Microorganisms | Chapter 16 | 8th Science - Bacteria | 8th Science : Chapter 16 : Microorganisms
Chapter: 8th Science : Chapter 16 : Microorganisms
Bacteria
Bacteria
Bacteria are single-celled
prokaryotes (cells without nuclei). They are considered to be the first living
organisms on earth. Bacteria are grouped under the kingdom Monera. The study of
bacteria is called bacteriology. The size of bacteria ranges from 1µm to 5µm
(micrometer). Bacteria are of two types based on respiration. They are:
* Aerobic bacteria (requires
oxygen).
* Anaerobic bacteria (does not
require oxygen).
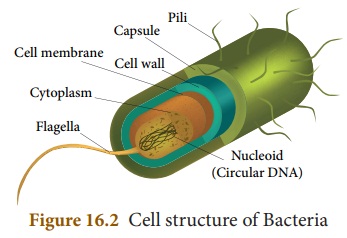
Cell structure of
Bacteria
A bacterium has an outer covering
known as the cell wall. Nuclear material is represented by a nucleoid without
nuclear membrane. An extra chromosomal DNA called plasmid is present in the
cytoplasm. Protein synthesis is carried out by 70S ribosomes. Other cell
organelles (mitochondria, golgi body, endoplasmic reticulum etc. ,) are absent.
Flagella aids in locomotion.
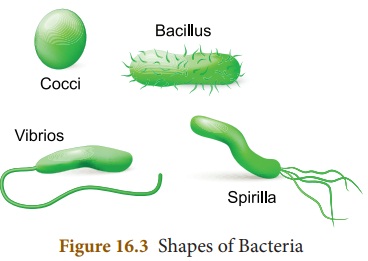
Bacteria are classified according to
the shape of their cells. They are:
* Bacilli: Rod shaped bacteria. Eg. Bacillus anthracis
* Spirilla: Spiral shaped bacteria. Eg.
Helicobacter pylori
* Cocci: Spherical or ball shaped
bacteria. They can stick together in pairs (diplococcus) or form a chain
(streptococcus) or occur in bunches (staphylococcus).
* Vibrio - Comma shaped bacteria. Eg.
Vibrio cholera.
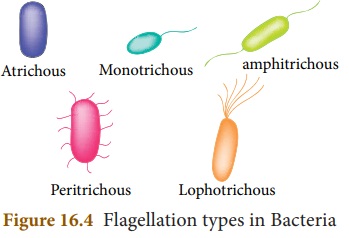
Bacteria are also classified
according to the number and arrangement of flagella. They are as follows.
* Monotrichous: Single flagella at
one end. Eg. Vibrio cholera
* Lophotrichous: Tuft of flagella at
one end. Eg. Pseudomonas.
* Amphitrichous: Tuft of flagella at
both ends. Eg. Rhodospirillum rubrum.
* Peritrichous: Flagella all around.
Eg. E.coli.
* Atrichous: Without any flagella. Eg.
Corynebacterium diptherae.
Bacteria get their food in many
ways. Photosynthetic bacteria make their own food (Eg. Cyanobacteria) . Bacteria that live in harsh environment use
chemicals (Ammonia, Hydrogen sulphide) to produce their food instead of
utilizing energy from the sun. This process is called chemosynthesis. Some
bacteria exhibit symbiotic relationship (Eg. E.coli lives in the intestine of
man). Bacteria reproduces by fission (Binary and multiple fission).
Activity 1
Take one or two drops
of butter milk on a slide and spread it. Heat the slide slightly on a lamp ( 3
– 4 seconds). Add a few drops of crystal violet and leave it for 30 to 60
seconds. Then wash the slide gently with water. Observe the slide under the
compound microscope.
Related Topics