Chapter: Civil : Principles of Solid Mechanics : Two Dimensional Solutions for Straight and Circular Beams
Polar Coordinates and Airy’s Stress Function
Polar
Coordinates and Airy’s Stress Function
The fundamental relationships for plane polar
coordinates as given in next pages were obtained as a special case of general
curvilinear coordinates. Since polar coordinates are so useful, let us
re-derive them from basic principles. First con-sider equilibrium of a
differential element as shown in Figure 6.3a.


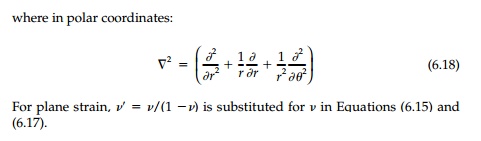
Thus, as with rectangular coordinates, there is the
question of these equations not being satisfied for plane stress. Again we will
assume loads are symmetric with z and we consider the plate to be thin
enough to avoid any serious difficulties.

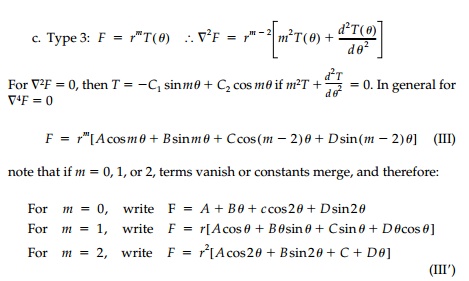
In every case there are
four terms with unknown coefficients, A, B, C, and D to determine. The choice
of which type of stress function and what terms to use will become apparent
from considering the anticipated structural action, the boundary conditions
available, and comparison to special cases approxi-mated by elementary
analysis.
Example 6.2
The casement for a
particle accelerator is a thick steel ring where the magnetic field introduces
a body force in the radial direction, which dies off linearly with the radius
as shown below.
Determine the elasticity solution. Assume plane
strain and determine both the stress field and the displacements.

Related Topics