Chapter: 11th Biochemistry : Chapter 10 : Biochemical Techniques
Principle of chromatography
Principle of chromatography
Chromatography
is defined as the method of separation of different substances based on their
partition coefficients in two immiscible phases. Chromatography involves a
stationary and a mobile phase. The sample to be analysed, when placed in the
stationary phase (solid, bonded coating) will gradually move along in the same
direction as the mobile phase (liquid or gas). A component that is soluble in
the stationery phase takes a longer time to travel as compared to the one that
is insoluble. Therefore, the differences in their mobility can be ascribed to
the interaction of the sample with the mobile and stationary phase. For a
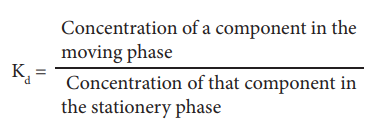
compound distributing itself between equal volumes of two immiscible solvents A
& B, the distribution or partition co-efficient (Kd) is given as,
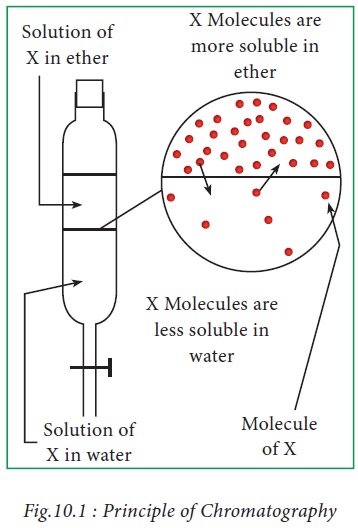
As shown in Fig.10.1, substances present in X will tend to cross the boundary between the two liquid layers, to form a dynamic equilibrium.
Related Topics