Chapter: 11th Botany : Chapter 13 : Photosynthesis
Definition, Significance and Site of Photosynthesis
Definition, Significance and
Site of Photosynthesis
1. Definition of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis
is referred as photochemical oxidation and reduction reactions carried out with
help of light, converting solar energy into Chemical energy. It is the most
important anabolic process. Plants and photosynthetic bacteria use simple raw
materials like carbon dioxide water and with the help of light energy
synthesize carbohydrates and evolve oxygen. The overall chemical equation for
photosynthesis is:
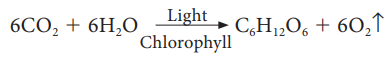
Ruben and Kamen (1941) demonstrated six
molecules of water as insufficient for the evolution of 6 molecules of O2
and modified the equation as:
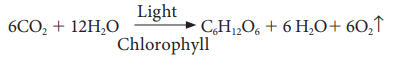
Photosynthesis
is a collection of oxidation and reduction reactions (Redox reaction).
Oxidation- Water is oxidised into oxygen (loss of electrons).
Reduction – CO2 is reduced into Carbohydrates (gain of electrons).
In some
bacteria, oxygen is not evolved and is called as non-oxygenic and anaerobic
photosynthesis. Examples: Green
sulphur, Purple sulphur and green filamentous bacteria.
2. Significance of Photosynthesis
a.
Photosynthetic organisms provide food for all
living organisms on earth either directly or indirectly.
b.
It is the only natural process that liberates
oxygen in the atmosphere and balances the oxygen level.
c.
Photosynthesis balances the oxygen and carbon cycle
in nature.
d.
Fuels such as coal, petroleum and other fossil
fuels are from preserved photosynthetic plants.
e.
Photosynthetic organisms are the primary producers
on which all consumers depend for energy.
f.
Plants provide fodder, fibre, fire wood, timber,
useful medicinal products and these sources come by the act of photosynthesis.
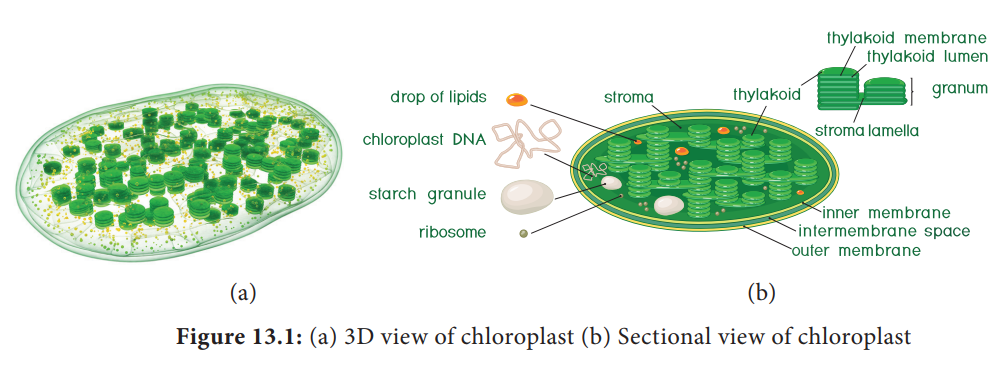
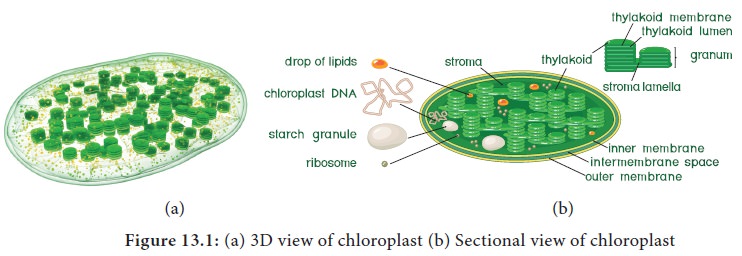
3. Site of Photosynthesis
Chloroplasts
are the main site of photosynthesis and both energy yielding process (Light
reaction) and fixation of carbon dioxide (Dark reaction)that takes place in
chloroplast. It is a double wall membrane bounded organelle, discoid or lens
shaped, 4–10 µm in diameter and 1–33 µm in thickness. The membrane is a unit
membrane and space between them is 100 to 200 A°. A
colloidal and proteinaceous matrix called stroma is present inside.
A sac
like membranous system called thylakoid or lamellae is present in stroma and they are arranged one above the
other forming a stack of coin like structure called granum (plural grana). Each chloroplast contains 40 to 80 grana and each granum consists of 5 to 30
thylakoids.
Thylakoids
found in granum are called grana lamellae and in stroma are called stroma
lamellae. Thylakoid disc size is 0.25 to 0.8 micron in diameter. A thinner
lamella called Fret membrane connects grana. Pigment system I is located on
outer thylakoid membrane facing stroma and Pigment system II is located on
inner membrane facing lumen of thylakoid. Grana lamellae have both PS I and PS
II whereas stroma lamellae have only PS I. Chloroplast contains 30–35 Proteins,
20–30% phospholipids, 5–10% chlorophyll, 4–5% Carotenoids, 70S ribosomes,
circular DNA and starch grains. Inner surface of lamellar membrane consists of
small spherical structure called as Quantasomes.
Presence of 70S ribosome and DNA gives them status of semi-autonomy and proves
endosymbiotic hypothesis which says chloroplast evolved from bacteria.
Thylakoid contains pigment systems which produces ATP and NADPH + H+
using solar energy. Stroma contains enzyme which reduces carbon dioxide into
carbohydrates. In Cyanobacteria thylakoid lies freely in cytoplasm without
envelope (Figure 13.1).
Related Topics