Movements in Animals | Chapter 19 | 8th Science - Movement and Locomotion | 8th Science : Chapter 19 : Movements in Animals
Chapter: 8th Science : Chapter 19 : Movements in Animals
Movement and Locomotion
Movement and Locomotion
Although both movement and
locomotion sound similar in their meaning, there are few interesting
differences between the two terms. Movement is generally defined “as the act of changing the place or
position by one or more parts of the body”. Movement helps to perform
necessary functions such as pumping of blood to different parts of the body in
an organism. Movement can be both voluntary
and involuntary. For example,
walking is a voluntary movement, while breathing is an involuntary movement.
The movement of an organism from one
place to another is known as locomotion. Locomotion helps an organism to find
food, avoid harsh weather conditions, escape from their predator etc. Walking,
running and swimming are few examples for different types of locomotion. In
this process, there is the action of appendages such as limbs, wings, flagella
and cilia. In most of the aquatic animals such as fish, whales, and shark, the
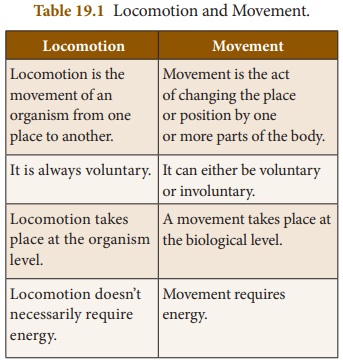
locomotion results from a series of wave-like muscle contractions. Table 19.1
gives the differences between locomotion and movement.
Related Topics