Chapter: 11th 12th standard bio zoology Human Body higher secondary school
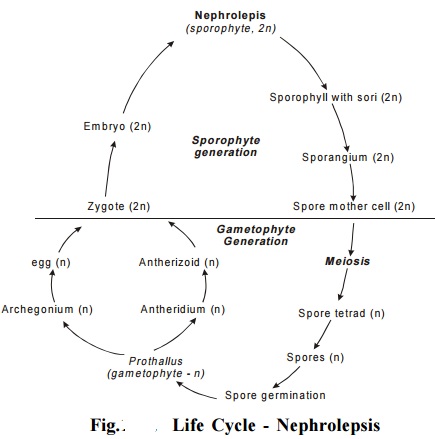
Nephrolepsis : Fertilization
Nephrolepsis
Division : Tracheophyta
Sub
division : Pteropsida
Class : Leptosporangiatae
Order
: Filicales
Family : Dennstaedtiaceae
Genus
: Nephrolepsis
The genus Nephrolepsis is a
tropical fern with about 30 species. Most of the species are found in terrestrial
habitats. Some species are epiphytes e.g., N.
volubilis and N. ramosa. Several
species are grown as ornamental
plants. In India, there are 5 species. Of these, N. acuta and N. tuberosa
are common species.
Fertilization:
Water is essential for fertilization. After the release of antherozoids from antheridium, they swim in a thin film of water
present on the surface of the prothallus. They are attracted towards the neck
of archegonia by chemicals oozing out of the neck. Thus the antherozoids are directed
towards the egg. Even though many antherozoids enter the neck only one fuses
with the egg and forms zygote.
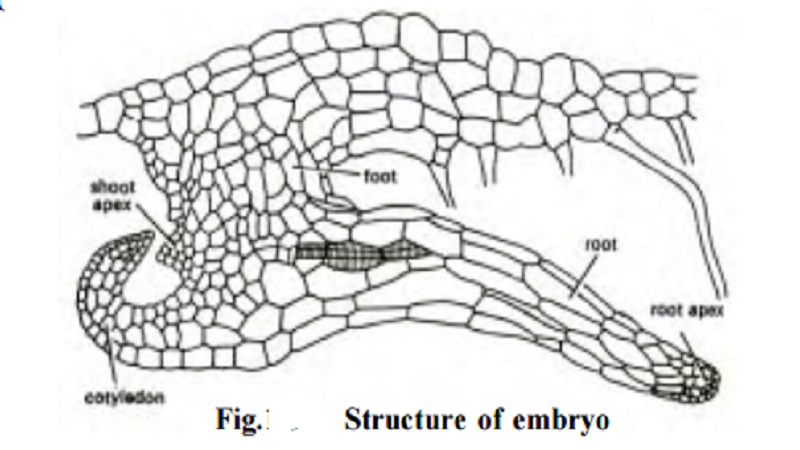
The zygote, formed by the fusion of antherozoid and egg, is the starting point for the next s p o r o p h y t e generation. It increases in size and almost completely occupies the venter. By repeated divisions, the zygote develops into an embryo consisting of shoot apex, cotyledon, foot and root. The foot absorbs nutrients for the developing embryo from the prothallus. The venter forms a protective cover called calyptra for the developing embryo. The root and cotyledon grow more rapidly than the shoot and finally form a new sporophyte plant. The prothallus gradually decays once the young sporophyte is well established.
Related Topics