Chapter: Paediatrics: Nephrology
Paediatrics: Hypertension: definition
Hypertension: definition
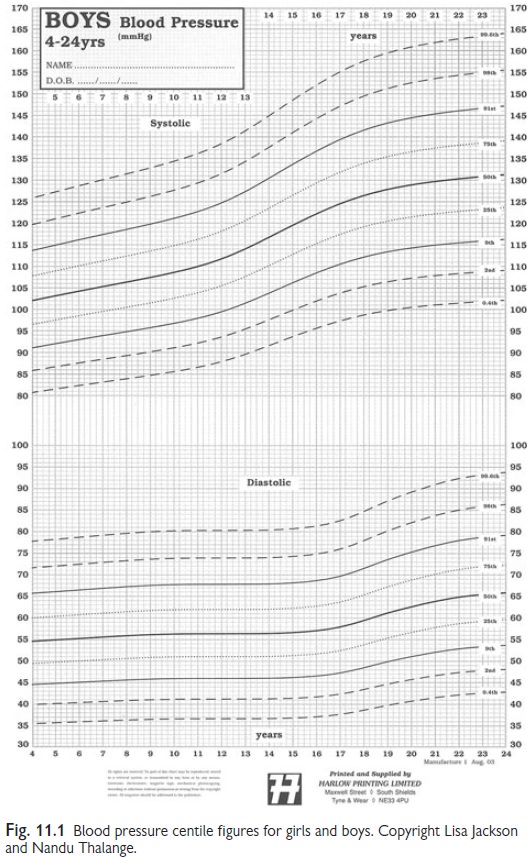
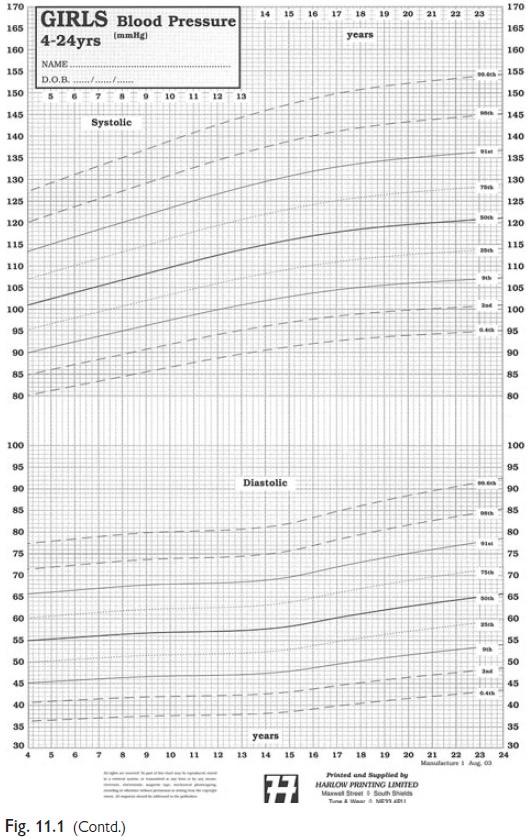
Defined by reference to sex,
height centile charts (see Fig. 11.1).
·
Normal: systolic and diastolic <90th
centile.
·
High normal: systolic or diastolic between 90th
and 95th centile.
·
Hypertension: systolic or diastolic >95th
centile.
·
Severe hypertension: systolic or diastolic >99th
centile.
BP measurement should be part of
routine examination.
Measurement technique
·
Cuff
size.
·
bladder width—70% of acromion olecranon
distance or 40%
o
mid-arm
circumference;
o
bladder length—should completely encircle arm.
o
Note: small cuff area is a common cause
of false positive high BP!
·
After
5min rest (ideally!).
·
Sitting
position with arm at level of heart (children).
·
Supine
position in infants.
·
On auscultation: 1st and 5th (disappearance)
Korotkoff sounds used for systolic
and diastolic values, respectively.
Measurement devices
· Manual oscillometric
sphygmomanometer (mercury now withdrawn).
·
Doppler: infants (for systolic pressure).
·
Automatic oscillometry: not all devices suitable.
·
Ambulatory
blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) for 24-hr profiles:
o
little
normative data in paediatrics;
o
significant
hypertension ≥30% readings above 95th centile.
·
Intra-arterial
(in intensive therapy unit (ITU) setting).
Related Topics