Chapter: 9th Science : Economic Biology
Dairy Farming
Dairy
Farming
Dairy farming involves
rising of cattle for milk production. It involves the proper maintenance of
cattle along with, collection and processing of milk and milk products which
are useful to man. Dairying is the production and marketing of milk and its
products.
1. Cattle breeds
The Indian cattle
include cows and buffaloes. They are domesticated for milk, meat, leather and
transportation. They belong to two different species, Bos indicus
(Indian cows and bulls) and Bos bubalis (buffaloes). These cattle
animals are reared for milk and farm labour.
They are classified into
three types:
(i) Dairy breeds
(ii) Draught (or) Draft breeds
(iii) Dual purpose breeds.
(i) Dairy breeds
Dairy animals are
domesticated for obtaining milk. The cows (milk producing females) are high
milk yielders (milch animals). The dairy breeds may be indigenous breeds
(or) exotic breeds.
Indigenous breeds are native of India. They
include Sahiwal, Red Sindhi, Deoni and Gir. These cattle are well
built with strong limbs, prominent hump and loose skin. Milk production depends
on the duration of the lactation period (the period of milk production after
the birth of a calf). These local breed animals show excellent resistant to
diseases.
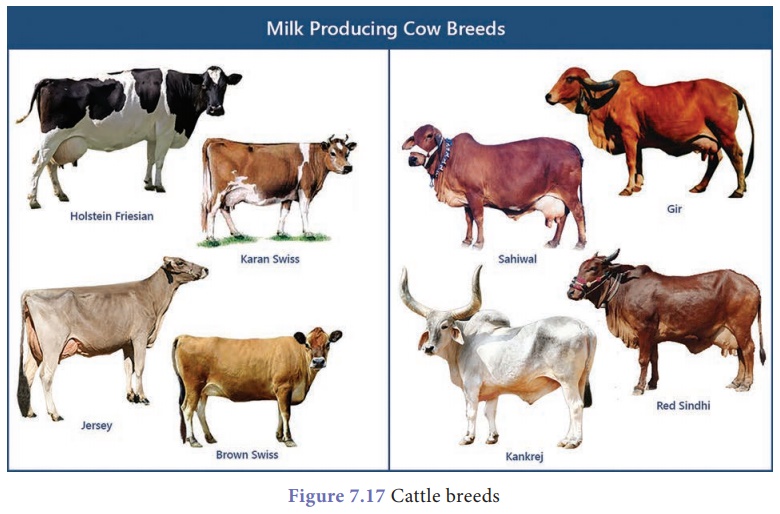
The exotic breeds
(Bos taurus) are imported from foreign countries. They include Jersey,
Brown Swiss and Holstein-Friesian etc. These foreign breeds are
selected for long lactation periods.
The Indian (local)
breeds and foreign breeds can be cross bred to produce animals with both
desired qualities.
(ii) Draught (or) Draft breeds
They are used for
agricultural work, such as tilling, irrigation and carting. These include Amritmahal,
Kangayam, Umblachery, Malvi, Siri and
Hallikar breeds. Bullocks are good draft animals while the cows are
poor milk yielders.
(iii) Dual purpose breeds
These breeds provide
milk and they are useful for farm work. In India these breeds are favoured by
farmers as the cows are fairly good milk yielders and bullocks are good for
draught work. They includes Haryana, Ongole, Kankrej and
Tharparkar.
Buffalo breeds
In India buffaloes are
domesticated in great number. They are the main milk producers. The milk
production of buffaloes is more than that of cows. Murrah, Mehsana
and Surti are indigenous buffalo breeds which are good milk yielders.

2. Composition of cattle feed and its requirements
The food requirement for
cattle should support healthy life of the animal and milk producing
requirement. The feed for dairy cattle is broadly classified into two:
(a) Roughages
(b) Concentrates
Roughage is a coarse and fibrous
fodder. It consists of succulent feed (cultivated grass, fodder and root
crops) and dry fodder (hay, straw and chaff).
Concentrates are low in fibre and
contain high level of carbohydrates, protein and other nutrients. A
variety of raw materials such as cholam (jowar), kambu (pearl millet), ragi
(finger millet), rice bran, wheat bran, cotton seed cake, mustard cake, linseed
cake, groundnut cake, mango seed, neem cake and yellu (sesame) cake can be used
to make concentrate feed. They should also be fed on green fodder (maize,
lucerne, berseem, millet, and elephant grass).
When green fodder is not
available, cattle can be fed with silage. Silage can be defined as fermented
high moisture stored food which can be fed to cows. It is prepared from green
grass, sorghum, cereals and weeds by using the entire green plant.
3. Feed Management
Dairy cattle need
balanced rations containing all nutrients in proportional amounts and food
additives which contain minerals, vitamins, antibiotics and hormones to promote
the growth of animals, good yield of milk and to protect from diseases. The
daily average feed ratio of a milking cow is:
(i) 15-25 kg of roughage (dry grass and green fodder)
(ii) 4-5 kg of grain mixture
(iii) 100-150 litres of
water
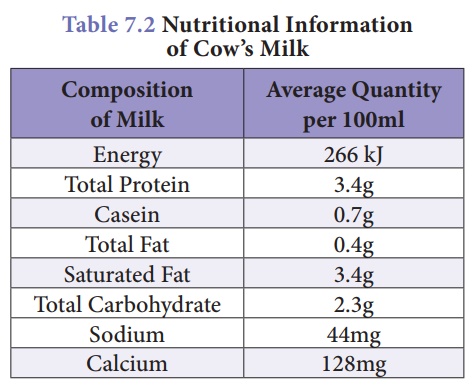
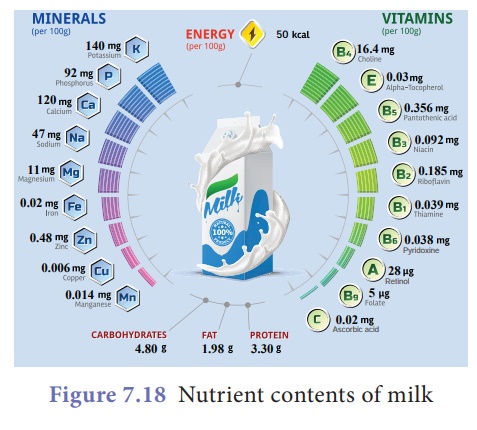
4. Improvement of Livestock development in India
Several policies have
been adopted by the Government to increase the livestock development in India.
Improved breeding techniques in cattle have tremendously increased the
production of new breeds with high capacities.
Intensive Cattle Development Programme
It is based on cross
breeding of indigenous cows with exotic European breeds to increase milk
production. New methods and modern equipments are made available for machine –
milking of cows.
Operation Flood Programme
It is based on dairy
commodity aid to increase milk supply in urban areas.
Related Topics