Matter Around Us | Term 1 Unit 3 | 6th Science - Physical Nature of Matter | 6th Science : Term 1 Unit 3 : Matter Around Us
Chapter: 6th Science : Term 1 Unit 3 : Matter Around Us
Physical Nature of Matter
Physical Nature of Matter
Matter occupies
space and has mass. But what is its nature? Ancient philosophers pondered over
such questions. In India a philosopher named Kanada and in Greece a philosopher
named Democritus came to somewhat similar idea.
Imagine you have a
piece of thread. You cut it into two with the same piece. Take again one of the
piece and cut it again into two. Repeat the above process for many times. At
some point piece of the thread will be so small to see, or we may not have sharp
enough knife to cut further. But this is imaginary ‘thought experiment’.
Therefore these are not possible practically.
Imagine if you can
cut as fine as possible and are able to see even the very small things. Can we
cut the rope into two without an end?
Kanada and
Democritus said, No; we cannot go on endlessly. There will be a point at which
we will not be able to cut the thread further. That is the point when we will
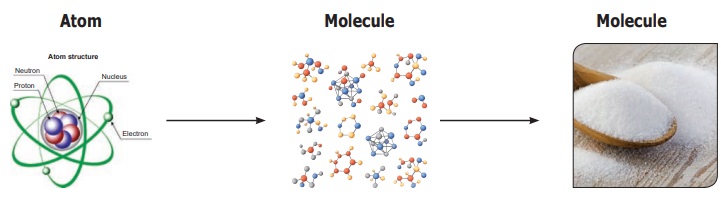
reach molecules or atoms.
We will read more
about molecules and atoms later. Suffice to say that all matter is made up of
very small particles. Gold is made up of tiny gold particles and water is made
up of tiny water particles. These tiny particles present in all matter are
called as atoms or molecules.
The particles in matter are extremely small and cannot be seen even with a powerful microscope. What we can see is only group of particles.
Do you know? that a drop of water contains
about 1021 water particles? One dot that you make with your pen has more
than two lakh molecules.
Characteristics
of the particles of matter
Particles of
matter have a lot of space in between them. In different forms of
matter this spacing will be different.
Let us add a spoon
full of sugar to a glass of water.
Stir well. Sugar
disappears completely. Where has it gone? Will the glass of water be now sweet?

1. Water particles have space between them and
sugar particles are now occupying those spaces.
2. Particles of matter attract each other. It is
this attraction which keeps the particles together. This attractive force will
be different for different forms of matter.
Grouping of Matter on the basis of Physical states
You already know
what grouping is all about.
Matter can be grouped
into Solids, Liquids and Gases based on the above characteristics. These are
called the physical states of matter.
Related Topics