Chapter: 10th Science : Chapter 4 : Electricity
OhmŌĆÖs Law
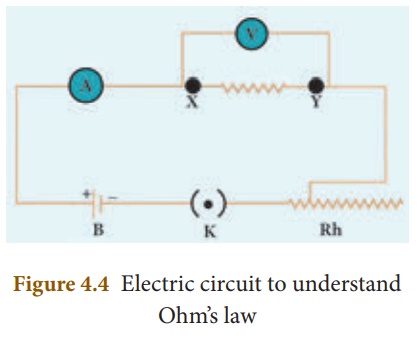
OHMŌĆÖS LAW
A German physicist,
Georg Simon Ohm established the relation between the potential difference and
current, which is known as OhmŌĆÖs Law. This relationship can be understood from
the following activity.
According to OhmŌĆÖs law,
at a constant temperature, the steady current ŌĆśIŌĆÖ flowing through a conductor
is directly proportional to the potential difference ŌĆśVŌĆÖ between the two ends
of the conductor.
I ŌłØ V. Hence, 1/V = constant.
The value of this
proportionality constant is found to be 1/R
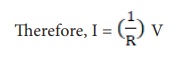
V = I R (4.3)
Here, R is a constant
for a given material (say Nichrome) at a given temperature and is known as the resistance
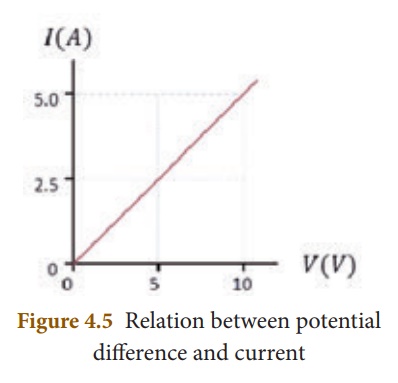
of the material. Since, the potential difference V is proportional to the
current I, the graph between V and I is a straight line for a conductor, as
shown in the Figure 4.5.
Related Topics