Solved Example Problems | Trigonometry | Mathematics - Problems involving Angle of Elevation and Depression | 10th Mathematics : UNIT 6 : Trigonometry
Chapter: 10th Mathematics : UNIT 6 : Trigonometry
Problems involving Angle of Elevation and Depression
Problems involving Angle of Elevation and
Depression
Let us consider the following situation.
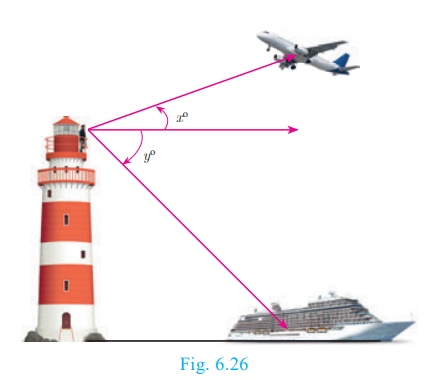
A man standing at a top of lighthouse located in a beach watch on
aeroplane flying above the sea. At the same instant he watch a ship sailing in
the sea. The angle with which he watch the plane correspond to angle of
elevation and the angle of watching the ship corresponding to angle of
depression. This is one example were one oberseves both angle of elevation and
angle of depression.
In the Fig.6.26, x° is the angle of elevation and y° is the angle of depression.
In this section, we try to solve problems when Angles of elevation
and depression are given.
Example 6.31
From the top of a 12 m high building, the angle of elevation of the top
of a cable tower is 60° and
the angle of depression of its foot is 30°. Determine the height of the tower.
Solution
As shown in Fig.6.27, OA is the building, O is the point of
observation on the top of the building OA. Then, OA = 12 m.
PP’ is the cable tower
with P as the top and P ' as the bottom.
Then the angle of elevation of P, ∠MOP = 60°
And the angle of depression of P’ , ∠MOP′ = 30°.
Suppose, height of the cable tower PP ' = h metres.
Through O, draw OM ┴ PP '
MP = PP′ − MP′ = h − OA =
h −12
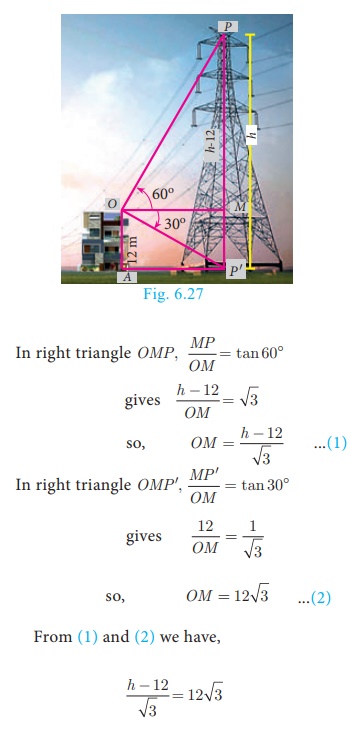
Hence, the required height of the cable tower is 48 m.
Example 6.32
A pole 5 m high is fixed on the top of a tower. The angle of elevation of the top of the pole
observed from a point ‘A’ on the ground is 60° and the angle of
depression to the point ‘A’ from the top of the tower is 45°. Find the
height of the tower. (√3=1.732)
Solution
Let BC be the height of the tower and CD be the height of the pole.
Let ‘A’ be the point of observation.
Let BC = x and AB = y.
From the diagram,
∠BAD = 60° and ∠XCA = 45° = ∠BAC
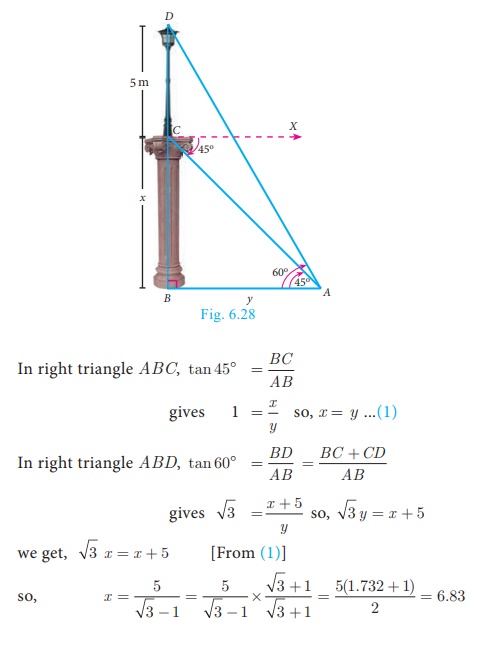
Hence, height of the tower is 6.83 m.
Example 6.33
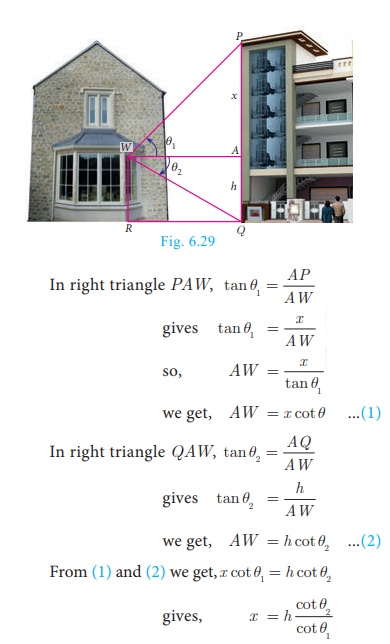
From a window (h metres high above the ground) of a house in a
street,
the angles of elevation
and depression of the top and the foot of another house on the opposite
side of the street are θ1 and θ2
respectively. Show that the height of the opposite house is 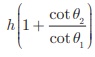 .
.
Solution
Let W be the point on the window where the angles of elevation and
depression are measured. Let PQ be the house on the opposite side.
Then WA is the width of the street.
Height of the window = h metres
=
AQ (WR = AQ)
Let PA = x metres.
Therefore,
height of the opposite house = PA+AQ = x
+ h = 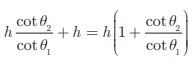
Hence Proved.
Related Topics