Chapter: Basic & Clinical Pharmacology : Immunopharmacology
Monoclonal Antibodies (MABs)
MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES (MABs)
Recent
advances in the ability to manipulate the genes of immu-noglobulins have
resulted in development of a wide array of humanized and chimeric monoclonal
antibodies directed against therapeutic targets. The only murine elements of
humanized monoclonal antibodies are the complementarity-determining regions in
the variable domains of immunoglobulin heavy and light chains.
Complementarity-determining regions are primarily responsible for the
antigen-binding capacity of antibodies. Chimeric antibodies typically contain
antigen-binding murine variable regions and human constant regions. The
following are brief descriptions of the engineered antibodies that have been
approved by the FDA.
Antitumor MABs
Alemtuzumab is a humanized IgG1with a kappa chain that bindsto CD52 found on normal and
malignant B and T lymphocytes, NK cells, monocytes, macrophages, and a small
population of granulocytes. Currently, alemtuzumab is approved for the
treatmentof B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia in patients who have been treated
with alkylating agents and have failed fludarabine therapy. Alemtuzumab appears
to deplete leukemic and normal cells by direct antibody-dependent lysis.
Patients receiving this antibody become lymphopenic and may also become
neutro-penic, anemic, and thrombocytopenic. As a result patients should be
closely monitored for opportunistic infections and hemato-logic toxicity.
Bevacizumab is a humanized IgG1monoclonal antibody thatbinds to vascular endothelial growth
factor (VEGF) and inhibits VEGF from binding to its receptor, especially on
endothelial cells. It is an antiangiogenic drug that has been shown to inhibit
growth of blood vessels (angiogenesis) in tumors. It is approved for first-line
treatment of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer alone or in combination
with 5-FU-based chemotherapy. It is also approved for treatment of non-small
cell lung cancer, glioblastoma multiforme that has progressed after prior
treatment, and meta-static kidney cancer when used with interferon-alpha. Since
beva-cizumab is antiangiogenic, it should not be administered until patients
heal from surgery. Patients taking the drug should be watched for hemorrhage,
gastrointestinal perforations, and wound healing problems. Bevacizumab has also
been used off label by intravitreal injection to slow progression of
neovascular macular degeneration (see ranibizumab under Other MABs, below).
Cetuximab is a human-mouse chimeric monoclonal antibodythat targets
epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). Binding of cetuximab to EGFR inhibits
tumor cell growth by a variety of mechanisms, including decreases in kinase
activity, matrix metal-loproteinase activity, and growth factor production, and
increased apoptosis. It is indicated for use in patients with EGFR-positive
metastatic colorectal cancer and, along with radiation therapy, in patients
with head and neck cancer. Cetuximab may be adminis-tered in combination with
irinotecan or alone in patients who cannot tolerate irinotecan. HAMAs are
generated by about 4% of patients being treated with cetuximab.
Ofatumumab is a human IgG1monoclonal antibody directedagainst a different epitope on CD20
than rituximab. It is approved for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia
(CLL) who are refractory to fludarabine and alemtuzumab. Ofatumumab binds to
all B cells including B-CLL. It is thought to lyse B-CLL cells in the presence
of complement and to mediate antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. There is
a slight risk of hepatitis B virus reac-tivation in patients taking ofatumumab.
Panitumumab is a fully human IgG2kappa light chain mono-clonal antibody. It is
approved for the treatment of EGFR-expressing metastatic colorectal carcinoma
with disease progression on or following fluoropyrimidine-, oxaliplatin-, and
irinotecan-containing chemotherapy regimens. Panitumumab binds to EGFR (similar
to cetuximab), inhibiting epidermal growth factor from binding to its receptor,
and prevents ligand-induced receptor autophosphorylation and activation of
receptor-associated kinases. It inhibits cell growth, induces apoptosis,
decreases vascular growth factor production, and suppresses internalization of
the EGFR. Although some dermatologic and infusion-related toxici-ties have been
observed following infusion of panitumumab, the distinct advantage over cetuximab
is that it is fully human, and therefore does not elicit HAMAs. This is the
first FDA-approved monoclonal antibody produced from transgenic mice expressing
the human immunoglobulin gene loci.
Rituximab is
a chimeric murine-human monoclonal IgG1(human
Fc) that binds to the CD20 molecule on normal and malignant B lymphocytes and
is approved for the therapy of patients with relapsed or refractory low-grade
or follicular B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
It is also approved for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in combination
with methotrexate in patients for whom anti-TNF-α therapy has failed. The mechanism
of action includes complement-mediated lysis, antibody-dependent cellular
cyto-toxicity, and induction of apoptosis in the malignant lymphoma cells. In
lymphoma this drug appears to be synergistic with che-motherapy (eg,
fludarabine, CHOP). Recent reports indicate that rituximab may also be very
useful in auto-immune diseases such as multiple sclerosis and systemic lupus
erythematosus.
Trastuzumab is a recombinant DNA-derived, humanizedmonoclonal antibody that
binds to the extracellular domain of the human epidermal growth factor receptor
HER-2/neu. This anti-body blocks the
natural ligand from binding and down-regulates the receptor. Trastuzumab is
approved for the treatment of HER-2/neu-positive
tumors in patients with breast cancer and patients with metastatic gastric or
gastroesophageal junction ade-nocarcinoma. As a single agent it induces
remission in about 15–20% of breast cancer patients; in combination with
chemo-therapy, it increases response rates and duration as well as 1-year
survival. Trastuzumab is under investigation for other tumors that express
HER-2/neu .
MABs Used to Deliver Isotopes to Tumors
Arcitumomab is a murine Fab fragment from an anti-carcinoembryonic antigen
(CEA) antibody labeled with techne-tium 99m (99mTc) that is used for imaging patients with
metastatic colorectal carcinoma (immunoscintigraphy) to determine extent of
disease. CEA is often upregulated on tumor in patients with gastrointestinal
carcinomas. The use of the Fab fragment decreases the immunogenicity of the
agent so that it can be given more than once; intact murine monoclonal
antibodies would elicit stronger HAMA.
Capromab pendetide is
a murine monoclonal antibody spe-cific for prostate specific membrane antigen.
It is coupled to isoto-pic indium (111In)
and is used in immunoscintigraphy for patients with biopsy-confirmed prostate
cancer and post-prostatectomy in patients with rising prostate specific
antibody level to determine extent of disease.
Ibritumomab tiuxetan is
an anti-CD20 murine monoclonalantibody labeled with isotopic yttrium (90Y)
or 111In. The radia-tion of the
isotope coupled to the antibody provides the major antitumor activity.
Ibritumomab is approved for use in patients with relapsed or refractory
low-grade, follicular, or B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, including patients
with rituximab-refrac-tory follicular disease. It is used in conjunction with
rituximab in a two-step therapeutic regimen.
Tositumomab is
another anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodyand is complexed with iodine 131 (131I).
Tositumomab is used in two-step therapy in patients with CD20-positive,
follicular non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma whose disease is refractory to rituximab and
standard chemotherapy. Toxicities are similar to those for ibritu-momab and
include severe cytopenias such as thrombocytopenia and neutropenia. Tositumomab
should not be administered to patients with greater than 25% bone marrow
involvement.
MABs Used as Immunosuppressants and Anti-Inflammatory Agents
A. Anti-TNF-Alpha MABs
Adalimumab,
certolizumab pegol, etanercept, golimumab, and infliximab are antibodies that
bind TNF-α,
a proinflammatory cytokine that is important in rheumatoid arthritis and
similar inflammatory diseases . Blocking TNF-α from binding to TNF receptors on inflammatory
cells results in suppres-sion of downstream inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1
and IL-6 and adhesion molecules involved in leukocyte activation and migration.
An increased risk of infection or reactivation of M tuber-culosis, hepatitis B virus, and invasive systemic fungi is
common toeach of these anti-TNF monoclonal antibodies. Patients may also be at
increased risk for malignancies including lymphoma.
Adalimumab is a completely human IgG1approved for use inpatients with rheumatoid
arthritis, juvenile idiopathic arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing
spondylitis, Crohn’s disease, and plaque psoriasis. Like the other anti-TNF-α biologicals, adali-mumab
blocks the interaction of TNF-α with TNF receptors on cell surfaces; it does
not bind TNF-β.
Adalimumab lyses cells expressingTNF-αinthepresenceofcomplement.Pharmacodynamic
studies showed that administration of adalimumab reduced levels of C-reactive protein,
erythrocyte sedimentation rate, serum IL-6, and matrix metalloproteinases MMP-1
and MMP-3.
Certolizumab pegol is a recombinant humanized Fab frag-ment that binds to TNF-α. It is coupled to a
40-kDa polyethylene glycol. It neutralizes the activity of membrane-associated
and sol-uble TNF-α
without lysing cells. Certolizumab is indicated for patients with Crohn’s
disease and rheumatoid arthritis.
Etanercept is a dimeric fusion protein composed of human IgG1constant regions fused
to the TNF receptor. Etanercept binds to both TNF-α and TNF-β and appears to have effects similar to those
of adalimumab and infliximab, ie, inhibition of TNF-α-mediated inflammation, but its half-life is
shorter due to its physical form (fusion protein) and the route of injection
(subcutaneously, twice weekly). Etanercept is approved for adult rheumatoid
arthritis, polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis
and psoriatic arthritis. It may be used in combination with meth-otrexate in
some patients with arthritis.
Golimumab is a human IgG monoclonal antibody that alsobinds to soluble and
membrane-associated TNF-α. It is an intact human IgG1 and, like
certolizumab pegol, it does not lyse cells expressing membrane-associated TNF-α. It is indicated for
patients with rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, and psoriatic
arthritis. It has the advantage of increased half-life such that subcu-taneous
injections may be self-administered only once per month.
Infliximab is
a human-mouse chimeric IgG1monoclonal anti-body
possessing human constant (Fc) regions and murine variable regions. It is
administered intravenously but has the same anti-TNF-α activity as adalimumab and
etanercept. Infliximab is cur-rently approved for use in Crohn’s disease,
ulcerative colitis, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, plaque
psoriasis, and psoriatic arthritis.
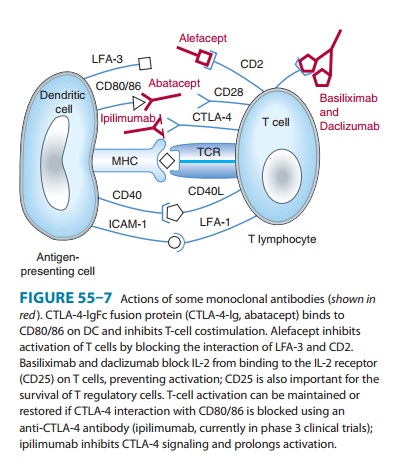
B. Abatacept
Abatacept
is a recombinant fusion protein composed of the extra-cellular domain of
cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 (CTLA-4) fused to hinge, CH2,
and CH3 domains of human IgG1.
CTLA-4 delivers an inhibitory signal to T cells. It binds more tightly to
CD80/86 than CD28 (Figure 55–7). This fusion protein blocks activation of T
cells by binding to CD80 or CD86 so that CD28 on T cells cannot bind and
stimulate the T cell and lead to cytokine release. Abatacept is approved for
patients with rheumatoid arthritis and juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Patients
should not take other anti-TNF drugs or anakinra while taking abatacept. As
with anti-TNF monoclonal agents, patients should be screened and treated for
latent tuberculosis infection before starting abatacept.
C. Alefacept
Alefacept is an
engineered protein consisting of the CD2-binding portion of
leukocyte-function-associated antigen-3 (LFA-3) fused to a human IgG1 Fc region (hinge, CH2, and CH3). It is approved for
the treatment of plaque psoriasis. It inhibits activation of T cells by binding
to cell surface CD2, inhibiting the normal CD2/LFA-3
Treatment of patients with alefacept also results in a dose-dependent
reduction of the total number of circu-lating T cells, especially CD4 and CD8
memory effector subsets that predominate in psoriatic plaques. Peripheral
T-cell counts of patients receiving alefacept must be monitored and the drug
dis-continued if CD4 lymphocyte levels fall below 250 cells/μL.
D. Basiliximab and Daclizumab
Basiliximab is a
chimeric mouse-human IgG1 that binds to CD25, the IL-2 receptor alpha chain on activated
lymphocytes. Daclizumab is a humanized IgG1 that also binds to the alpha subunit of the
IL-2 receptor. Both agents function as IL-2 antago-nists, blocking IL-2 from
binding to activated lymphocytes, and are therefore immunosuppressive. They are
indicated for prophy-laxis of acute organ rejection in renal transplant
patients and either may be used as part of an immunosuppressive regimen that
also includes glucocorticoids and cyclosporine A.
E. Natalizumab
Natalizumab
is a humanized IgG4 monoclonal antibody that binds to the α4-subunit
of α4β1 and α4β7 integrins
expressed on the surfaces of all leukocytes except neutrophils, and inhibits
the α4-mediated
adhesion of leukocytes to their cognate receptor. It isindicated for patients
with multiple sclerosis and Crohn’s disease who have not tolerated or had
inadequate responses to conven-tional treatments.
F. Omalizumab
Omalizumab
is an anti-IgE recombinant humanized monoclonal antibody that is approved for
the treatment of allergic asthma in adult and adolescent patients whose
symptoms are refractory to inhaled corticosteroids . The antibody blocks the
binding of IgE to the high-affinity Fc ε receptor on basophils and mast
cells, which suppresses IgE-mediated release of type I allergy mediators such
as histamine and leukotrienes. Total serum IgE levels may remain elevated in
patients for up to 1 year after admin-istration of this antibody.
G. Tocilizumab
Tocilizumab
is recombinant humanized IgG1 that binds
to soluble and membrane-associated IL-6 receptors. It inhibits IL-6-mediated
signaling on lymphocytes, suppressing inflammatory processes. It is indicated
for treatment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis who are refractory to other
anti-TNF-α
biologicals. It may be used alone or in combination with methotrexate or other
disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs. Patients taking tocilizumab have the
same increased risk of infection as those taking anti-TNF-α monoclonal
antibodies.
H. Ustekinumab
Ustekinumab
is a human IgG1 monoclonal antibody that binds to
the p40 subunit of IL-12 and IL-23 cytokines. It blocks IL-12 and IL-23 from
binding to their receptors, therefore inhibiting recep-tor-mediated signaling
in lymphocytes. Ustekinumab is indicated for patients with moderate to severe
plaque psoriasis. The advantageof ustekinumab over anti-TNF-α drugs for
psoriasis is faster and longer term improvement in symptoms along with very
infre-quent dosing.
Other MABs
Abciximab is a Fab fragment of a murine-human monoclonalantibody that binds to the integrin GPIIb/IIIa receptor on acti-vated platelets and inhibits fibrinogen, von Willebrand factor, and other adhesion molecules from binding to activated platelets, thus preventing their aggregation. It is indicated as an adjunct to per-cutaneous coronary intervention for the prevention of cardiac ischemic complications.
Denosumab is
a human IgG2monoclonal antibody specific
forhuman RANKL (receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand). By
binding RANKL it inhibits the maturation of osteoclasts, the cells responsible
for bone resorption. Denosumab is indicated for treatment of postmenopausal
women with osteoporosis at high risk for fracture. Before starting denosumab,
patients must be evaluated to be sure they are not hypocalcemic. During
treatment, patients should receive supplements of calcium and vitamin D.
Eculizumab is a humanized IgG monoclonal antibody thatbinds the C5
complement component, inhibiting its cleavage into C5a and C5b thereby
inhibiting the terminal pore-forming lytic activity of complement. Eculizumab
is approved for patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) and
dramatically reduces the need for red blood cell transfusions. It prevents PNH
symptoms of anemia, fatigue, thrombosis, and hemoglobinemia by inhibiting
intravascular hemolysis due to red cell lysis. Clinicians must be aware of
increased risk of meningococcal infec-tion in patients receiving this anti-C5
monoclonal antibody.
Palivizumab is a monoclonal antibody that binds to the fusionprotein of
respiratory syncytial virus, preventing infection in sus-ceptible cells in the
airways. It is used in neonates at risk for this viral infection and reduces
the frequency of infection and hospi-talization by about 50% .
Ranibizumab is a recombinant human IgG1Fab that binds toVEGF-A. It also prevents new
blood vessel formation by blocking VEGF from binding to its receptor.
Ranibizumab is labeled for intravitreal injection in patients with neovascular
age-related macu-lar degeneration and sudden blurring or vision loss secondary
to macular edema following retinal vein occlusion. Pegaptanib is a pegylated oligonucleotide that binds extracellular
VEGF and is also given by intravitreous injection to slow macular degeneration.
Related Topics