Movements in Animals | Chapter 19 | 8th Science - Questions Answers | 8th Science : Chapter 19 : Movements in Animals
Chapter: 8th Science : Chapter 19 : Movements in Animals
Questions Answers
TEXTBOOK EXERCISES
I. Choose the best
answer.
1.
Which of the following parts of our body help us in movement?
(i)
Bones (ii) Skin (iii) Muscles (iv) Organs
Choose
the correct answer from the options below.
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iv)
c) (i) and (iv)
(d) (iii) and (ii)
[Answer: (a) (i) and (iii)]
2.
Which one of the following organisms lack muscles and skeleton for movement?
(a) Dog
(b) Snail
(c) Earthworm
(d) Human being
[Answer: (b) Snail]
3.
__________ joints are immovable.
(a) Shoulder and arm
(b) Knee and joint
(c) Upper jaw and skull
(d) Lower jaw and upper jaw
[Answer: (c) Upper jaw and skull]
4.
Why do underwater divers wear fin-like flippers on their feet ?
(a) To swim easily in water.
(b) To look like a fish.
(c) To walk on water surface.
(d) To walk over the bottom of the
sea (sea bed)
[Answer: (a) To swim easily in water]
5
External ear (pinna )is supported by
(a) bone
(b) cartilage
(c) tendon
(d) capsule
[ Answer: (b) cartilage]
6
Cockroach moves with the help of its
(a) leg
(b) bone
(c) muscular foot
(d) whole body
[Answer: (d) whole body]
7.
Which one of the following categories of vertebrae are correctly numbered?
(a) Cervical-7
(b) Thoracic-10
(c) Lumbar - 4
(d) Sacral – 4
[Answer: (a) Cervical-7]
II. Fill in the
blanks.
1. Movement of organisms from place to
place is called locomotion.
2. Movement refers to change in
position of the part of an organisms body.
3. A structure which provides rigid
frame work to the body is called
4. Axil skeleton in human consists of Skull, facial bones, sternum, ribs and vertebral column.
5. Appendicular skeleton in human
consists of Pelvic and Pectoral girdle.
6. The place where two bones meet is
termed as Joint.
7. Smooth muscle is attached to soft
parts of the body like blood vessels, iris, bronchi and the skin
8. Radial muscle makes pupil of
eyes wider.
III. State true or
false. If false, correct the statement.
1. Skull in humans consists of 22
bones.
2. There are 12 pairs of ribs in
human body.
3. Pelvic girdle is a part of axial
skeleton.
Correct statement: Pelvic girdle is a part of appendicular skeleton.
4. Hinge joint is slightly movable
joint.
5. Cardiac muscle is a voluntary
muscle.
Correct statement: Cardiac muscle is a involuntary muscle.
6. The flexor and extensor muscle of
the arm are antagonistic muscles.
IV. Answer very
briefly.
1.
What is skeleton?
Answer:
(i) The skeleton system provides the hard structure or framework
to the human body which supports and protects the body.
(ii) It is composed of connective tissues like bones, cartilage,
tendons and ligaments.
2.
What is cranium?
Answer:
(i) Skull has 22 bones of which 8 bones are fixed together to
form the cranium.
(ii) It is called brain box since it protects the brain.
3.
Why our backbone is slightly moveable?
Answer: In the backbone, vertebrae are joined by gliding points, which allow
the body to be bent back, front or side wards.
4.
Differentiate axial and appendicular skeleton.
Answer:
axial
skeleton
The axial skeleton consists of the bones along the axis, or
central line of the human body and consists of the skull, facial bones,
sternum, ribs, and vertebral column.
appendicular skeleton
The appendicular skeleton contains the bones in the appendages
of the body, as well as the structures that connect the appendages to the axial
skeleton. It comprises the shoulder girdle; the arm, wrist, and hand bones; the
pelvic girdle; and the leg, ankle, and foot bones.
5.
What is ligament?
Answer: A ligament is a band of strong fibrous tissue which connects a bone to
a bone.
6.
Define muscle.
Answer: Muscles are long bundles of contractile tissue, which has a fixed end
(Origin) and movable end which pulls some other part.
7.
Differentiate tendons and ligament.
Answer:
Tendon
1. They are made of elastic tissue.
2. They attach muscle to a bone
Ligament
They are short bands of tough fibrous connective tissues.
They connect one bone to another
V. Answer briefly.
1.
Differentiate between the following.
a. Movement and Locomotion.
Answer:
(a)
Movement and Locomotion]
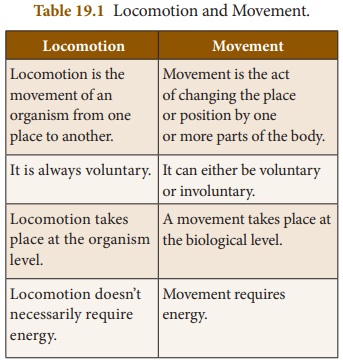
Movement
1. Movement is the act of changing the place or position by one
or more parts of the body.
2. It can either be voluntary or involuntary.
3. A movement takes place at the biological level.
4. Movement requires energy.
Locomotion
1. Locomotion is the movement of an organism from one place to
another.
2. It is always voluntary.
3. Locomotion takes place at the organism level.
4. Locomotion doesn’t necessarily require energy.
b. Endoskeleton and Exoskleton
b)
Endoskeleton and Exoskleton

Endoskeleton
1. It is the skeleton found inside the body.
2. It originals from mesoderm.
3. Eg. Human beings.
Exoskleton
1. It is the skeleton found on the exterior layer of the body.
2. It originals from embryonic ectoderm or mesoderm.
3. Eg. Scales of fish feathers of birds
c. Pectoral and Pelvic girdle
(c)
Pectoral and Pelvic girdle

Pectoral
girdle
1. It is situated in the shoulder region.
2. It gives articulation to forelimbs.
3. The shoulder blade and collar bone remain separate.
4. They are comparitively lighter.
Pelvic
girdle
1. It is situated in the hip region.
2. It gives articulation to legs or hind limb.
3. Three bones (ilium, ischium and pubis) are fused to form a
single hip bone.
4. They are strong to take upto lot of stress
d. Ball and socket Joint and hinge Joint
(d) Ball
and socket Joint and Hinge Joint
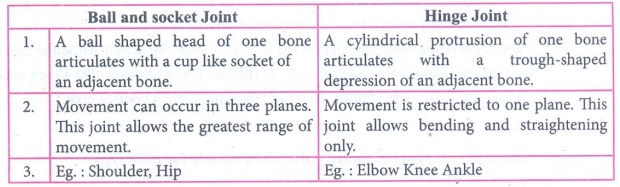
Ball and
socket Joint
1. A ball shaped head of one bone articulates with a cup like
socket of an adjacent bone.
2. Movement can occur in three planes. This joint allows the
greatest range of movement.
3. Eg.: Shoulder, Hip
Hinge
Joint
1. A cylindrical, protrusion of one bone articulates with a
trough-shaped depression of an adjacent bone.
2. Movement is restricted to one plane. This joint allows
bending and straightening only.
3. Eg.: Elbow Knee Ankle
e. Voluntary and Involuntary muscle
(e)
Voluntary and Involuntary muscle

Voluntary
muscle
1. They are striated (Multinucleate muscles and unbranched)
muscles.
2. They are attached to bones. Eg.: found in arms, legs
3. They are used as per our will.
Involuntary
muscle
1. They are non-striated (Single muscle, central nucleus)
muscles.
2. They are attached to soft parts of the body like blood
vessels, Iris, Skin etc.
3. They are not under our control.
2.
What are antagonistic muscles? Give one example.
Answer:
(i) Muscles often work in pairs which work against each other.
These are called antagonistic pairs.
(ii) The muscles in the upper arm control the bending and
straightening of the arm.
(iii) The two muscles, the biceps and triceps are working
against each other.
(iv) When the biceps contracts the lower arm is raised and the
arm bends.
(v) In this position the triceps muscle is relaxed.
(vi) To straighten the arm the reverse happens.
(vii) The triceps contracts straightening the arm, while the
biceps relaxes.
3.
How is the skeleton of a bird well-suited for flying?
Answer:
(i) A bird has streamlined body. Its bones are light and strong.
(ii) They are hollow and have air spaces between them.
(iii) The hind limbs of birds are modified as claws, which help
them to walk and to perch.
(iv) The breast bones are modified to hold massive flight
muscles which help in moving wings up and down.
(v) Birds have special flight muscles and the forelimbs are
modified as wings.
(vi) The wings and tail have long feathers, which help in
flying. Birds show two types of flight: gliding
and flapping.
4.
What are the functions of skeleton in human body?
Answer: The skeletal system serves five important functions in the
human body.
(i) It provides structure and shape to the body.
(ii) It supports and surrounds the internal organs of the body.
(iii) Calcium and phosphorus, the two minerals that the body
needs for important regulatory functions, are stored inside the bones.
(iv) Red blood cells are produced in the bone marrow.
(v) The bones of the skeletal system act as levers for muscular
action. Muscular movement would not be possible without tendons (fibrous cords of tissue that attach muscle to bone) and ligaments (fibrous cords of tissue that
attach bone to bone).
VI. Answer in detail.
1.
Name the different types of joints? Give one example for each type.
Answer:
Different types of joints.
Joint :
Examples
Ball and Socket : Shoulder Hip
Hinge : Elbow Knee Ankle
Pivot : Spine (Atlas / Axis joint at the top)
Condyloid : Wrist
Gliding : Spine (between the bony processes of the vertebrae)
Saddle : Thumb, shoulder and inner ear.
2.
Write about the human axial skeleton, giving suitable labelled diagram.
Answer:
The axial skeleton consists of the bones along the axis or
central line of the human body. It consists of the skull, facial bones sternum,
ribs and vertebral column.
Skull :
(i) It is a hard structure made of 22 bones.
(ii) 8 bones are fixed together to form the cranium and 14 hones
fuse to form the face.
(iii) The lower jaw is the only movable bone of the skull.
Vertebral
column :
(i) It is called the backbone and runs of the back of the body.
(ii) It is made of 33 individual bones called vertebrae as
follows :
7 Cervical vertebrae
12 Thoracic vertebrae
5 Lumbar vertebrae
5 Fused sacral vertebrae
4 Fused coccygeal vertebrae
(iii) The hollow tube of the vertebral column contains the
spinal cord.
(iv) Vertebrae are joined by gliding points which allow the body
to be bent back, front or sidewards.
Function
of vertebral column
(i) It protects the spinal cord
(ii) It supports the head
(iii) It serves as an attachment for ribs
(iv) Helps in walking, standing erect and posture.
Sternum
or Ribcage
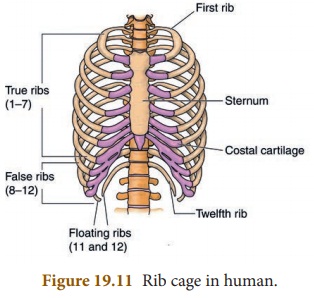
(i) It is a cone shaped structure in the chest region and made
up of 12 pairs of ribs.
(ii) The ribs attached to the vertebral column at the back and
the breast bone in the front.
(iii) There are 12 pairs of ribs.
❖ First 10 pairs are
attached to breast bone.
❖ 2 pairs are called free
floating ribs and are free in the front.
(iv) Rib cage can contract and expand during breathing.
(v) It protects the lungs, hearts and a part to the liver.
3.
Discuss various types of movements seen in living organisms.
Answer:
There are
three types of movements:
(i) Amoeboid
movement : It is brought about by pseudopodia
which are appendages which move with movement of protoplasm within a cell.
(ii) Ciliary
movement: This movement is brought about by
appendages called as cilia which are the hair-like extensions of the
epithelium. Both these kinds of movements are seen with cells of the lymphatic
system.
(iii) Muscular
movement : It is a more complex movement which
is brought about by the musculoskeletal system. This type of movement is seen
in the higher vertebrates. Eg. : Human beings.
The movements brought about by the musculoskeletal system,
comprising of the joints, skeleton and types of muscles.
Some of the movements in body parts of human are:
(a) Movement of eyelids.
(b) Movement of the heart muscles.
(c) Movement of teeth and jaw.
(d) Movement of arms and legs.
(e) Movements of head.
(f) Movements of neck.
4.
What is a streamlined body? How does it help in the movement of animals that
fly or swim in water?
Answer:
(i) A streamlined body is one which is pointed at the ends and
broad in the middle. When such a body travels through a fluid or gaseous medium
it exhibits minimum friction or resistance. A body shape which is streamlined
helps cut against the friction created by the medium around the moving body.
(ii) Streamlined body lowers the friction drag between a fluid,
air or water and an object moving trough that fluid. Drag is a force that slows
down motion. Streamlining reduces the surface area of the moving object.
(iii) Streamlining reduces friction of movement to a minimum
thus decreasing overall drag. Fishes can save energy while swimming because of
the streamlined body. Similarly birds can fly easily since streamlined body
reduces resistance to air.
5.
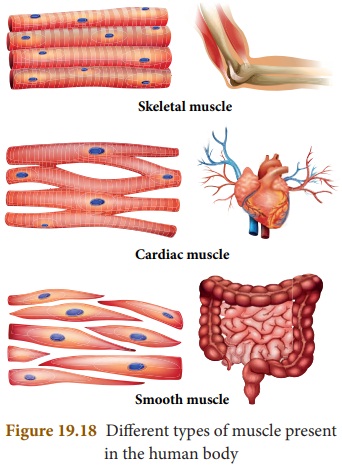
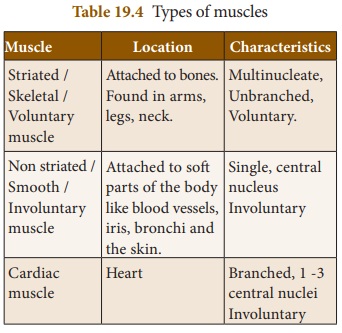
Write a short note on different types of muscles.
Answer: Muscles found in higher vertebrates are of three types:
(i) Striated or skeletal muscles or voluntary muscles.
(ii) Unstriated or smooth muscles or involuntary muscles.
(iii) Cardiac muscles.
Related Topics