Crop Production and Management | Chapter 21 | 8th Science - Questions Answers | 8th Science : Chapter 21 : Crop Production and Management
Chapter: 8th Science : Chapter 21 : Crop Production and Management
Questions Answers
TEXTBOOK EXERCISES
I. Choose the best
answer
1.
The process of placing seeds in the soil iscalled as
a. ploughing
b. sowing
c. crop production
d. crop rotation
[Answer: (b) sowing]
2.
Organism that control insects and pests of plant crops is
a. bio-pesticides
b. bio-fertilizers
c. earthworms
d. neem leaves
[Answer: (a) bio-pesticides]
3.
The method in which water flows over the soil surface and allow it to
infiltrate is
a. irrigation
b. surface irrigation
c. springler irrigation
d. drip irrigation
[Answer: (b) surface irrigation]
4.
Effective microorganism preparation is not used in
a. seed treatment
b. foliar spray
c. soil treatment
d. bio-predators
[Answer: (a) seed treatment]
5.
Which of the following is not present in Panchagavya?
a. Cow dung
b. Cow’s urine
c. Curd
d. Sugar
[Answer: (d) sugar]
II. Fill in the blanks
1. The process of actively growing seedling from one place and planting in the main field for further growth is called Transplantation.
2. Weed is a plant growing in a
place where it is not wanted.
3. The chemicals used for killing the
weeds or inhibiting their growth are called as
4. Heirloom seeds seeds transfer their
unique characteristics to the descents.
5. Krishi Vigyan Kendra centers serve as the
ultimate link between ICAR and farmers.
6. Several popular high yielding
varieties of major crops have been developed by
III. Match the
following.
1. Bio-pesticide - Neem Leaves
2. Bio-predators - Bacillus
thuringiensis
3. Bio-fertilizer - Control white
flies
4. Bio-indicators - Improve soil
fertility
5. Bio-repellants - Quality of
environment
[ Answer:
(1 - b, 2 - c, 3 - d, 4 - e, 5 - a)]
1. Bio- pesticide - b) Bacillus thuringiensis
2. Bio-predators - c) Control white flies
3. Bio-fertilizer - d) Improve soil fertility
4. Boi-indicators - e) Quality of environment
5. Bio-repellants - a) Neem Leaves
IV. Answer briefly.
1. Define ploughing.
Answer: Ploughing or tilling is the process of loosening and turning the soil up
and down to facilitate the availability of nutrients in the root zone of that
cultivating crop.
2.
Name the methods of sowing.
Answer: The different methods of sowing are
(i) Sowing by hand
(ii) Seed drill
(iii) Dibbling
3.
What is foliar spray?
Answer:
(i) Foliar feeding is a technique of feeding plants by applying
liquid fertilizer directly to their leaves.
(ii) Plants are able to absorb essential elements through the
stomata in their leaves.
4.
Give a brief account on Krishi Vigyan Kendra.
Answer:
(i) Krishi Vigyon Kendra is a farm science centre.
(ii) This centre serve as a ultimate link between ICAR and
farmers.
(iii) They operate small farms to test new technologies.
(iv) They also provide advice to farmers about weather and
pricing of crops.
5.
What is bio-indicator? How does it help human beings?
Answer:
(i) A bio-indicator or biological indicator is any species or
group of species whose function or status reveals the qualitative status of the
environment.
(ii) Biological indicators are used to document and understand
changes in Earth’s living systems especially changes caused by the activities
of an expanding human population.
6.
What do you mean by weeding?
Answer: The undesirable plants growing naturally with crop plants are called
weeds. The removal of weeds is called weeding.
7.
What is crop rotation?
Answer: Crop rotation is planting a series of different crops in the same field
following a defined order. This helps to maintain fertility of the soil.
8.
What is green manure?
Answer:
(i) Some plants like Sun hemp or guar are grown in the field
prior to the sowing of the crop seeds.
(ii) These plants gradually decompose and turn into green manure
which helps in ensuring the soil in nitrogen and phosphorous.
(iii) Application of green manure always enhance the growth and
yield of the crops.
V. Answer in detail.
1.
Explain the agricultural practices.
Answer:
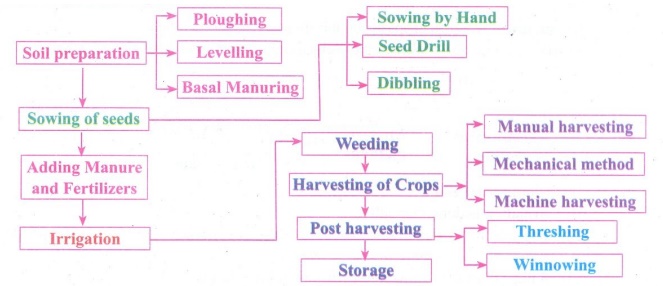
Agricultural practices :
(a) Soil
preparation : (Loosening of top soil)
(i) Ploughing : Process of loosening and turning the soil up and down to
facilitate nutrient availability.
(ii) Levelling : Done with leveller and helps in uniform distribution of water
for irrigation
(iii) Basal
Manuring : Increase soil fertility by manuring
(b) Sowing
of seeds :
(i) Hand
: Scattering of seeds by hand.
(ii) Seed
Drill: Sowing seeds by iron drills attached
to a tractor.
(iii) Dibbling : Placing seed in furrow or pits or hole by hand.
(c) Adding
manure and fertilisers :
(i) Manure is a substance added to the soil in the form of Nutrients
to enhance plant growth.
(ii) Organic
Sources : Plant and animal waste
(iii) Synthetic
Sources : Urea, Super phosphate.
(d) Irrigation:
Supply of water to crops :
1) Traditional method : Irrigation done manually.
2) Modern method : Involve two systems. Sprinkler system Drip
system
(e) Harvesting
of crops :
(i) Manual
harvesting: Harvested without tools. Eg.:
Groundnut crop, green gram, black gram, house gram.
(ii) Mechanical
method : Harvesting by instruments small
sized farms Eg.: Sickle.
(iii) Machine
harvesting : Used for large sized farms.
(f) Threshing and Winnowing :
Process of separating the grains from their chaffs or pods.
(g) Storage:
(i) Supply of the produce has to be stored properly.
(ii) Grains must be free from moisture to avoid growth of
microorganism.
(iii) Need to be dried in Sun before storing.
(iv) Collected in Gunny bags and stored in godowns.
2.
Give a detailed account on irrigation.
Answer:
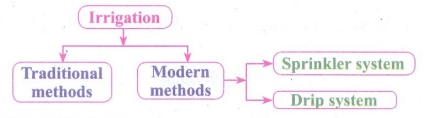
Irrigation
:
(i) The supply of water to crops at regular intervals is called
irrigation.
(ii) Source of irrigation : Wells, tube wells, ponds, lakes, rivers, dams and canal.
a. Traditional
Methods
(i) Irrigation is done manually.
(ii) Here, a farmer pulls out water from wells or canals by
himself or using cattle and carries to farming fields.
(iii) Pumps used for lifting water from various sources.
(iv) Diesel, biogas, electricity and solar energy are the
sources of energy needed to run these pumps.
b. Modern
Methods :
(i) It helps to overcome the problems exist in the traditional
methods.
(ii) It also facilitates the even distribution of moisture in
the field.
a. Sprinkler
system :
(i) Sprinkles water over the crop and helps in an even
distribution of water.
(ii) This method is advisable in areas facing water scarcity.
(iii) Pump is connected to pipes which generate pressure and
water is sprinkled through the fine nozzles of pipes.
b. Drip
System :
(i) Here, water is released drop by drop exactly at root zone
using a hose or pipe.
(ii) This method is effective one in regions where the
availability of water is less.
3.
What is weed? Explain the different methods of weed control.
Answer:
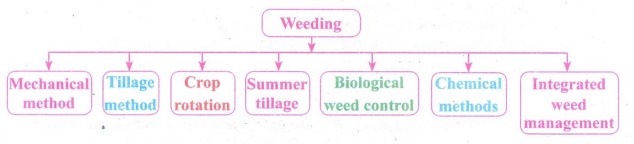
Weed : The undesirable plants may grow naturally along with the main
crop, and these undesirable plants are called weeds.
Weeding : The removal of weeds is called weeding. It is an important
process because weeds compete with the crop plants for the nutrients, sunlight,
water, space and other resources. It results in the undernourishment of crops
and it leads to low yield.
Mechanical
methods :
(i) Here, weeds are destroyed physically.
(ii) Hand pulling or weeding with the help of weeding hole is
the oldest and most efficient method for controlling weeds.
Tillage
methods :
(i) It is the practical methods of destroying weeds of all
categories.
(ii) Weeds are buried in the soil and also exposed to Sun heat
by deep ploughing.
Crop
Rotation :
Proper rotation of crops is followed for controlling crop associated and parasitic weeds.
Summer
tillage :
Deep ploughing after harvest of Rabi crop and exposing
underground parts of weeds to strong sunlight during summer months is useful
for destroying many annual and perennial weeds.
Biological
weed control:
(i) Bio agents like insects and pathogens are used to control weeds.
(ii) The objectives are not eradication, but reduction and
regulation of the weed population. :
Chemical
methods :
(i) Very effective in certain cases and have great scope in weed
control.
(ii) The chemicals used for killing the weeds or inhibiting their
growth are called herbicides.
(iii) Chemicals are mixed with water and sprayed over the crops.
Integrated
weed management:
(i) Integrated weed management combines different agronomic
practices and herbicides use to manage
weeds, so that the reliance on any one weed control technique is reduced.
(ii) Mechanical, biological, cultural and chemical methods are included in integrated weed managements.
Related Topics