Chapter: 10th Science : Chapter 4 : Electricity
Electric Circuit
ELECTRIC CIRCUIT
An electric circuit is a
closed conducting loop (or) path, which has a network of electrical components
through which electrons are able to flow. This path is made using electrical
wires so as to connect an electric appliance to a source of electric charges
(battery). A schematic diagram of an electric circuit comprising of a battery,
an electric bulb, and a switch is given in Figure 4.2.
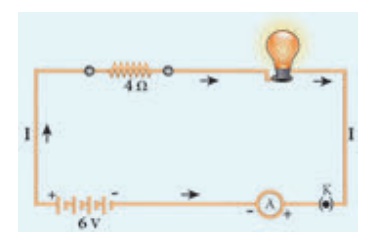
Figure 4.2 A simple electric circuit
In this circuit, if the
switch is ŌĆśonŌĆÖ, the bulb glows. If it is switched off, the bulb does not glow.
Therefore, the circuit must be closed in order that the current passes through
it. The potential difference required for the flow of charges is provided by
the battery. The electrons flow from the negative terminal to the positive
terminal of the battery.
By convention, the
direction of current is taken as the direction of flow of positive charge (or)
opposite to the direction of flow of electrons. Thus, electric current
passes in the circuit from the positive terminal to the negative
terminal.
Electrical components
The electric circuit
given in Figure 4.2 consists of different components, such as a battery, a
switch and a bulb. All these components can be represented by using certain
symbols. It is easier to represent the components of a circuit using their
respective symbols.
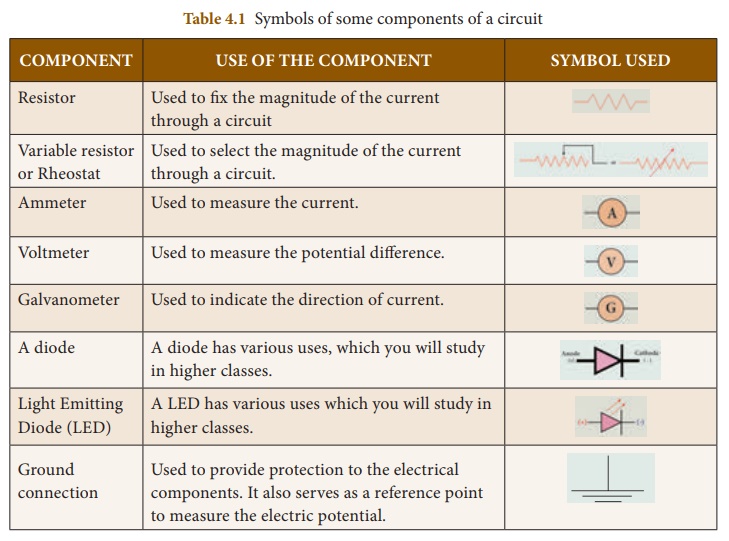
The symbols that are
used to represent some commonly used components are given in Table 4.1. The
uses of these components are also summarized in the table.
Related Topics