Human circulatory system - Origin and conduction of heart beat | 11th Zoology : Chapter 7 : Body Fluids and Circulation
Chapter: 11th Zoology : Chapter 7 : Body Fluids and Circulation
Origin and conduction of heart beat
Origin and
conduction of heart beat
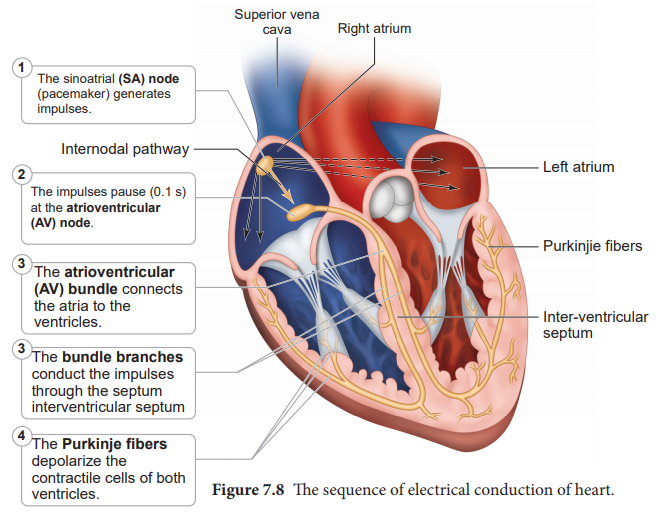
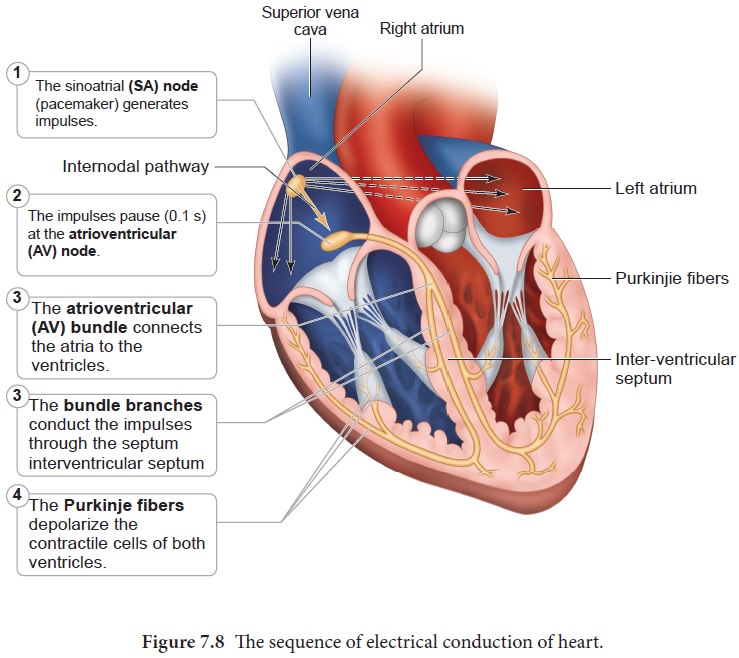
The heart in human is myogenic (cardiomyocytes can produce spontaneous rhythmic depolarisation that initiates contractions). The sequence of electrical conduction of heart is shown in Figure 7.8. The cardiac cells with fastest rhythm are called the Pacemaker cells, since they determine the contraction rate of the entire heart. These cells are located in the right sinuatrial (SA) node/ Pacemaker. On the left side of the right atrium is a node called auriculo ventricular node (AV node).
Two special cardiac muscle fibres originate from the auriculo
ventricular node and are called the bundle of His which runs down into the
interventricular septum and the fibres spread into the ventricles. These fibres
are called the Purkinje fibres.
Pacemaker
cells produce excitation through depolarisation of their cell membrane. Early
depolarisation is slow and takes place by sodium influx and reduction in
potassium efflux. Minimumpotential is required to activate voltage gated
calcium (Ca+) channels that causes rapid depolarisation which
results in action potential. The pace maker cells repolarise slowly via K+
efflux.
HEART BEAT- Rhythmic contraction and expansion of heart is called heart beat. The contraction of the heart is called systole and the relaxation of the heart is called diastole. The heart normally beats 70-72 times per min in a human adult. During each cardiac cycle two sounds are produced that can be heard through a stethoscope.
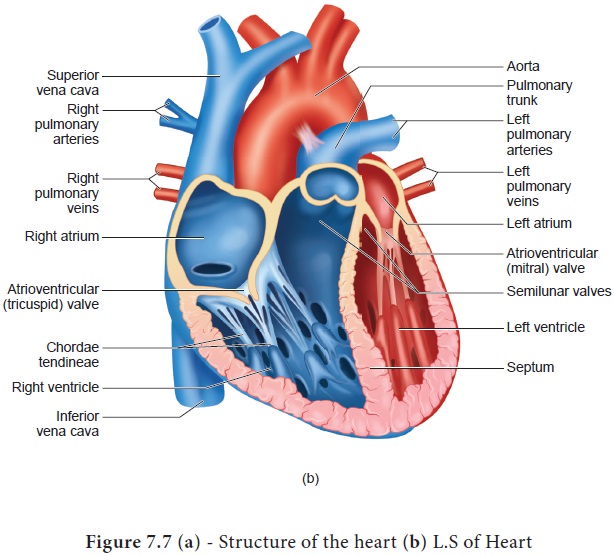
The first heart sound (lub) is associated with the closure of the tricuspid and
bicuspid valves whereas second heart sound (dub) is associated with the closure
of the semilunar valves. These sounds are of clinical diagnostic significance.
An increased heart rate is called tachycardia and decreased heart rate is
called bradycardia.
Related Topics