Chapter: Medical Surgical Nursing: Management of Patients With Oral and Esophageal Disorders
Neck Dissection
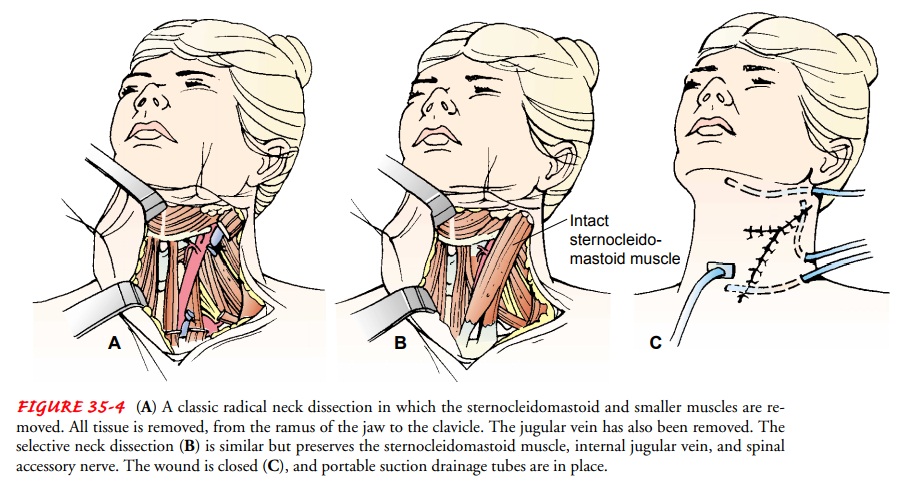
Neck Dissection
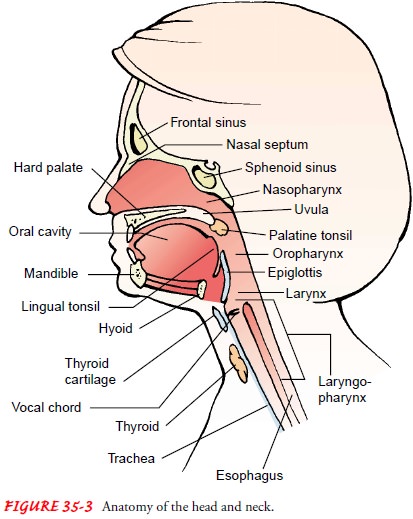
Malignancies of the head and neck include those of the oral cavity, oropharynx, hypopharynx, nasopharynx, nasal cavity, paranasal sinus, and larynx (Fig. 35-3).
These
cancers account for fewer than 5% of all cancers. Depending on the location and
stage, treat-ment may consist of radiation therapy, chemotherapy, surgery, or a
combination of these modalities. Deaths from malignan-cies of the head and neck
are primarily attributable not to re-currence at the primary site but to
local-regional metastasis to the cervical lymph nodes in the neck. This often
occurs by way of the lymphatics before the primary lesion has been treated.
This local-regional metastasis is not amenable to surgical re-section and
responds poorly to chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
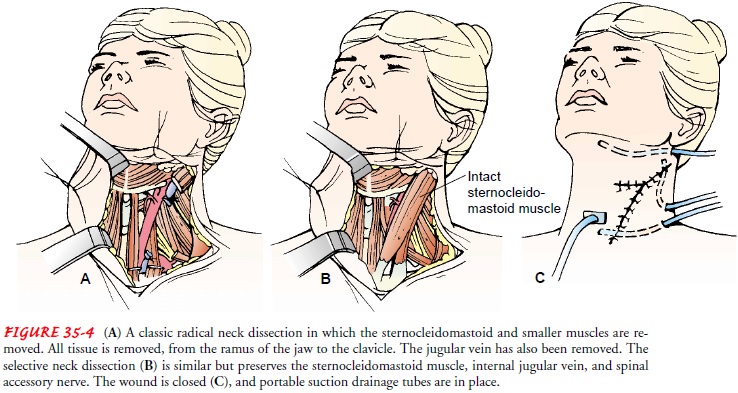
A
radical neck dissection involves removal of all cervical lymph nodes from the
mandible to the clavicle and removal of the ster-nocleidomastoid muscle,
internal jugular vein, and spinal acces-sory muscle on one side of the neck.
The associated morbidities include shoulder drop and poor cosmesis (visible
neck depres-sion). Modified radical neck dissection, which preserves one or
more of the nonlymphatic structures, is used more often. A se-lective neck
dissection (in comparison to a radical dissection) pre-serves one or more of
the lymph node groups, the internal jugular vein, the sternocleidomastoid
muscle, and the spinal accessory nerve (Fig. 35-4).
Reconstructive techniques may be performed with a variety of grafts. A cutaneous flap (skin and subcutaneous tissue), such as the deltopectoral flap, may be used. A more frequently used graft for head and neck reconstruction is a myocutaneous flap (subcutaneous tissue, muscle and skin). The pectoralis major muscle is usually used. A microvascular free flap may be used for large defects. This involves the transfer of muscle, skin, or bone with an artery and vein to the area of reconstruction, using microinstrumentation. Areas used for a free flap include the scapula, the radial area of the forearm, or the fibula. The fibula, which provides a larger bone area, may be used if mandibular reconstruction is involved.
Related Topics