Chapter: 11th Botany : Chapter 13 : Photosynthesis
Photo-Oxidation Phase of Light Reaction
Photo-Oxidation Phase of Light
Reaction
The
action of photon plays a vital role in excitation of pigment molecules to
release an electron. When the molecules absorb a photon, it is in excited
state. When the light source turned off, the high energy electrons return to
their normal low energy orbitals as the excited molecule goes back to its
original stable condition known as ground
state. When molecules absorb or emit light they change their electronic
state. Absorption of blue light excites the chlorophyll to higher energy state
than absorption of Red light, because the energy of photon is higher when their
wavelength is shorter. When the pigment molecule is in an excited state, this
excitation energy is utilised for the phosphorylation. Phosphorylation takes
place with the help of light generated electron and hence it is known as photophosphorylation.
1. Fluorescence and Phosphorescence
Normal
state of an atom or molecule is called ground
state. When a photon of light collides with the chlorophyll molecule, an
electron from outer most orbit is moved to higher energy orbit causing
excitation of chlorophyll. This is known as excited state. There are three excited states such as:
1)
First singlet state (S1)
2)
Second singlet state (S2)
3)
First Triplet Sate (T1)
When a
red light strikes chlorophyll molecule, one electron is released from its
ground level (S0) to first singlet state (S1). It is in
unstable state having half-life period of 10-9 seconds. When a blue light
strikes chlorophyll molecule, one electron is released from its ground level (S
0) to second singlet state (S2). It is because blue light
has shorter wavelength and more energy than red light. This state is also
unstable having half-life period of less than 10–12 seconds. Both S1
and S2 states being unstable move to ground state S0 by
releasing energy through the several possible ways.
i. Fluorescence
The
electron from first singlet state (S1) returns to ground state (S0)
by releasing energy in the form of radiation energy (light) in the red region
and this is known as fluorescence.
Fluorescence is the immediate emission of absorbed radiations (Figure 13.11).
Pathway of electron during fluorescence: S1 → S0
p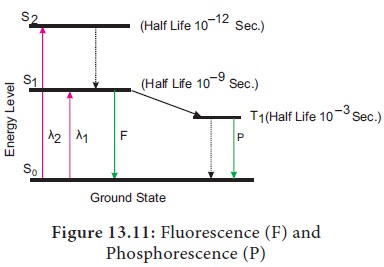
ii. Phosphorescence
Electron from Second Singlet State (S2) may return to next higher energy level (S1) by losing some of its extra energy in the form of heat. From first singlet state (S1) electron further drops to first triplet state (T1). Triplet State is unstable having half life time of 10-3 seconds and electrons returns to ground state with emission of light in red region called as phosphorescence (Figure 13.11). Phosphorescence is the delayed emission of absorbed radiations. Pathway of electron during Phosphorescence: S2 → S1 → T1 → S0
2. Photosystem and Reaction Centre
•
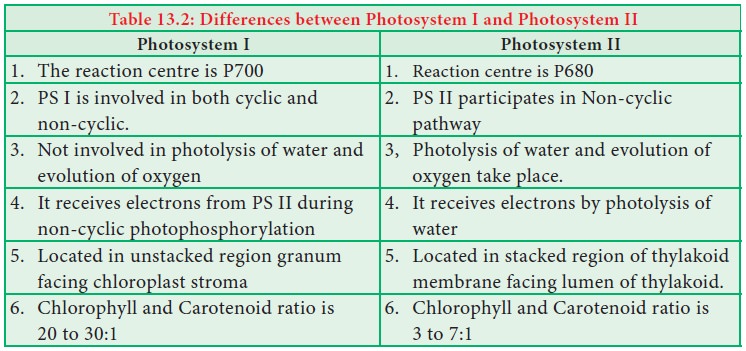
Thylakoid membrane contains Photosystem I (PS I) and Photosystem II (PS II).
• PS I is
in unstacked region of granum facing stroma of chloroplast.
• PS II
is found in stacked region of thylakoid membrane facing lumen of thylakoid.
• Each
Photosystem consists of central core complex (CC) and light harvesting Complex
(LHC) or Antenna molecules(Figure 13.12).
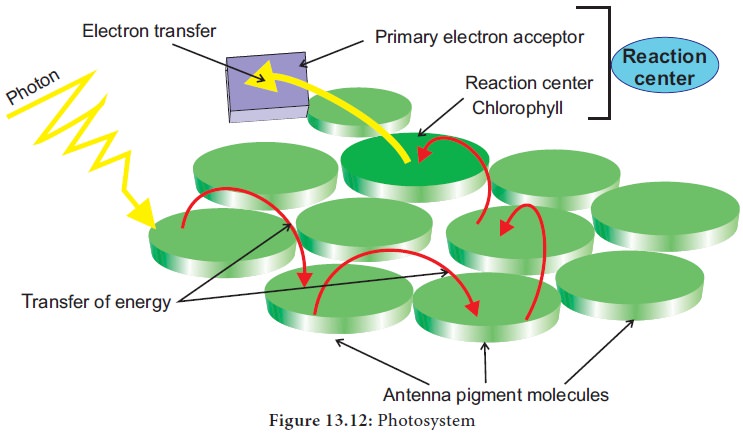
• The
core complex consists of respective reaction centre associated with proteins,
electron donors and acceptors.
• PS I –
CC I consists of reaction centre P700 and LHC I.
• PS II –
CC II consists of reaction centre P680 and LHC II (Table 13.2).
• Light
Harvesting Complex consists of several chlorophylls, carotenoids and xanthophyll
molecules.
• The
main function of LHC is to harvest light energy and transfer it to their
respective reaction centre.
Related Topics