Chapter: Clinical Anesthesiology: Clinical Pharmacology: Adjuncts to Anesthesia
Postoperative Nausea & Vomiting PONV
Postoperative Nausea & Vomiting PONV
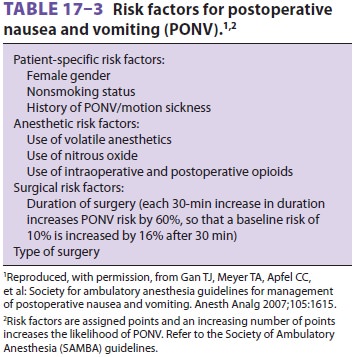
Without any prophylaxis, PONV occurs in
approx-imately 20–30% of the general surgical population and up to 70–80% in
patients with predisposing risk factors (Table 17–3). As anesthetic duration increases,
so, too, does PONV risk. When the risk is sufficiently great, prophylactic
antiemetic medications are administered and strategies to reduce its incidence
are initiated. The Society of Ambulatory Anesthesia (SAMBA) provides
sim-plified risk scoring systems, which assign points for specific risk
factors, as well as guidelines that assist in the management of at-risk
patients (Table
17–4). Obesity, anxiety, and reversal of neuromuscular blockade are
not independent risk factors for PONV.
Drugs used in the prophylaxis and
treatment of PONV include 5-HT3 antagonists, butyrophe-nones,
dexamethasone, neurokinin-1 receptor antagonists (aprepitant, Emend);
antihistamines and transdermal scopolamine may also be used. At-risk patients
often benefit from one or more prophylactic measures.

Related Topics