Non Communicable Diseases - Causes, Risk factor, Signs and Symptoms, Diagnosis, Management - Renal Disorders | 12th Nursing : Chapter 3 : Non Communicable Diseases
Chapter: 12th Nursing : Chapter 3 : Non Communicable Diseases
Renal Disorders
RENAL
DISORDERS
·
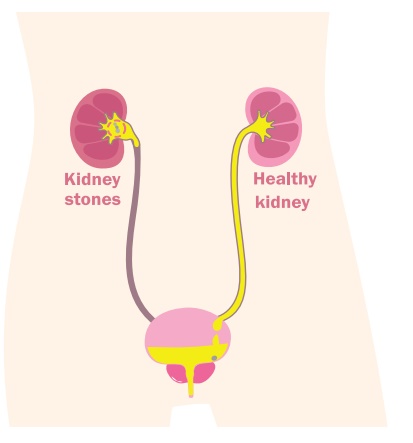
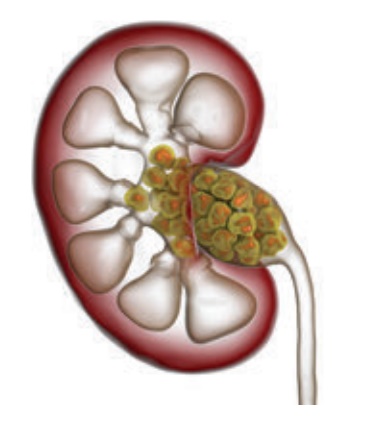
Renal Calculi
·
Acute renal failure
1. Renal Calculi
Classification
·
Urolithiasis and nephrolithiasis
Causes
·
Urinary stasis
·
Super saturation of urine
Risk factors
·
Immobility
·
Sedentary life style
·
Dehydration
·
Metabolic disturbances
·
Increases calcium
·
A diet high in purine oxalates calcium and animal proteins
Signs & Symptoms
·
Renal colic or ureteric colic
·
Sharp severe pain originates deep in the lumbar region and
radiate around the sides and down towards the genital or thigh
·
Nausea
·
Vomiting
·
Pallor
·
Increased blood pressure and pulse
·
Urgency and frequency of urine Hematuria
·
Fever and chills
Investigations
·
USG - Abdomen
·
Intravenous pyelogram
·
X- ray KUB (Kidney, Urethra, Bladder) or
·
CT KUB
·
Blood test may shows increased WBC, uric acid, serum Calcium and
Phosphorous
·
Cystoscopy
Management
Medical management
·
Pain management
·
Analgesics and anti spasmodic drugs Hydration with oral fluids and IV fluids
·
Minimize the calculus formation by dietary changes (less calcium
diet)
Surgical Management
·
URSL (Ureteroscopic Lithotripsy)
·
Intra corporeal Lithotripsy (crushing the stones)
·
Laser lithotripsy
·
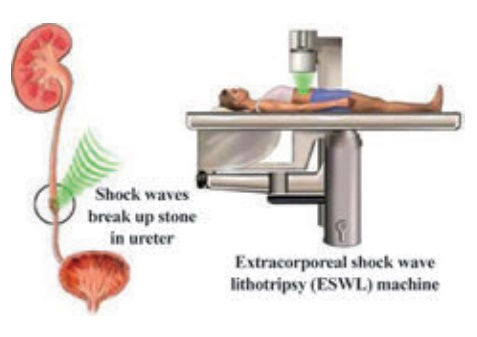
ESWL (extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy)
·
PCNL (Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy)
·
Ureterolithotomy
·
Cystolithotomy
·
Nephrolithotomy
·
Nephrectomy
Nursing Management
·
Pain control
·
Minimize the vomiting by antiemetics
·
Increased fluid intake and relaxation technique
·
Provide comfortable position
·
Maintain fluid intake chart (intake output)
·
Advice dietary modification
2. Acute Renal Failure
Acute renal failure is a
syndrome of varying causation that results in a sudden decline in renal
function.
Kidneys are a pair of
organs located toward lower back. One kidney is on each side of spine. They
filter blood and remove toxins from body. Kidneys send toxins to your bladder.
Later body removes toxins during urination. Kidney failure occurs when kidneys
abruptly lose their function of filtering waste products from the blood.
Causes
·
Pre–renal causes: It results from the condition that decreases
renal blood flow (e.g. Hypovolemia, shock, hemorrhage, burns, diuretic therapy)
·
Post–renal causes: It comes from obstruction or distruption of urine
flow anywhere along the urinary tract
·
Intra – renal causes: It results from injury in the renal tissue and is
usually associated with intra renal ischemia, toxins immunologic process,
systematic and vascular disorders
Signs and Symptoms
·
Decreased tissue turger, dryness of mucous membrane, weight loss,
hypotension, oliguria
·
Difficulty in voiding and changes in urine flow
·
Fever and skin rashes, edema
·
Changes in urine volume, increases blood urea, creatinine, uric
acid, potassium levels etc
Investigations
·
Urine analysis: Reveals protenuria, haematuria
·
Raise of Serum creatinine in blood Urine culture
·
Renal ultrasonography
·
Renal biopsy
Management
·
Correct any reversible cause of acute renal failure E.g:
Improve renal perfusion maximize cardiac output, surgical release of
obstruction
·
Be alert for fluid excess or deficit
·
Monitor the signs of hypovolemia or hypervolemia
·
Monitor Intake and output chart Weigh the patient daily
·
Monitor vital signs
·
Correct and control biochemical imbalances Restore and maintain B/P Maintain nutrition
·
Initiate haemodialysis
·
Renal replacement therapy
Prevention
·
Maintaining healthy lifestyle – performing regular physical
activity, limiting alcohol intake, and refraining from smoke can keep you away
from illness
·
Be attentive while taking over the counter (OTC) medications, especially
NSAIDs as they can be nephrotoxic
·
Undergo urine test and blood test at least once in 6 months to
monitor kidney disease
·
Consult a doctor immediately if you find any changes in your
urine output
Complication
·
Infection
·
Arrhythmias due to hyperkalemia Electrolyte
abnormalities
·
Gastrointestinal bleeding Multiple organ system
failure
Related Topics