Database Management System (DBMS) - DBMS Database Models | 12th Computer Applications : Chapter 3 : Introduction to Database Management System (DBMS)
Chapter: 12th Computer Applications : Chapter 3 : Introduction to Database Management System (DBMS)
DBMS Database Models
DBMS
Database Models
The database technology came into existence in
terms of models with relational and object-relational behavior. The major
database models are listed below:
1. Hierarchical Database Model
The famous Hierarchical database model was IMS
(Information Management
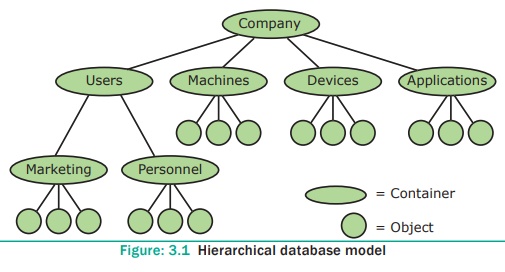
In this model each
record has information in parent/ child relationship like a tree structure. The
collection of records is called as record types, which are equivalent to tables
in relational model. The individual records are equal to rows. See Figure 3.1
In the above model we have many advantages like
less redundant data, efficient search, data integrity and security. This model
also has few limitations like complex to implement and difficulty in handling
many to many relationships.
2. Network model
The first developed network data model was IDS
(Integrated Data Store) at Honeywell. Network model is similar to Hierarchical
model except that in this model each member can have more than one owner. The
many to many relationships are handled in a better way. This model identified
the three database components Network schema, Sub schema and Language for data
management. See Figure 3.2
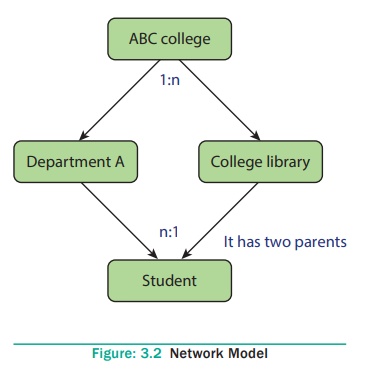
Network
schema – schema defines all about
the structure of the database.
Sub
schema – control on views of the database
for the user
Language – basic
procede for accessing the database.
The major advantage of this model is the ability to
handle more relationship types, easy data access, data integrity and
independence. The limitation of network model is difficulty in design and
maintenance.
3. Relational model
Oracle and DB2 are few commercial relational models
in use. Relational model is defined with two terminologies Instance and Schema.
See Figure 3.3
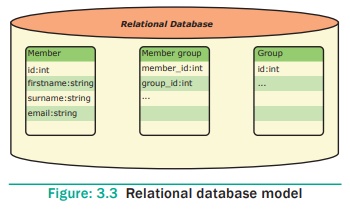
Instance – A table
consisting of rows and columns
Schema –
Specifies the structure including name
and type of each column.
A relation (table) consists of unique attributes
(columns) and tuples (rows).
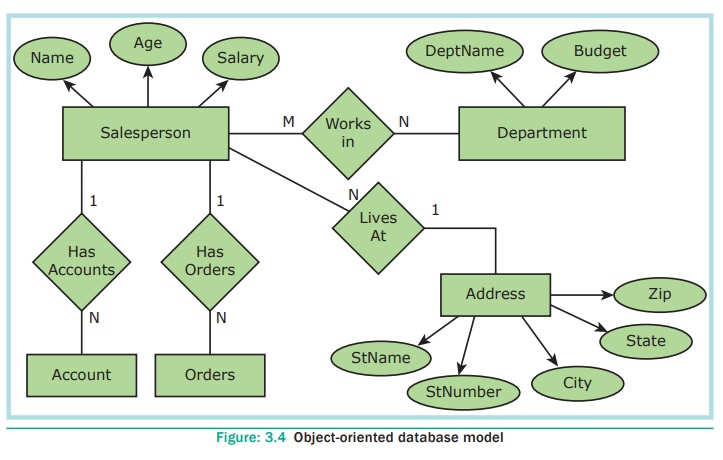
4. Object-oriented database model
This model incorporates the combination of Object
Oriented Programming(OOP’s) concepts and database technologies. Practically,
this model serves as the base of Relational model. Object oriented model uses
small, reusable software known as Objects. These are stored in object oriented
database. This model efficiently manages large number of different data types.
Moreover complex behaviors are handled efficiently using OOP’s concepts. See
Figure 3.4
Related Topics