Chapter: Mechanical : Engineering materials and metallurgy : Non-Metallic Materials
Elastomer
ELASTOMER
POLYISOPRENE (NATURAL RUBBER)
Excellent abrasion resistance; Excellent tear
strength;
Excellent
resilinence;
Excellent
low temperature flexibility; Excellent dielectric strength;
Poor resistance to ozone and oxygen; Poor
resistance to sunlight and heat; Poor resistance to solvents.
Applications:
automobile tires, gaskets, hoses.
Elastomer
ELASTOMER BUTYL (ISOBUTENE-ISOPRENE)
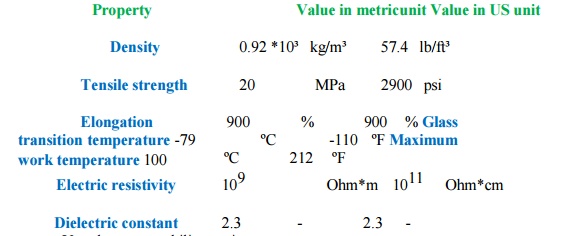
Applications: inner lining of automobile tires, steam hoses and diaphragms.
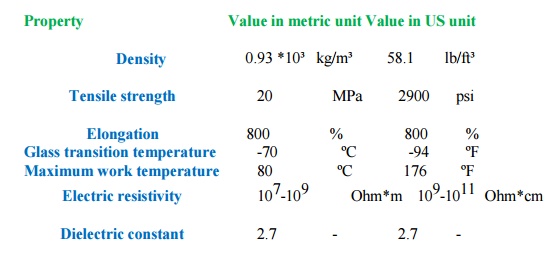
ELASTOMER
NEOPRENE (CHLOROPRENE)
Property Value
in metric unit Value in US unit
Density 1.23 *10³ kg/m³ 76.8 lb/ft³
Tensile
strength 25 MPa 3630 psi
Elongation 1000 % 1000 %
Glass
transition temperature -50 ºC -58 ºF
Maximum
work temperature 100 ºC 212 ºF
Electric
resistivity 103 Ohm*m 105 Ohm*cm
Dielectric
constant 9 - 9 -
Excellent
abrasion resistance;
Good
resistance to oil, fuel and petroleum based solvents; Excellent resistance to
ozone;
Very good
resistance to sunlight; Poor resistance to lacquer solvents.
Applications:
oil and crude oil hoses, gaskets, diaphragms, lining of chemical vessels.
Elastomer
ELASTOMER
ETHYLENE-PROPYLENE (EPDM)
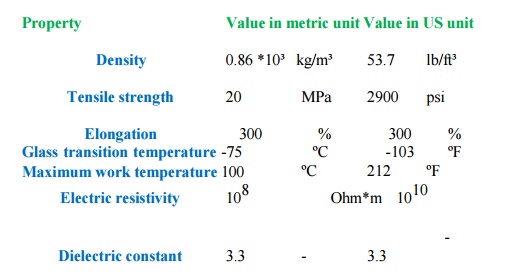
Property Value
in metric unit Value in US unit
Density 0.86 *10³ kg/m³ 53.7 lb/ft³
Tensile
strength 20 MPa 2900 psi
Elongation 300 % 300 %
Glass
transition temperature -75 ºC -103 ºF
Maximum
work temperature 100 ºC 212 ºF
Electric
resistivity 108 Ohm*m 1010
Dielectric
constant 3.3 - 3.3 -
Excellent
resistance to sunlight and heat;
Excellent resistance to ozone and oxygen; Excellent resistance to water and steam; Excellent low temperature flexibility; Good dielectric strength;
Good abrasion resistance;
Poor resistance to fuel, oil, alcohol.
Applications: electrical insulation, shoe soles, hoses, conveyor belts.
ELASTOMER SILICONE
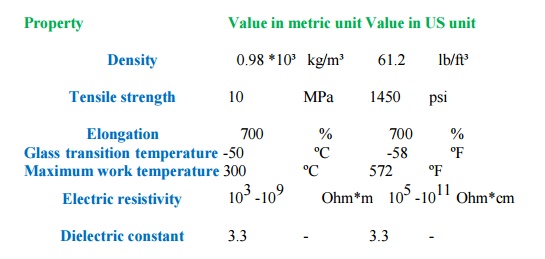
Excellent
resistance to ozone and oxygen;
Excellent resistance to heat and sunlight; Excellent weather resistance;
Wide work
temperature interval: -150ºF…600 ºF (-100ºC…315 ºC) Poor resistance to fuel, oil, hydrocarbons;
Poor
abrasion resistance Poor tear resistance
Applications: high temperature sealant, adhesives, vibration damping components.
THERMOPLASTICS
Thermoplastics
are polymers, which soften (becomes pliable and plastic) and melt when heated.
In the melted conditions thermoplastics may be formed by various methods
(injection molding, extrusion, Thermoforming). No new cross-links form (no
chemical curing) when a thermoplastic cools and harden. Thermoplastics may be
reprocessed (re-melt) many times.
Molecules of most of thermoplastics combine long
polymer chains alternating with monomer units.
Thermoplastic materials may contain filler
materials in form of powder or fibers, providing improvement of specific
material properties (strength, stiffness, lubricity, color etc.).
Thermoplastic groups:
Polyolefines:
Low Density Polyethylene (LDPE), High Density Polyethylene (HDPE), Polypropylene
(PP).
Styrenics:
Polysterene (PS), Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene (ABS),
Styrene-Acrylonitrile (SAN), Styrene/Acrylic (S/A), Styrene-Maleic Anhydride
(SMA).
Vinyls: Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC), Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride (CPVC).
Acrylics:
Polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA), Polyvinilchloride-Acrylic Blend (PVC/MA).
Fluoropolymers: Polychlorotrifluoroethylene (CTFE), Polytetrafluoroethylene
(PTFE),
Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF).
Polyesters:
Polyethylene Terephtalate (PET), Polyester PETG (PETG), Polybutylene
Terephtalate (PBT), Polyarilate (PAR), Liquid Crystal Polyester (LCP).
Polyamides (Nylons): Nylon 6 (N6), Nylon 66 (N66), Nylon 11 (N11), Nylon
12 (N12),
Polyphtalamide (PPA), Polyamidemide (PAI).
Polyimides: Polyimide (PI), Polyetherimide (PEI).
Polyethers:
Polyacetal (POM), Polycarbonate (PC), Polyphenylene Oxide Blend (PPO),
Polyaryletherketone (PAEK), Polyetheretherketone.
Sulfur Containing Polymers: Polyphenylene Sulfide
(PPS), Polysulfone (PSF), Polyethersulfone (PES),
Polyarylsulfone (PAS).
Properties and
applications of some thermoplastics
Thermoplastic Low Density Polyethylene (LDPE)
Thermoplastic High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) Thermoplastic Polypropylene (PP)
Thermoplastic
Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene (ABS) Thermoplastic Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Thermoplastic
Polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) Thermoplastic Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)
Thermoplastic Polyethylene Terephtalate (PET) Thermoplastic Polyamide (Nylon 6)
Thermoplastic
Polyimide (PI)
Thermoplastic
Polycarbonate (PC) Thermoplastic Polysulfone (PSF)
Related Topics