Chapter: Mechanical : Engineering materials and metallurgy : Non-Metallic Materials
Polymer synthesis
Polymer synthesis
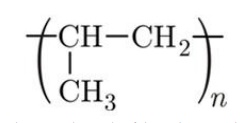
The
repeating unit of the polymer polypropylene.
Polymerization
is the process of combining many small molecules known as monomers into a
covalently bonded chain. During the polymerization process, some chemical
groups may be lost from each monomer. This is the case, for example, in the
polymerization of PET polyester. The monomers are terephthalic acid (HOOC-C6H4-
COOH) and ethylene glycol (HO-CH2-CH2-OH) but the repeating unit is -OC-C6H4-
COO-CH2-CH2-O-, which corresponds to the combination of the two monomers with
the loss of two water molecules. The distinct piece of each monomer that is
incorporated into the polymer is known as a repeat unit or monomer residue.
Laboratory
synthesis
Laboratory synthetic methods are generally divided
into two categories, step-growth polymerization and chain-growth
polymerization. The essential difference between the two is that in chain
growth polymerization, monomers are added to the chain one at a time
only,whereas in step-growth polymerization chains of monomers may combine with
one another directly. However, some newer methods such as plasma polymerization
do not fit neatly into either category. Synthetic polymerization reactions may
be carried out with or without a catalyst. Laboratory synthesis of biopolymers,
especially of proteins, is an area of intensive research.
Biological synthesis
There are
three main classes of biopolymers: polysaccharides, polypeptides, and polynucleotides.
In living cells, they may be synthesized by enzyme-mediated processes, such as
the formation of DNA catalyzed by DNA polymerase. The synthesis of proteins
involves multiple enzyme-mediated processes to transcribe genetic information
from the DNA to RNA and subsequently translate that information to synthesize
the specified protein from amino acids. The protein may be modified further
following translation in order to provide appropriate structure and
functioning.
Related Topics