Body Fluids and Circulation | Zoology - Answer the following questions | 11th Zoology : Chapter 7 : Body Fluids and Circulation
Chapter: 11th Zoology : Chapter 7 : Body Fluids and Circulation
Answer the following questions
Zoology
Body Fluids and Circulation
Answer the following questions
15. Distinguish between arteries and veins
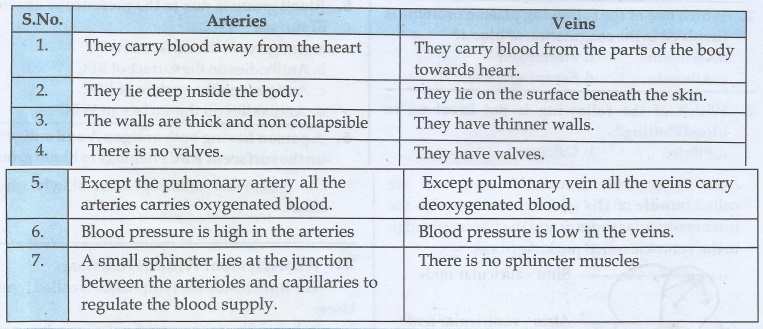
Arteries
1.
They carry blood away from the heart
2.
They lie deep inside the body.
3.
The walls are thick and non collapsible
4.
There is no valves.
5.
Except the pulmonary artery all the arteries carries oxygenated blood.
6.
Blood pressure is high in the arteries
7.
A small sphincter lies at the junction between the arterioles and capillaries to
regulate the blood supply.
Veins
1.
They carry blood from the parts of the body towards heart.
2.
They lie on the surface beneath the skin.
3.
They have thinner walls.
4.
They have valves.
5.
Except pulmonary vein all the veins carry deoxygenated blood.
6.
Blood pressure is low in the veins.
7.
There is no sphincter muscles
16. Distinguish between open and closed circulation
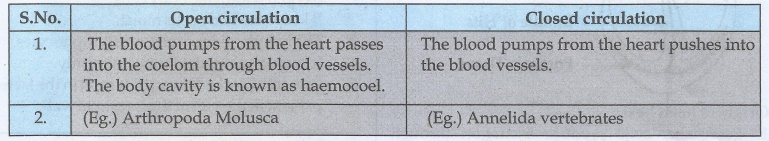
Open
circulation
1.
The blood pumps from the heart passes into the coelom through blood vessels.
The
body cavity is known as haemocoel.
2.
(Eg.) Arthropoda Molusca
Closed
circulation
1.
The blood pumps from the heart pushes into the blood vessels.
2.
(Eg.) Annelida vertebrates.
17. Distinguish between mitral valve and semi lunar valve
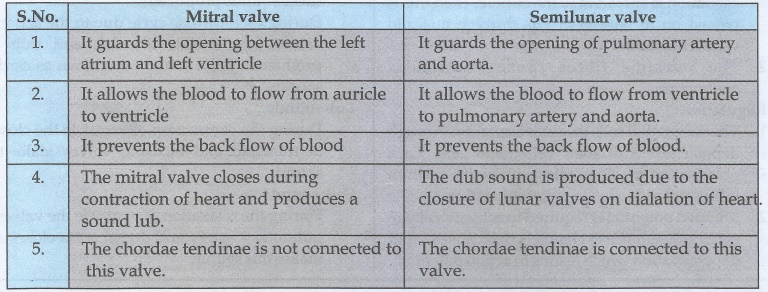
Mitral
valve
1.
It guards the opening between the left atrium and left ventricle.
2.
It allows the blood to flow from auricle to ventricle.
3.
It prevents the back flow of blood.
4.
The mitral valve closes during contraction of heart and produces a sound lub.
5.
The chordae tendinae is not connected to this valve.
Semilunar
valve
1.
It guards the opening of pulmonary artery and aorta.
2.
It allows the blood to flow from ventricle to pulmonary artery and aorta.
3.
It prevents the back flow of blood.
4.
The dub sound is produced due to the closure of lunar valves on dialation of
heart.
5.
The chordae tendinae is connected to this valve.
18. Right ventricular wall is thinner than the left ventricular wall. Why?
The wall of left ventricle is thick
Reason:
1. As the right ventricle constricts the deoxygenated
blood through pulmonary vein goes to lungs only. These may not be necessary for
much blood pressure for this.
2. As the left ventricle constricts through
dorsal aorta blood goes to all the parts of the body.
3. For this action more pressure is needed.
Hence the wall of the left ventricle is thick. It gives more pressure on the contraction
of ventricle to distribute the blood
19. What might be the effect on a person whose diet has less iron content?
1. The number of red blood cells decreases.
2. Due to the depletion of haemoglobin he finds
it difficult to breath.
3. Due to the deficiency of iron anaemia may
develope.
4. Due to the deficiency of iron the oxygen
carrying capacity of haemoglobin reduces.
20. Describe the mechanism by which the human heart beat is initiated and controlled.
1. Human heart is myogenic in nature.
2. The heart beat is originated from pacemaker.
The total rate of heart beat is decided by this node.
3. This pacemaker is situated in the right sinu
atrial node.
4. On the left side of the right atrium is a
node called auricula ventricular node.
5. Two special cardiac muscle fibres originate
from the auriculo
ventricular node and are called bundle of
His which runs down into the inter ventricular septum and the fibres spread
in to the ventricle called purkinje fibres.
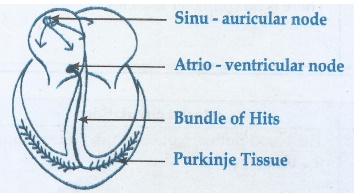
Origin of heart beat:
1. Pacemaker cells produce excitation through depolarisation
of their cell membrane. The excitation is spread in to the auricle. Then this is
passed on to bundle of His through auriculo ventricular node.
2. The purkinje fibres cause ventricular contraction.
Regulation:
1. The pacemaker cells produce excitation through depolarisation
of their cell membrane. Each polarisation is slow taken place by sodium influx and
reduction in potassium efflux.
2. Minimal potential is required to activate voltage gated
calcium (Ca+) channels that causes rapid depolarisation which results
in action potential.
3. The pacemaker cells repolarise slowly via K+
efflux.
21. What is lymph? Write its function.
The fluid inside the lymphatics is called lymph.
Uses:
1. It helps in transporting nutrients hormones oxygen within
the body cells.
2 It keeps the body cells moist.
3. The lymph nodes synthesize lymphocytes.
4. It keeps the blood volume uniformly.
5. Fats are absorbed through lymph in the lacteals present
in the villi of the intestinal wall.
22. What are the heart sounds? When and how are these sounds produced?
During each cardiac cycle due to the action of valves two
sounds like lub and dub are produced. These sound are known as cardiac sounds.
Lub sound:
During the contraction of ventricle the closure of tricuspid
and bicuspid valves make this sound.
Dub sound:
During the relaxation of ventricle the valves of pulmonary
artery and dorsal aorta closes and makes this sound
23. Select the correct biological term.
Lymphocytes, red cells, leucocytes, plasma, erythrocytes, white cells, haemoglobin, phagocyte, platelets, blood clot.
a. Disc shaped cells which are concave on both sides - erythrocytes
b. Most of these have a large, bilobed nucleus - Lymphocytes
c. Enable red cells to transport blood
d. The liquid part of the blood - plasma
e. Most of them move and change shape like an amoeba. - phagocyte
f. Consists of water and important dissolved substances. - plasma
g. Destroyed in the liver and spleen after circulating in the blood for four months. - erythrocytes
h. The substances which gives red cells their colour. - haemoglobin
i. Another name for red blood cells. - erythrocytes
j. Blood that has been changed to a jelly. - blood clot
k. A word that means cell eater. - phagocyte
l. Cells without nucleus. - erythrocytes /phagocyte
m. White cells made in the lymphatic tissue. - Lymphocytes
n. Blocks wound and prevent excessive bleeding. - blood clot
o. Fragment of cells which are made in the bone marrow. - red cells
p. Another name for white blood cells. - leucocytes
q. Slowly releases oxygen to blood cells. - haemoglobin
r. Their function is to help blood clot in wounds. - platelets
a. Disc shaped cells which are concave on both sides. Red cells
b. Most of these have a large bilobed nucleus Leucocytes
c. Enable red cells to transport blood. Haemoglobin
d. The liquid part of the blood Plasma
e. Most of them move and change shape like an amoeba Leucocytes
f. Consists of water and important dissolved substances. Plasma
g. Destroyed in the liver and spleen after circulating in the blood for four months. Red cells
h. The substances which gives red cells their colour Haemoglobin
i. Another name for red cells Erythrocytes
j- Blood that has been change to a jelly Blood clot
k. A word that mean cell eater Phagocytes
l. Cells without nucleus Red cells
m. White cells made in the lymphatic tissue Lymphocytes
n. Blocks wound and prevent excessive bleeding. Blood clot
o. Fragment of cells which are made in the bone marrows Platelets
p- Another name for white blood cells. Leucocytes
q- Slowly releases oxygen to blood cells. Haemoglobin
r. Their function is to help blood clot in wounds. Platelets
Q. Select the correct biological term.
Cardiac muscle, atria, tricuspid systole, auricles, arteries, diastole, ventricles, bicuspid valve, pulmonary artery, cardiac cycle, semi lunar valve, veins, pulmonary vein, capillaries, vena cava, aorta.
a. The main artery of the blood. - aorta
b. Valves between the left atrium and ventricle. - bicuspid valve
c. Technical name for relaxation of the heart. - diastole
d. Another name for atria. - auricles
e. The main vein. - vena cava
f. Vessels which carry blood away from the heart. - arteries
g. Two names for the upper chambers of the heart. – atria/ auricles
h. Thick walled chambers of the heart. - ventricles
i. Carries blood from the heart to the lungs. - pulmonary artery
j. Takes about 0.8 sec to complete. - cardiac cycle
k. Valves situated at the point where blood flows out of the heart. - semi lunar valve
l. Vessels which carry blood towards the heart. - veins
m. Carries blood from the lungs to the heart. - pulmonary vein
n. The two lower chambers of the heart. - ventricles
o. Prevent blood from re entering the ventricles after entering the aorta. . - semi lunar valve
p. Technical name for one heart beat. - Cardiac muscle
q. Valves between right atrium and ventricles. - tricuspid systole
r. Technical name for contraction of the heart. - Systole
s. Very narrow blood vessels. - Capillaries
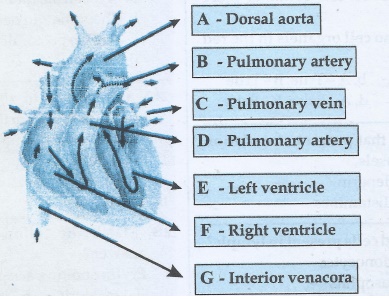
25. Name and Label the given diagrams to show A, B, C, D, E, F, and G
Related Topics