Microorganisms | Chapter 16 | 8th Science - Protozoa | 8th Science : Chapter 16 : Microorganisms
Chapter: 8th Science : Chapter 16 : Microorganisms
Protozoa
Protozoa
A protozoan (In Greek, ‘protos’
means first and ‘zoan’ means animal) is a single-celled eukaryote. They are
included under the kingdom Protista.
The study of protozoa is called Protozoology.
They are found in ponds, ocean, in moist soil, and in the cells and tissues of
plants and animals causing diseases. They range from 2 to 200 microns.
Protozoans have specialized organelles. These organelles are used for movement,
feeding, and other functions. The types of protozoans are as follows:
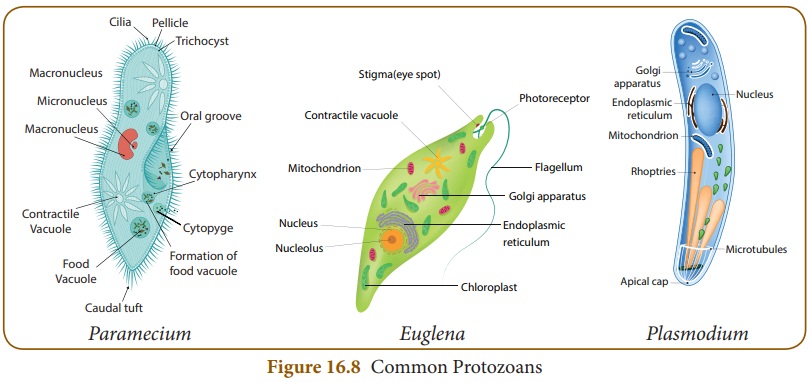
Ciliates: Presence of cilia for
locomotion.
Eg. Paramecium
Flagellates: Presence of flagella
for locomotion.
Eg. Euglena
Pseudopods: Presence of pseudopodia
for locomotion.
Eg. Amoeba
Sporozoans: Parasites.
Eg. Plasmodium
Activity 2
Take one or two drops
of hay (In tamil, vaikol) decoction on a slide and observe it under the
microscope.
Cell structure of
Protozoa
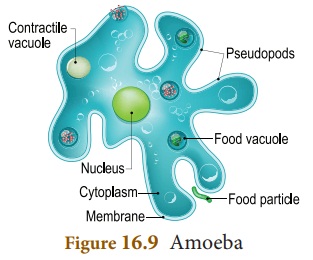
Amoeba is a unicellular microscopic
organism. It is found in ponds. Amoeba
is irregular in shape. It has cell membrane, cytoplasm and nucleus. It is a
protozoan that moves by means of pseudopodia (In Latin, ‘false feet’).
Pseudopodia are the extended part of cell membrane. It helps to catch its prey
(Algae) . The body flows around the food particle and engulfs it forming food
vacuoles. Contractile vacuoles are seen in the cytoplasm that help in
excretion. Amoeba reproduces by means
of fission and sporulation.
Related Topics