient’s level of consciousness by Glasgow coma scale.
·
Responses to command
·
Eye opening
·
Verbal responses
·
Motor responses
Glasgow Coma Scale
Assessment
Interpretation
·
Best score
·
Worst Score
·
7 or less generally indicates coma (Changes from baseline are most
important)
Nursing Management
Maintenance of effective airway:
·
An adequate airway must be maintained at all times.
·
It must be necessary to hold the patients jaw forward or place the
patient in the lateral position to prevent the tongue obstructing airway by
falling back.
·
Loosen the garments to allow free movements of the chest and
abdomen.
·
Frequent suction is required to prevent the pooling of secretion
in the patients pharynx.
·
If necessary insert oral airway for easy breathing.
Maintenance of fluid
& electrolyte balance and nutrition:
·
The diet must contain an adequate supply of all nutrients required
for life. Nutrition may be supplied by intravenous fluids or gastric tube
feeding. (refer practicals)
·
Administer prescribed intravenous fluids with electrolytes and
vitamins (refer practicals).
·
Maintain Intake and output chart accurately.
·
Monitor vital signs and record.
Maintenance of personal
hygiene and care of pressure areas including prevention of foot drop:
·
Sponging is performed as frequently as necessary
·
Keep the skin dry, clean and free of moisture to prevent bed sore.
·
Apply back care every 4th hourly and 2nd hourly position changing
to relieve pressure on pressure areas.
·
Clip the nails
·
Range of motion exercises atleast 4 times a day.
·
Cleanse the mouth with the prescribed solution every 2nd hourly and
apply emollients to prevent parotitis.
·
Irrigate the eye with sterile prescribed solution to remove
discharge and debris.
·
Clean the ear with swab and dry carefully, especially behind the
ears.
·
The bed linen must be kept wrinkle free and dry.
·
Side railing on both sides are helpful to protect the patient.
·
The feet should be kept at right angles to the legs with help of
pillow or sand bags to prevent foot drop.
Promoting elimination:
·
If the patient is observed for any sign of urinary incontinency,
retention and constipation, report to the physician.
·
If the patient has incontinence of urine – provide bedpan or
catheterization can be done according to Doctor’s order to record the accurate
output. (refer practicals).
·
If the patient has retention of urine, apply gentle pressure over
the bladder region. It will help in partially emptying the bladder.
·
If the patient is constipated, a glycerine suppository or enema is
advised according to Doctor’s prescription.
·
Perineal care, vaginal douch, catheter care to be provided (refer
practicals).
·
Palpate the abdomen for distension.
·
Auscultate bowel sounds.
Family education:
·
Develop an interpersonal relationship with the family.
·
Provide frequent update information on patient condition.
·
Involve the relatives in routine care.
·
Provide comfortable physical environment.
·
Teach family to report any unusual symptoms.
Related Topics