Chapter: Mechanical Engineering : Power Plant Engineering
Nuclear power plant
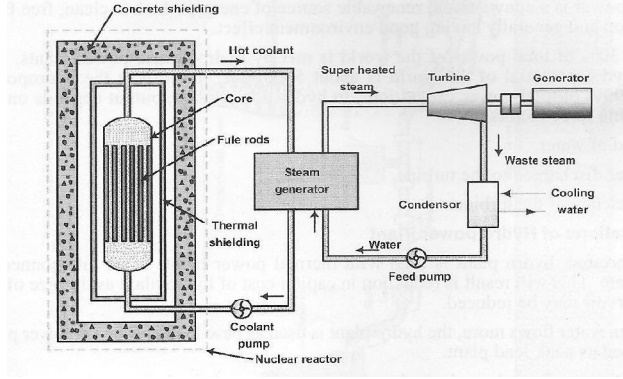
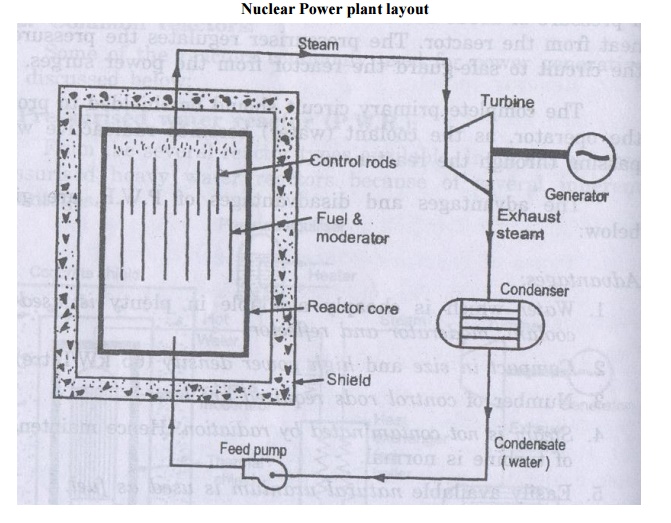
NUCLEAR POWER PLANT
•
Nuclear power plant uses nuclear energy from
radioactive element for generating electrical energy.
•
More than 15% of the world’s electricity
i
•
It is generally located far away from populated
areas.
•
In future generation of electricity will be
depending on Nuclear Power Plant, as it is economical.
• 1
kg of uranium U -235 can produce electrical power electrical that
can be
produced by using 3000 -4500
tonnes of high grade coal or 2000 tonnes of oil.
COMPONENTS OF NUCLEAR POWER PLANT:
Nuclear
Fuel :
Normally
used nuclear fuel is uranium (U235)
Fuel
Rods:
The fuel
rods hold nuclear fuel in a nuclear power plant.
Neutron Source: A source of neutron is required to initiate
the fission for the first time. A mixture of beryllium with plutonium is
commonly used as a source of neutron.
Reactor:
•
Nuclear fission takes place in the reactor only.
•
Nuclear fission produces large quantity of heat.
•
The heat generated in the reactor is carried by
coolant circulated through the reactor.
Control
Rods:
•
They are used to control the chain reaction.
•
They are absorbers of neutrons.
•
The commonly used control rods are made up of
cadmium or boron.
Moderator:
•
Moderators are used to slow down the fast
neutrons.
•
It reduces 2 MeV to an average velocity of 0.025
eV.
•
Ordinary or heavy water are used as moderators.
Fuel
Rods:
•
The fuel rods hold nuclear fuel in a nuclear power
plant.
Neutron
Reflectors:
•
To prevent the leakage of neutrons to large
extent.
•
In PHWR, the moderator itself acts as reflectors.
Shielding:
To protect from harmful
radiations the reactor is surrounded b a concrete wall of thickness about 2 to
2.5 m.
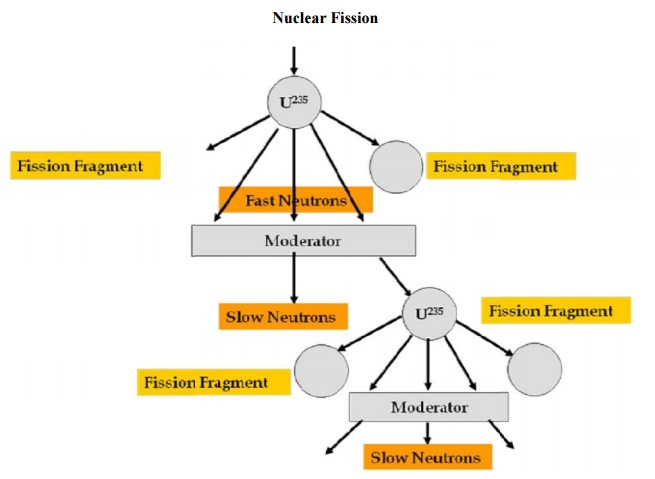
•
It is a process of splittin g up of nucleus of
fissionable material like uranium into two or more fragments with release of
enormous amount of energy.
•
The nucleus of U235 is bombarded with
high energy neutrons
U235+0n1 Ba 141+Kr92+2.50n1+200
MeV energy.
•
The neutrons produced are very fast and can be
made to fission other nuclei of U235, thus setting up a chain
reactio n.
•
Out of 2.5 neutrons relea sed one neutron is used
to sustain the chain rea ction.
1 eV =
1.6X10-19 joule.
1 MeV = 106
eV
WORKING PRINCIP LE OF NUCLEAR POWER PLANT:
•
The heat generated in the reactor due to the
fission of the fuel is taken up by the coolant.
• The hot
coolant then lea ves the reactor and flows through the steam gen erator.
•
In the steam generator the hot coolant transfers
its heat to the feed water which gets converted into steam.
•
The steam produced is passed through the turbine,
which is coupled wit h generator.
•
Hence the power is produced during the running of
turbine.
•
The exhaust steam from the turbine is condensed in
the condenser.
•
The condensate then flows to the steam generator
through the feed pump.
•
The cycle is thus repeated.
Advantages of Nuclear Power Plant:
•
Requires less space compared to steam power plant.
•
Fuel required is negligible compared to coal
requirement.
•
Fuel transport cost is less.
•
Reliable in operation.
•
Cost of erection is less.
•
Water required is very less.
Disadvantages of Nuclear Power Plant:
•
Initial Cost is higher.
•
Not suitable for varying load condition.
•
Radioactive wastes are hazardous. Hence these are
to be handled with much care.
•
Maintenance cost is higher.
•
Trained workers are required to operate the plant.
Nuclear Power Plants in India:
•
IGCAR, Kalpakkam in Chennai.
•
Rana Pratap Sagar in Rajasthan
•
Narora in Uttar Pradesh
•
Kakarpur near Surat at Gujarat
Related Topics