Chapter: Plant Biology : Spore bearing vascular plants
Reproduction and Gametophyte in Equisetopsida
Reproduction in Equisetopsida
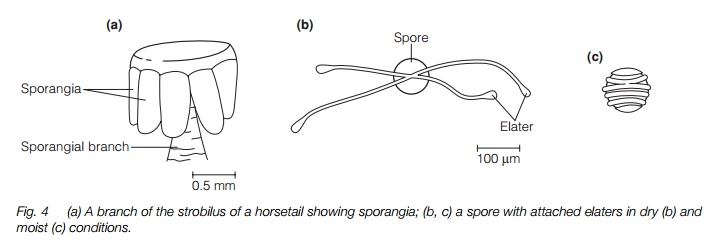
Sporangia are produced in strobili at the tip of either a vegetative shoot or a distinct, brownish fertile shoot (Fig. 3). The strobilus has short side branches each with an umbrella-shaped tip bearing 5–10 sporangia on the underside (Fig. 4), similar in structure to those of Lycopsida. The spores are unusual in that they contain chloroplasts and, at maturity, have four elaters (Fig. 4). These are short band-like structures with a spoon-shaped tip that coil around the spore at high humidity and uncoil as they dry, aiding dispersal. All horsetails are homosporous.
Gametophyte of Equisetopsida
Although the spores are apparently all identical in horsetails, gametophytes show a partial division of the sexes. They are green structures on a damp soil surface, with a colorless base and a much branched upper part, though they remain < 1 cm long. Gametophytes may produce antheridia or archegonia or both, any archegonial plants usually producing antheridia as they get older. The determination of sex seems to be at least partly environmental, and is flexible. The antheridia have a two-layered jacket and produce multi-flagellate sperm; the archegonia are similar to those of bryophytes .
Related Topics