Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) - RDBMS Jargons | 12th Computer Applications : Chapter 3 : Introduction to Database Management System (DBMS)
Chapter: 12th Computer Applications : Chapter 3 : Introduction to Database Management System (DBMS)
RDBMS Jargons
RDBMS (Relational
Database Management System) Jargons
1. Database
The most popular Relational Database is MySQL. It
is an open source SQL database supporting different platforms like Windows,
Linux and MAC Operating Systems. The other relational databases available are
Oracle, MS SQL Server and MS Access. The features of RDBMS are
• High Availability
• High Performance
• Robust Transactions and support
• Ease of management
• Less cost
2. Table
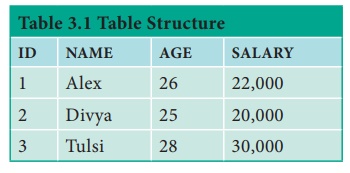
In relational database model, table is defined as
the collection of data organized in terms of rows and columns. Table is the
simple representation of relations. The true relations cannot have duplicate
rows where as the table can have. The example of Employee table is shown below
in Table 3.1.
3. Column
The table consists of several rows and columns.
Table can be divided into smaller parts, in terms of columns. Each column is
known as attributes. In the Employee table four attributes are available namely
Id, Name, Age and Salary. The attribute is defined in a table to hold values of
same type. This is known as Attribute Domain. In the Employee table, the Name
field will hold only characters not the numbers in it.The vertical entity in a
table is known as Attribute or Column.
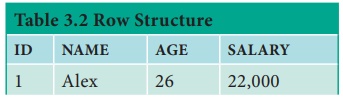
4. Row
A single entry in a table is called as Row or
Record or Tuple. Set of related data’s are represented in a row or tuple. The
horizontal entity in a table is known as Record or row. See Table 3.2
5. Key
The candidate key that is chosen to perform the
identification task is called the primary key and any others are Alternate
keys. Every tuple must have, by definition, a unique value for its primary key.
A primary key which is a combination of
more than one attribute is called a composite primary key.
6. Foreign Key
A foreign key is a “copy” of a primary key that has
been exported from one relation into another to represent the existence of a
relationship between them. A foreign key is a copy of the whole of its parent
primary key i.e if the primary key is composite, then so is the foreign key.
Foreign key values do not (usually) have to be unique. Foreign keys can also be
null. A composite foreign key cannot have some attribute(s) null and others
non-null.
7. Super Key
An attribute or group of attributes, which is
sufficient to distinguish every tuple in the relation from every other one is
known as Super Key. Each super key is called a candidate key. A candidate key
is selected from the set of Super Key. While selecting candidate key, redundant
attributes should not be taken. The candidate key is also known as minimal
super keys.
8. Composite Key
A key with more than one attribute to identify rows
uniquely in a table is called Composite key. This is also known as Compound
Key.
Related Topics