Non Communicable Diseases - Causes, Risk factor, Signs and Symptoms, Diagnosis, Management - Musculo Skeletal | 12th Nursing : Chapter 3 : Non Communicable Diseases
Chapter: 12th Nursing : Chapter 3 : Non Communicable Diseases
Musculo Skeletal
MUSCULO
SKELETAL
·
Osteoarthritis
·
Osteoporosis
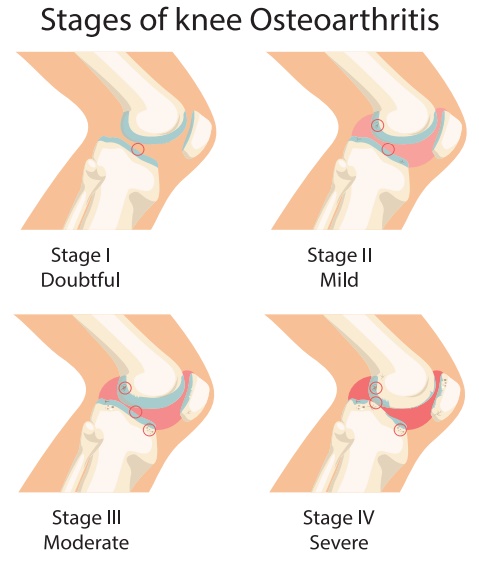
1. Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a very
common chronic disorder involving the joints. It is a degenerative change in
the joints. The degenerative changes take place because the rubbing of the
joint surfaces causes a wearing away and disintegration of the tissues.
Causes and Risk factors
Age: people above the age of
45 have the risk for developing osteoarthritis. It is, however, most
commonly found in people over age of 65.
Gender: This disease of
osteoarthritis is more common in women, particularly after the age of 55
Obesity: This can be one of the
causes for osteoarthritis as every kilogram puts three extra kilogram of
pressure on knees
Injury : Joint injuries are an
increased risk of developing osteoarthritis
Weakness of muscles: Weak thigh muscles
lead to osteoarthritis knee joint pain.
Signs & Symptoms
·
Knee pain
·
Swelling
·
Joint stiffness
·
Loss of movement
Investigation
·
X–ray of affected joints
·
Serum CRP
·
Serum ESR, RA factor
Management
Medical management:
·
Analgesics
·
Exercise to strengthen muscles
Surgical management:
·
Arthodesis (practised earlier)
·
TKR
(Total Knee Replacement)

·
Use knee cap supports
·
Use hot water formentation to relieve pain
·
Wear comfortable, fitting shoes to reduce stress on joints
·
Walk regularly to keep yourself active, it helps to avoid
stiffness
·
Maintain a healthy weight to reduce strain and pain in your knee

·
Don’t lift heavy weights, it puts stress on the knees
·
Don’t sit cross- legged
·
Avoid prolonged activities that put strain on the knee like
gardening
·
Avoid jerky movements
·
Don’t smoke. Research shows that smoking leads to joint pain along
with other damaging effects
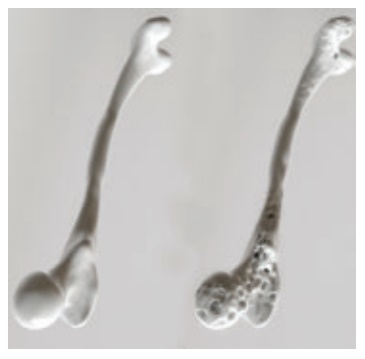
2. Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a
disease characterised by low bone mass and deterioration of bone tissue, which
can lead to increased risk of fracture.
Risk factors
·
Genetics
·
Lack of exercise
·
Lack of calcium and vitamin D3 Diet calcium / vitamin D
deficiency
·
Osteoporosis means “porous bones”
Signs and Symptoms
·
Pain
·
Height loss or dull pain in the bones or muscles
·
Swelling
·
Redness
·
Limited movement
Pathophysiology
Osteoporosis is a
reduction in skeletal mass caused by an imbalance between bone reabsorption and
bone formation. A change in either that is increased bone reabsorption or
decreased bone formation may result is osteoporosis.
Investigation
·
Blood: Test Calcium & Phosphorus
·
BMD
·
X–ray
Causes of Osteoporosis
·
Low calcium diet
·
Lack of physical activity
·
Family history
·
Women are more likely to develop osteoposis
·
Hypercalciuria
·
Anticonvulsant medications
·
Hyperthyroidism
·
Hyper parathyroidism
·
Neoplastic disease – cancer
Management
·
Medication – vitamins and calcium Dietary supplements Weight bearing exercises
Related Topics