Chapter: BIOLOGY (ZOOLOGY) Standard XI first year 11th text book Assignment topics question and answer Explanation Definition
Phylum : Protozoa, Porifera and Coelenterata or Cnidaria
Phylum : Protozoa, Porifera and Coelenterata or Cnidaria
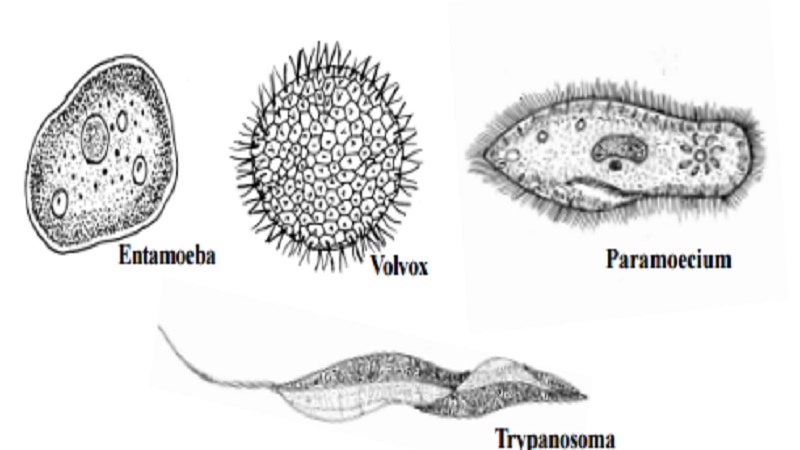
Phylum : Protozoa
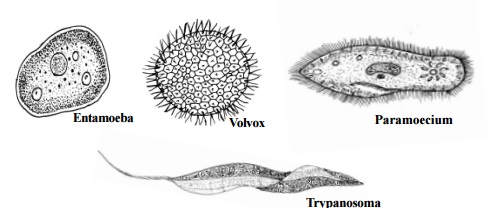
This phylum includes a great diversity of small, microscopic organ-isms. These are single celled eukaryotes. Their locomotion happens using pseudopodia, cilia or flagella.
The nutrition is either autotrophic or heterotrophic. They reproduce either asexually or by sexual methods. Ex : Amoeba, Paramoecium, Plasmodium.
Phylum : Porifera.
These are multicellular, aquatic organisms. They have a cellular grade of construction without the occurrence of tissues. The sponges belonging to this phylum are characterised by the presence of a canal system in their body. The body wall contains spicules. They can reproduce both by asexual
and sexual methods. Ex : Sponges.
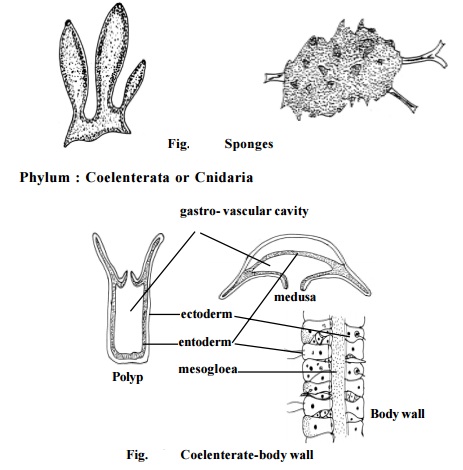
Phylum : Coelenterata or Cnidaria
All coelenterates are aquatic animals. They are mostly marine. The body is radially symmetrical. The body wall is of two layers of cells. The outer layer is called the ectoderm. The inner layer, entoderm is seperated from the ectoderm by a non-cellular mesogloea. The mesogloea is a jelly-like sub-stance. Due to the presence of two layers in the body wall, these are said to be diploblastic animals.
Many coelenterates exhibit polymorphism. In this phylum, organisms exist in two different body forms namely, a polyp, and a medusa.The ectoderm contains stinging cells called nematocysts (cnidoblasts). These cells when triggered can explosively penetrate prey and inject poison.
The layers in the body wall contain several cells and tissues such as muscle cells epithelial tissues, gland-cells and sensory cells.
They reproduce both asexually and sexually. They are divided into three classes, namely Hydrozoa, Scyphozoa and Anthozoa. In Hydrozoa, the animal has a dominant polyp body form and a reduced medusa stage. (e.g)
Hydra, Obelia.
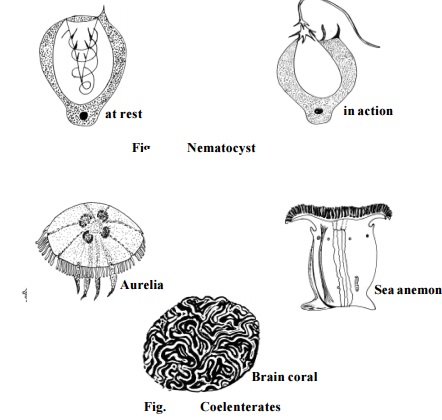
In Scyphozoa the medusa form is permanent. This group includes jelly fishes such as Aurelia. They swim in the surface waters. They have a bell shaped medusa stage.
The Anthozoans mostly remain as polyps. Their body cavity is divided by large radial partitions called mesenteries .
(eg) sea-anemone and corals.
All animals of subsequent phyla show the following general characters.
1. All of them have three layers in the body wall. They are named as outer ectoderm, middle mesoderm, and inner endoderm. Thus they are called as Triploblastic animals.
2. The body is bilaterally symmetrical.
Related Topics