Chapter: 11th Botany : Chapter 13 : Photosynthesis
Modern Concept of Photosynthesis
Modern Concept of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis
is an Oxidation and Reduction process. Water is oxidised to release O2
and CO2 is reduced to form sugars. The first phase requires light
and is called light reaction or Hill’s
reaction.
1.
Light
reaction: It is a photochemical reaction
whereas dark reaction is a thermochemical reaction.
Solar
energy is trapped by chlorophyll and stored in the form of chemical energy
(assimilatory power)as ATP and reducing power NADPH + H+. NADPH + H+
alone are known as reducing powers.
This reaction takes place in thylakoid membrane of the chloroplast. Oxygen is
evolved as a result of splitting of water molecules by light.
Light
reaction is discussed in two phases:
i. Photo-oxidation
Phase:
•
Absorption of light energy.
•
Transfer of energy from accessory pigments to
reaction centre.
•
Activation of Chlorophyll 'a' molecule.
ii. Photo
Chemical Phase:
o
Photolysis of water and oxygen Âevolution
o
Electron transport and synthesis of assimilatory
power.
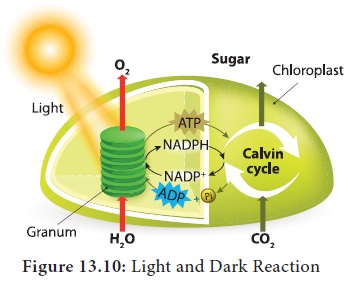
2. Dark reaction (Biosynthetic phase): Fixation and reduction of CO2 into carbohydrates with the help of assimilatory power produced during light reaction. This reaction does not require light and is not directly light driven. Hence, it is called as Dark reaction or Calvin-Benson cycle (Figure 13.10).
Related Topics