Chapter: 9th Science : Economic Biology
Pisciculture
Pisciculture
Pisciculture or Fish
culture is the process of breeding and rearing of fishes in ponds, reservoirs
(dams), lakes, rivers and paddy fields. It is the farming of economically
important fishes under controlled conditions. Pisciculture helps in integrated
rural development by generating employment and income to fishing community and
fish farmers.
1. Types of fish culture practices
a)
Extensive fish culture: Culture of fishes in large areas with
low stocking density and natural feeding.
b)
Intensive fish culture: Culture of fishes in small areas with
high stocking density and providing artificial feed to increase production.
c)
Pond culture: Rearing of fishes in pond water.
d)
Riverine fish culture: Rearing of fishes in lotic water.
e)
Dam culture (Culture in Reservoir): Culture of
fishes in artificial man made constructed reservoirs.
f)
Lake culture (Culture in Lake): Rearing of fishes in lakes which are
natural standing water bodies.
g)
Monoculture: Culture of single type of fish in a water body. It is
also called mono species culture.
h)
Polyculture: Culture of more than one type of fish in a water body. It
is also called composite fish culture.
i)
Integrated fish farming: It is the culture of fishes along with
agricultural crops or
j)
animal husbandry farming. Rearing of fish along with paddy,
poultry, cattle, pig and ducks.
2. Types of ponds for fish culture
Fish farm requires
different types of pond for the various developmental stages of fish growth.
They are:
a)
Breeding pond: Healthy and sexually mature male and female fishes are
collected and introduced in this pond for breeding. The eggs released by the
female are fertilized by the sperm and fertilized eggs float in water as frothy
mass.
b)
Hatchling pits: The fertilized eggs are transferred to
hatching pits for hatching. Two types of hatching pits are hatcheries and
hatching hapas.

c)
Nursery ponds: The hatchlings are transferred from hatching pits after 2
to 7 days. The hatchlings grow into fry and are cultured in these ponds for
about 60 days with proper feeding till they reach 2 - 2.5 cm in length.
d)
Rearing ponds: Rearing ponds are used to culture the fry. The fish fry
are transferred from nursery pond to rearing ponds and are maintained for about
three months till they reach 10 to 15 cm in length. In these rearing ponds the
fry develops into fingerlings.
e)
Stocking pond: The stocking pond is also called as culture pond or
production pond. These ponds are used to rear fingerlings upto the marketable
size. Before releasing the fingerlings, the pond is manured with organic manure
and inorganic fertilizers.

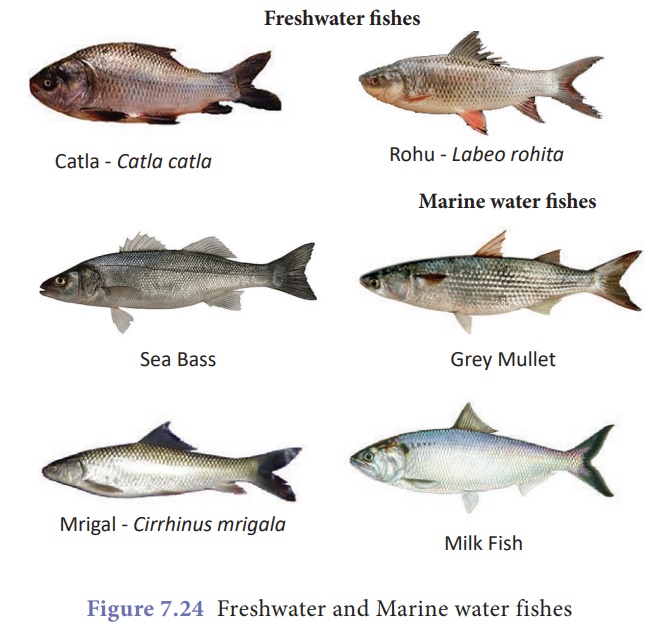
3. Cultivable food fishes in India
Freshwater cultivable
fishes: Indian
major carps (Kendai) – Catla, Rohu, Mrigal, catfishes (Keluthi), Murrels
(Veral) and Tilapia (Jilebi kendai) are cultured in freshwater.
Marine water cultivable
fishes: Sea
bass (Koduva), Grey mullet (Madavai) and Chanos chanos (Milk
fish) are the fishes cultured in marine water.
4. Nutritional value of fishes
Cultivable freshwater
and marine food fishes are highly nutritious, rich source of animal proteins
and are easily digestible. They are rich in essential amino acids such as
lysine and methionine, minerals like calcium, phosphorus, iron, sodium,
potassium and magnesium. Fat soluble vitamins A, D and water soluble B-complex
vitamins like pyridoxine, cyanocobalamine and niacin are found in fishes.
Polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) which are helpful in regulation of
cholesterol are present in plenty in fishes and thus promote cardiac health.
5. Fishery by-products
In addition to providing
food, most of the fishing industries yield a number of by-products of
commercial importance. These processed byproducts are used for human
consumption and also for other purposes. These include:
a. Fish oil: It comprises of liver oil and body oil.
Liver oil of Cod, Tuna,
Halibut and Shark are of great medicinal value and are rich in vitamin A, D and
E.
Body oil is extracted
from Sardines, Herrings, Salmons, Mackerels and Anchovies. They are used in
industries for the preparation of lubricants, paints, varnishes and cosmetics.
b. Fish Meal
It is prepared from the
wastes of fish oil or from whole fish and contains nutritents like protein,
fat, minerals and vitamins. It is used as feed for cattle and poultry farming
animals.
Other by-products
obtained from fishing industry are fish flour, fish manure, fish silage, fish
guano, fish sausage, fish glue, fish leather and isinglass.
Related Topics