Human circulatory system - Cardiac Cycle | 11th Zoology : Chapter 7 : Body Fluids and Circulation
Chapter: 11th Zoology : Chapter 7 : Body Fluids and Circulation
Cardiac Cycle
Cardiac Cycle
The
events that occur at the beginning of heart beat and lasts until the beginning
of next beat is called cardiac cycle. It lasts for 0.8 seconds. The series of
events that takes place in a cardiac cycle.
PHASE 1:
Ventricular diastole- The pressure in the auricles increases than that of the
ventricular pressure. AV valves are open while the semi lunar valves are
closed. Blood flows from the auricles into the ventricles passively.
PHASE 2:
Atrial systole - The atria contracts while the ventricles are still relaxed.
The contraction of the auricles pushes maximum volume of blood to the
ventricles until they reach the end diastolic volume (EDV). EDV is related to
the length of the cardiac muscle fibre. More the muscle is stretched, greater
the EDV and the stroke volume.
PHASE 3:
Ventricular systole (isovolumetric contraction) - The ventricular contraction
forces the AV valves to close and increases the pressure inside the ventricles. The blood is then pumped from the ventricles into
the aorta without change in the size of the muscle fibre length and ventricular
chamber volume (isovolumetric contraction).
PHASE 4:
Ventricular systole (ventricular ejection) - Increased ventricular pressure
forces the semilunar valves to open and blood is ejected out of the ventricles
without backflow of blood. This point is the end of systolic volume (ESV).
PHASE 5:
(Ventricular diastole) -The ventricles begins to relax, pressure in the arteries
exceeds ventricular pressure, resulting in the closure of the semilunar valves.
The heart returns to phase 1 of the cardiac cycle.
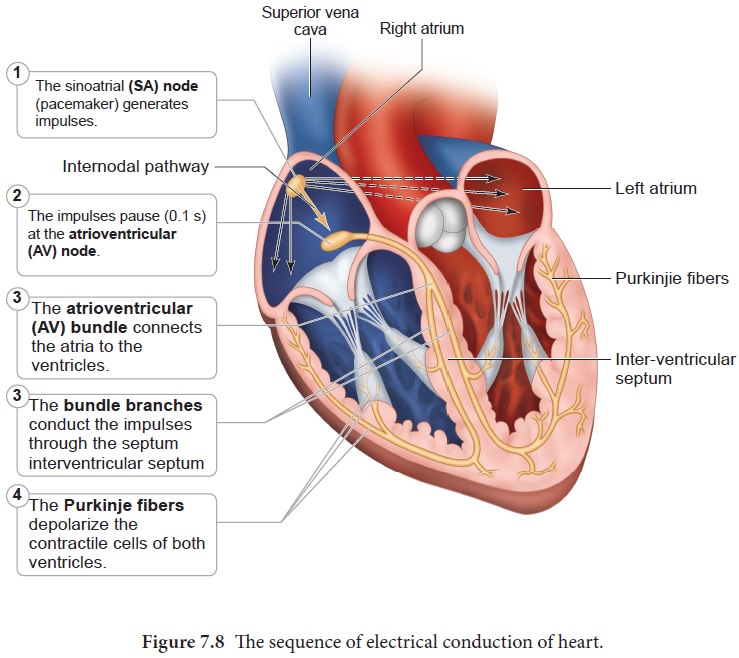
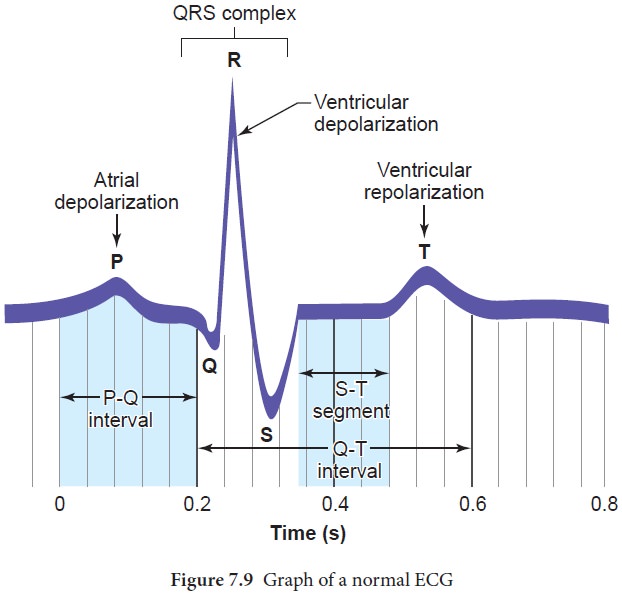
Related Topics