Chapter: Paediatrics: Growth and puberty
Paediatrics: Disorders of sex development
Disorders of sex development
Terminology
┬Ę Sexual
determination refers
to the process that occurs from the time of
conception until the foetal bipotential gonad has been fully determined as
either an ovary or testis.
┬Ę Sexual
differentiation refers
to the process that occurs from the time gonadal
sex is determined until s sexual
characteristics are fully expressed and fertility achieved.
Disorders of sexual development
The complex process of sexual
determination and differentiation may be interrupted. Numerous disorders that
can result in genital ambiguity and uncertainty about an infantŌĆÖs sex are
recognized. Disorders of sexual dif-ferentiation may be classified as genetic
defects of gonadal determination or defects in androgen biosynthesis,
metabolism, and action (excess or deficiency).
Assessment
History
A detailed history should be
obtained and should include:
┬ĘFamily
history: ambiguous
genitalia; disorders/problems of puberty;
inguinal hernia.
┬ĘPrenatal
history: maternal health;
drugs taken during pregnancy; maternal
virilization during pregnancy.
┬ĘHistory of previous stillbirths or
neonatal death?
Examination
┬ĘGeneral
examination: dysmorphic
features or midline defects; state of hydration;
BP.
┬ĘAre
the gonads palpable? If
ŌĆśyesŌĆÖ they are likely to be testes or ovotestes.
┬ĘAssess
the degree of virilization:
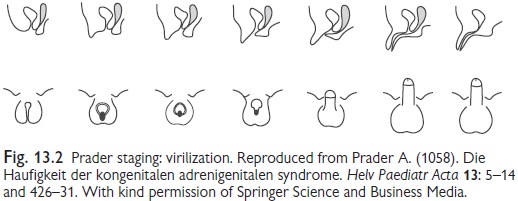
┬Ę Prader stage (Fig 13.2).
┬Ę External masculinization score.
┬ĘMeasure
the length of the phallus:
┬Ę Normal term penis is about 3cm
(stretched length from pubic tubercle to tip of penis).
┬Ę Micropenis is a length
<2.0ŌĆō2.5cm.
┬ĘPenis:
presence of chordee.
┬ĘVagina:
locate opening?
┬ĘAppearance of labioscrotal folds.
┬ĘPosition of urethral opening.
┬ĘSkinŌĆöpigmentation
of genital skin: hyperpigmentation
with excessive adrenocorticotrophin
(ACTH) and opiomelanocortin in CAH.
In preterm girls clitoris and labia minora are relatively prominent. In pre-term boys, testes remain undescended until 34wks gestation.
Related Topics