Chapter: Civil : Railway Airport Harbour Engineering : Railway Engineering : Track and Track Stresses
Railway Track as an Elastic Structure
Track as an
Elastic Structure
In
the year 1888, Zimmerman propounded the theory that the track is an elastic
structure. Rails are continuous beams carried on sleepers, which provide
elastic support. The elastic nature of the rail supports affects the distribution
of the wheel load over a number of sleepers in a rather complicated manner. The
mode of distribution of load depends on the stiffness of the rails as well as
the elasticity of the bed (sleepers and the ballast and formation taken
together) on which the rail rests.
Track Modulus
Track
modulus, like the modulus of elasticity, is an index of measurement of
resistance to deformation. It is defined as the load in kilograms per unit rail
length required to produce one unit depression in the rail bottom. The unit of
track modulus is kg/cm2.
The Research, Designs and Standards Organisation
(RDSO) of Indian Railways has carried out a large number of investigations to
determine the track modulus and vertical bending stresses in rails due to
static loads on BG and MG tracks. These empirical studies reveal that the rail
depression immediately below the load is not directly proportional to the load
in the entire load range. Due to slacks and voids in the track structure, the
track depression is disproportionately higher in the initial stages of loading.
These slacks and voids get closed under the initial load and thereafter further
depression per unit load is smaller and becomes proportionate to the increase
in the load. It is found that an initial load of 4 t for BG and 3 t for MG
gives the best results.
There are, thus, two well-designed load ranges, and
the value of the track modulus is not able to completely define the
load-depression characteristics of a track. The complete relationship can be
expressed by assuming that a linear load-depression relationship exists in the
initial stage of the load and that there are two values of track modulus-one is
the initial track modulus ( Ui) and the other is the elastic
track modulus (Ue).
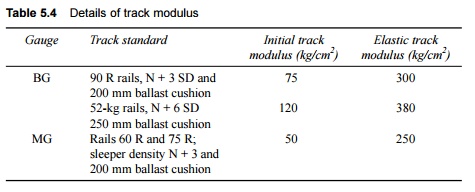
The track modulus varies with the gauge as well as
with the track standard, namely, the type of rails, sleepers, sleeper density,
and ballast cushion. The values of track modulus adopted on Indian Railways are
given in Table 5.4.
Table
5.4 Details of track
modulus
Related Topics