Chapter: Basic & Clinical Pharmacology : The Alcohols
Pharmacology of Methanol
METHANOL
Methanol
(methyl alcohol, wood alcohol) is widely used in the industrial production of
synthetic organic compounds and as a constituent of many commercial solvents.
In the home, methanol is most frequently found in the form of “canned heat” or
in windshield-washing products. Poisonings occur from accidental ingestion of
methanol-containing products or when it is misguid-edly ingested as an ethanol
substitute.
Methanol
can be absorbed through the skin or from the respi-ratory or gastrointestinal
tract and is then distributed in body water. The primary mechanism of
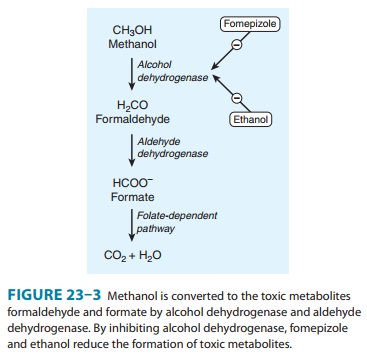
elimination of methanol in humans is by oxidation to formaldehyde, formic acid,
and CO2 (Figure 23–3).Animal species show great variability in mean
lethal doses of methanol. The special susceptibility of humans to methanol
toxic-ity is due to metabolism to formate and formaldehyde, not to methanol itself.
Since the conversion of methanol to its toxic metabolites is relatively slow,
there is often a delay of 6–30 hours before the appearance of severe toxicity.
Physical
findings in early methanol poisoning are generally nonspecific, such as
inebriation and gastritis, and possibly an ele-vated osmolar gap . In severe
cases, the odor of formaldehyde may be present on the breath or in the urine.
After a delay, the most characteristic symptom in methanol poisoning— visual
disturbance—occurs along with anion gap metabolic acido-sis. The visual
disturbance is frequently described as “like being in a snowstorm” and can
progress to blindness. Changes in the retina may sometimes be detected on
examination, but these are usually late. The development of bradycardia,
prolonged coma, seizures, and resistant acidosis all imply a poor prognosis.
The cause of death in fatal cases is sudden cessation of respiration. A serum
methanol concentration higher than 20 mg/dL warrants treatment, and a
concentration higher than 50 mg/dL is considered serious enough to require
hemodialysis. Serum formate levels are a better indica-tion of clinical
pathology but are not widely available.
The
first treatment for methanol poisoning, as in all critical poisoning
situations, is support of respiration. There are three specific modalities of
treatment for severe methanol poisoning: suppression of metabolism by alcohol
dehydrogenase to toxic products, hemodialysis to enhance removal of methanol and
its toxic products, and alkalinization to counteract metabolic acidosis.
The
enzyme chiefly responsible for methanol oxidation in the liver is alcohol
dehydrogenase (Figure 23–3). Fomepizole,
an alcohol dehydrogenase inhibitor, is approved for the treatment of methanol
and ethylene glycol poisoning. It is administered intra-venously in a loading
dose of 15 mg/kg followed by 10 mg/kg every 12 hours for 48 hours and then 15
mg/kg every 12 hours thereafter until the serum methanol level falls below
20–30 mg/dL. The dosage increase after 48 hours is based on evidence that
fomepizole rapidly induces its own metabolism by the cytochrome P450 system.
Patients undergoing hemodialysis are given fomepizole
for
alcohol dehydrogenase; thus, saturation of the enzyme with ethanol reduces
formate production. Ethanol is used intravenously as treatment for methanol and
ethylene glycol poisoning. The dose-dependent characteristics of ethanol
metabolism and the variability of ethanol metabolism require frequent
monitoring of blood ethanol levels to ensure appropriate alcohol concentration.
In
cases of severe poisoning, hemodialysis can be used to eliminate both methanol
and formate from the blood. Two other measures are commonly taken. Because of
profound metabolic acidosis in methanol poisoning, treatment with bicarbonate
often is necessary. Since folate-dependent sys-tems are responsible for the
oxidation of formic acid to CO2 in humans (Figure 23–3), folinic and
folic acid are often adminis-tered to patients poisoned with methanol, although
this has never been fully tested in clinical studies.
Related Topics